Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Good response could be observed after applying glucocorticoids (GCs) in patients with IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), however, the risk of disease relapse was reported relatively high during or after GCs tapering. Recurrent relapses may lead to more damages precipitated in involved organs and high cumulative dose of GCs correlating to severe adverse effects. Hence, it¡¯s important to find an effective immunosuppressive agent (IM) to maintain remission in IgG4-RD. However, to date, studies about IMs in IgG4-RD are all exploratory and the existing evidences are far from enough to identify which IM is more effective. This study was conducted to identify the efficacy and safety of leflunomide (LEF) combined with GCs in treating IgG4-RD.
Methods: Data of patients diagnosed as IgG4-RD between November 2012 and November 2015 were summarized retrospectively. Only patients treated by LEF plus GCs and had been followed up with more than 3 visits and 6 months were enrolled. During all subsequent visits, clinical symptoms, laboratory and imaging findings, changes in treatment, LEF-related adverse events and disease activity reflected by IgG4-RD Responder Index (IgG4-RD RI) were obtained. All available medical records were reviewed combined with additional information through telephone follow-up. Clinical outcomes were assessed by IgG4-RD RI as well as laboratory and imaging examinations.
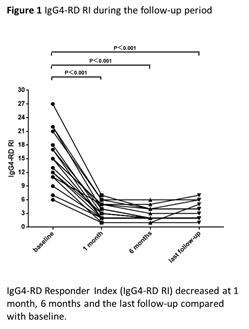
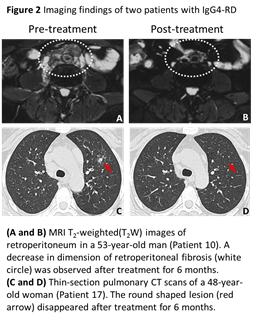
Results: Eighteen patients including 14 untreated patients and 4 retreated patients with relapsing disease were enrolled. The mean (S.D.) onset age was 54.0 (9.6) years with a male to female ratio of 2.6:1. The mean (S.D.) follow-up period was 11.1 (6.9) months. All patients had active disease with mean (S.D.) IgG4-RD RI of 15.0 (5.6) at baseline and obtained disease response at 1 month. At the last follow-up, the mean (S.D.) IgG4-RD RI was declined to 3.1(1.7) and was 2.5(1.2) in patients without relapse. The mean (S.D.) serum level of IgG4 was declined from 1451.2(1956.8) mg/dl to 254.5(321.1) mg/dl. GCs were all tapered to maintenance dose at 6 months and the mean (S.D.) dose was 7.3 mg/d at the last follow-up. 66.7% (12/18) and 61.1% (11/18) patients were in remission at 6 months and the last follow-up, respectively. 16.7% (3/18) patients relapsed in the clinical course. Adverse effects (AEs) were observed in 1 patient with elevated hepatic enzymes and 1 patient with rashes. These AEs resolved immediately after withdrawn of LEF.
Conclusion: LEF and GCs combination therapy is effective in treating IgG4-RD with a few reversible adverse effects, and LEF is a promising steroid-sparing agent for IgG4-RD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wang Y, Gao D, Luo G, Li K, Zhao Z, Zhu J. Leflunomide and Glucocorticoids Combination Therapy for the Induction and Maintenance of Remission in Patients with IgG4-Related Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/leflunomide-and-glucocorticoids-combination-therapy-for-the-induction-and-maintenance-of-remission-in-patients-with-igg4-related-disease/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/leflunomide-and-glucocorticoids-combination-therapy-for-the-induction-and-maintenance-of-remission-in-patients-with-igg4-related-disease/