Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: SLE – Animal Models Poster
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor A3 (LILRA3) is a soluble member of LILR family. We previously reported that LILRA3 is a novel genetic risk for multiple autoimmune diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). However, it is unclear how LILRA3 contributes to the pathogenesis of SLE. This study was undertaken to examine the in vivo role of LILRA3 and its possible mechanism(s) in development of lupus in a chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD) model.
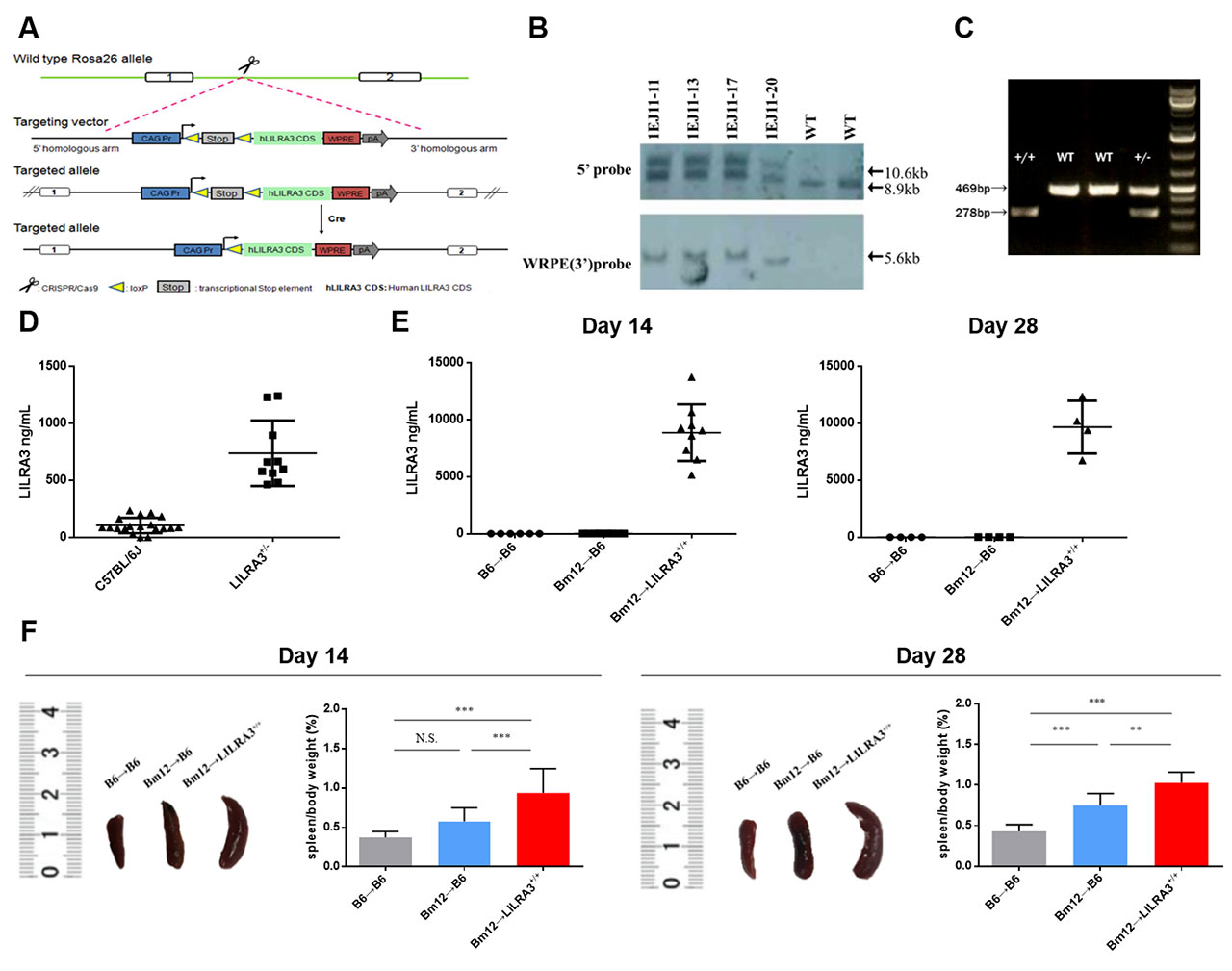
Methods: To functionally study the role of LILRA3 in lupus pathogenesis, we generated a novel LILRA3 knock-in (LILRA3-KI) mouse and evaluated clinical and immunological phenotypes in the bm12-induced cGVHD model. Human LILRA3 gene (Gene ID: 11026) was inserted into Rosa26 allele in C57BL/6 (B6) mice based on Cas9/sgRNA system. The cGVHD was induced by an intraperitoneal injection of the bm12 donor splenocytes into recipients, either B6 wild-type (B6-WT) or LILRA3-KI mice. Mice were assessed for the development of splenomegaly, immune cellular response, autoantibody production, and renal pathology.
