Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III: Comorbidities
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patients with RA have an augmented cardiovascular mortality up to 50% compared to controls. Chronic inflammation of the disease causes endothelial dysfunction and accelerated atherosclerosis. Key molecular pathways in this process are dependent on cytokines like TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, among others, which are shared with RA. Increased disease activity could contribute to atherosclerosis. Carotid ultrasound (US) has recently been recommended as a screening tool for early detection of subclinical atherosclerosis. Thus, the aim of this study was to compare different cytokines between Mexican-mestizo RA-subjects with/without carotid plaque (CP).
Methods: An observational cross-sectional trial was designed. Inclusion criteria: age between 40-75 years old, fulfillment of the 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria, and detection of a CP during a carotid US. Subjects with a prior diagnosis of cardiovascular disease or a poor US window were excluded. RA subjects were matched to controls (RA patients without CP) by age and cardiovascular (CV) comorbidities. Every subject had a carotid US performed; reviewed by two board-certified radiologists. Cytokines measured were IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, VCAM-1, ICAM-1 and MMP-9, using an ELISA reader (Glomax E9032). Descriptive analysis was done with frequencies (%), median (q25-q75), and comparisons between groups with Chi square and Mann-Whitney U tests.
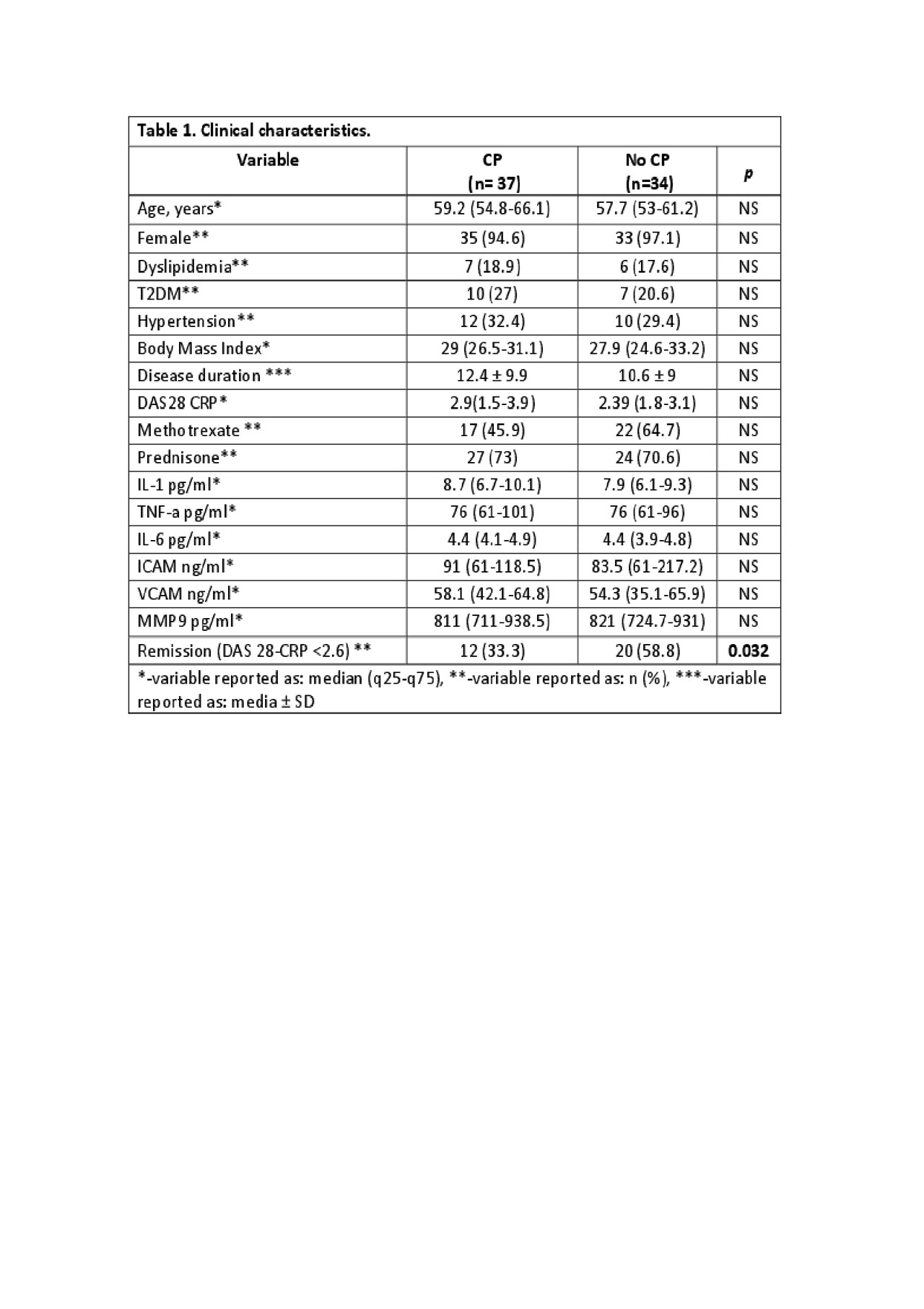
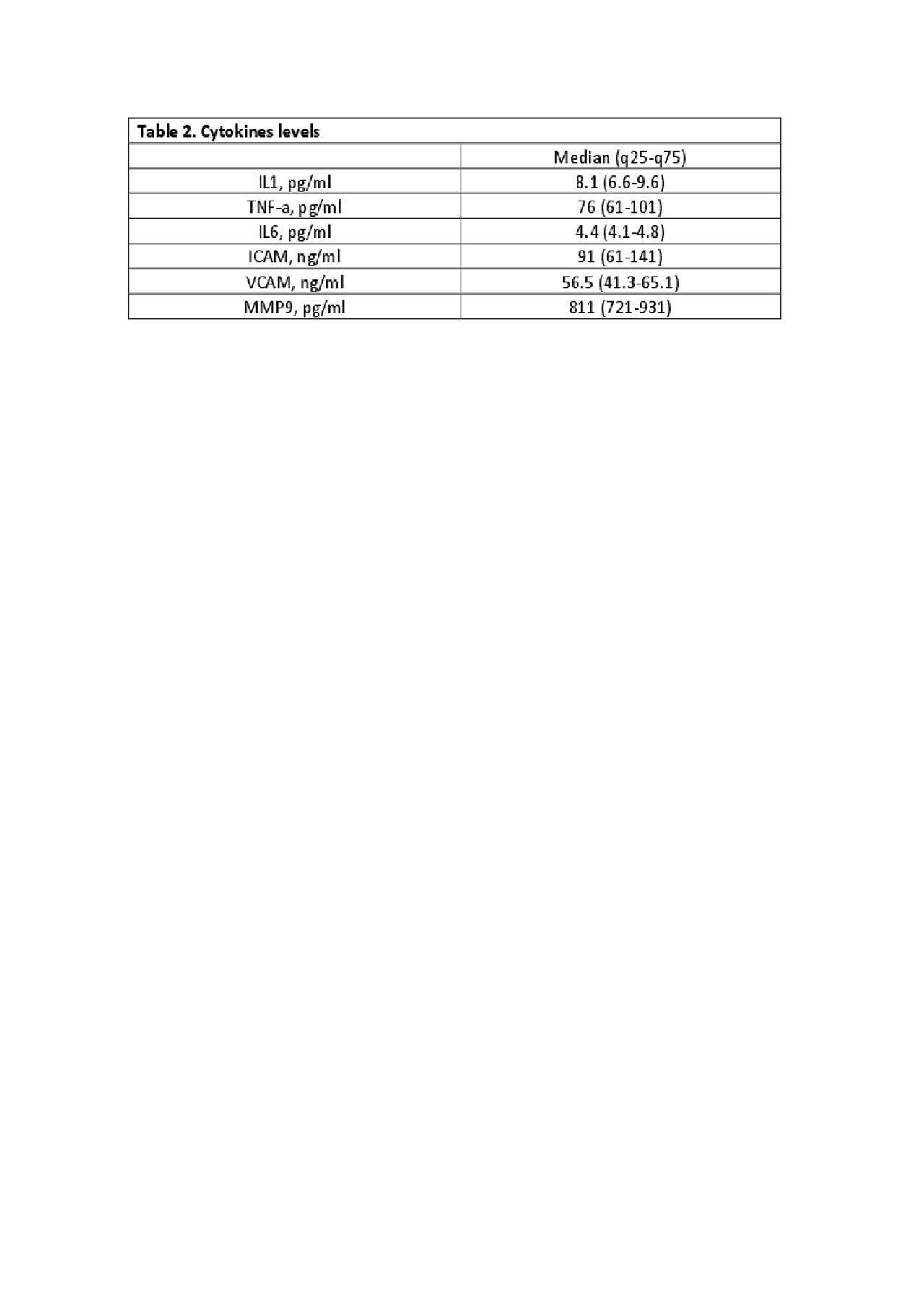