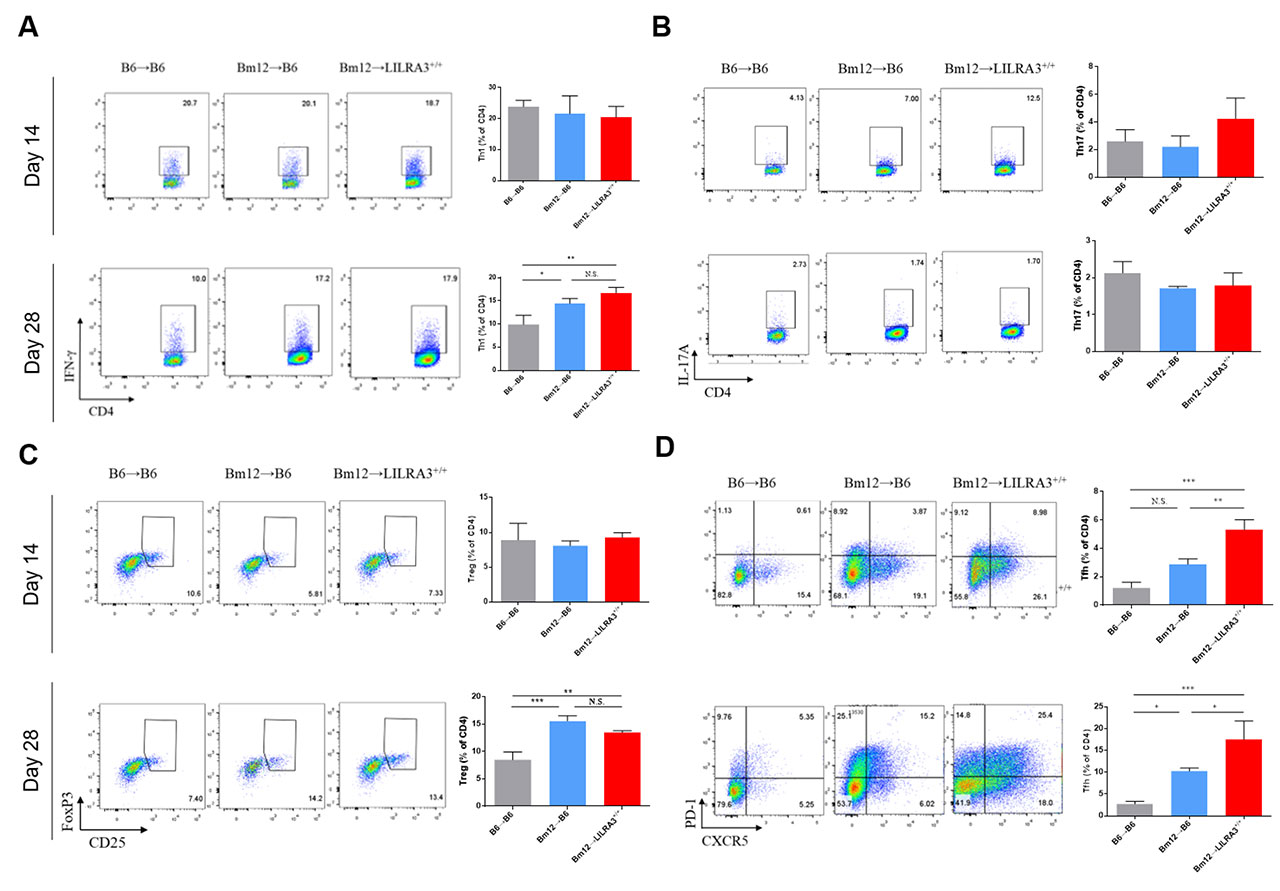
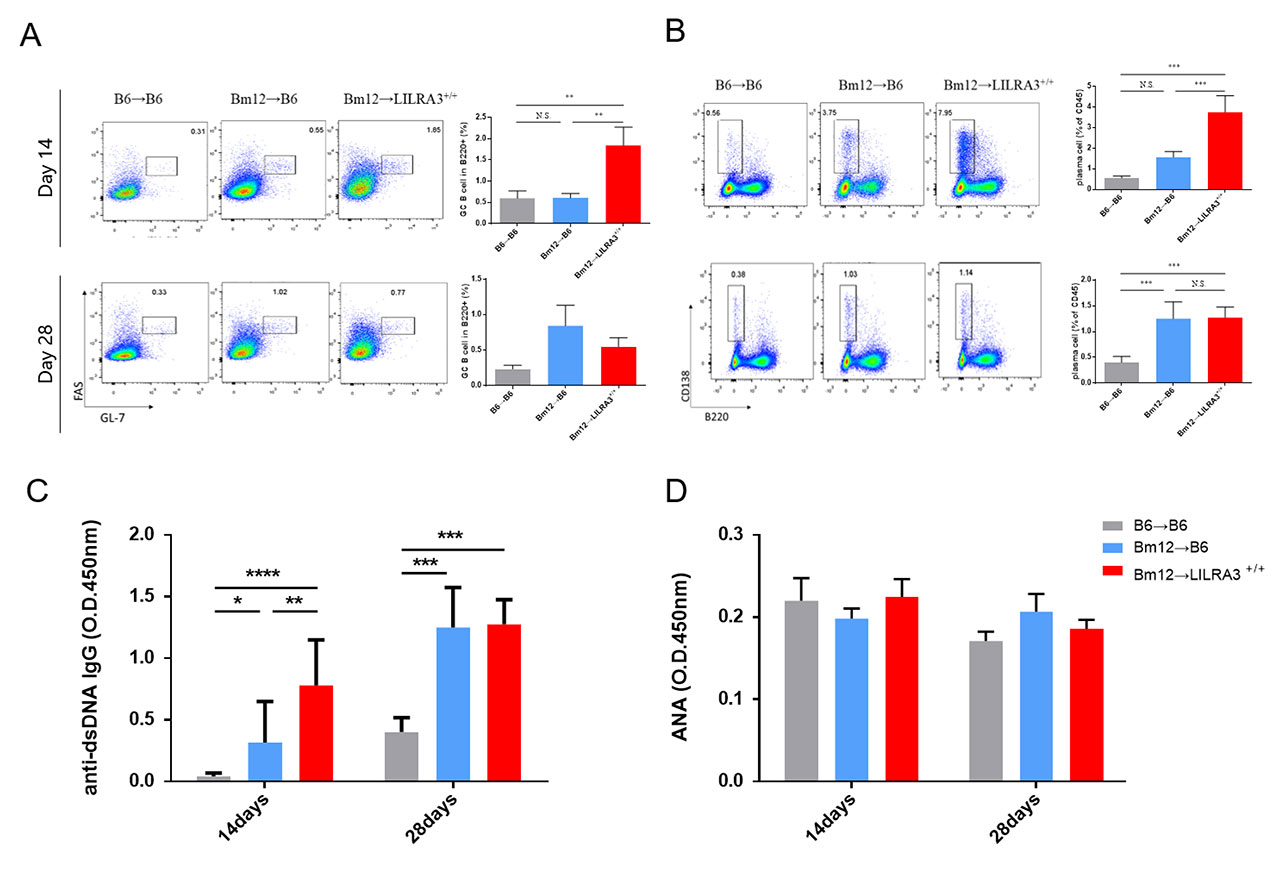
Results: Compared with B6-WT recipient mice, the LILRA3-KI mice displayed a more pronounced lupus-like phenotype and immune response, which includes an apparent spleen enlargement (p < 0.001); expansion of Tfh cells (p < 0.001), germinal center (GC) B cells (p < 0.01), and plasma B cells (p < 0.001); and elevated levels of serum anti-double-stranded DNA IgG autoantibodies (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Our data indicate that LILRA3 promotes lupus-like disease probably through the excessive expansion of Tfh, GC B, and plasma cells, and subsequently leading to an excessive production of anti-dsDNA autoantibodies.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tang Y, Wang Y, Zou Y, Liu M, Du Y, Guo J. LILRA3 Promotes Lupus-like Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease by Expansion of Follicular Helper T Cells and Anti-dsDNA Autoantibodies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lilra3-promotes-lupus-like-chronic-graft-versus-host-disease-by-expansion-of-follicular-helper-t-cells-and-anti-dsdna-autoantibodies/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lilra3-promotes-lupus-like-chronic-graft-versus-host-disease-by-expansion-of-follicular-helper-t-cells-and-anti-dsdna-autoantibodies/