Results: 71 subjects were included, 95.8% were females, with a median age of 58 years (54-65). Comparisons between groups are in Table 1 and levels of cytokines in Table 2. Groups were well balanced, with no differences in CV comorbidities (p >0.05). No significant differences among cytokine levels regarding CP were found. Subjects in remission (n=12, 33%) had a lower prevalence of CP (p< 0.05, OR: 0.3; 95% CI: 0.1-0.9) and a lower median IL-1 level than those with higher disease activity (p< 0.05). No significant differences were found among any other of the compared cytokines.
Conclusion: In our cohort subjects in remission had a lower prevalence of CP. No difference was found between cytokines regarding CP. Subjects with active disease had a higher level of IL-1 than subjects in remission. To our best knowledge, this is the first study to evaluate levels of cytokines in Mexican RA-subjects.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Galarza-Delgado D, Azpiri-Lopez J, Colunga-Pedraza I, Arvizu-Rivera R, Cuellar-Calderon K, Garcia-Arellano G, Reynosa-Silva I, Castro-Gonzalez M, Martinez-Flores C, Vera-Pineda R, Cardenas-De la Garza J, Elizondo-Riojas G, Guillen-Gutierrez C. Levels of Proinflammatory Cytokines in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients with Carotid Plaque: A Case-Control Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/levels-of-proinflammatory-cytokines-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-with-carotid-plaque-a-case-control-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/levels-of-proinflammatory-cytokines-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-with-carotid-plaque-a-case-control-study/