Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Numerous biologic and targeted synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARDs) have been approved for treating rheumatoid arthritis (RA), including Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi), rituximab, abatacept, interleukin-6 inhibitors (IL-6i) and tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi). Real-world data regarding treatment persistence and drug survival in the time period following the approval of JAKi are limited.
The aim of this analysis of the pseudonymized RheumaDataRhePort (Rhadar) database was to compare persistence on different bDMARDs (rituximab, abatacept, IL-6 inhibitors, TNFi) and JAKi.
Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis of the Rhadar database (Kleinert, S., P. Bartz-Bazzanella et. al. (2021). “A Real-World Rheumatology Registry and Research Consortium: The German RheumaDatenRhePort (RHADAR) Registry.” J Med Internet Res 23(5): e28164.s). RA patients who received newly prescribed therapy with a bDMARD or JAKi between January 15, 2015 and October 17, 2023 were included. We used Cox regression analysis adjusted for age, gender and disease duration to compare drug survival between the different mode of actions. The statistical analysis was performed with R (version 4.3.2) (R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. 2018) or RStudio (version 2023.12.0+369) (RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R. RStudio, Inc, Boston, MA. 2016.RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R. RStudio, Inc, Boston, MA. 2016).
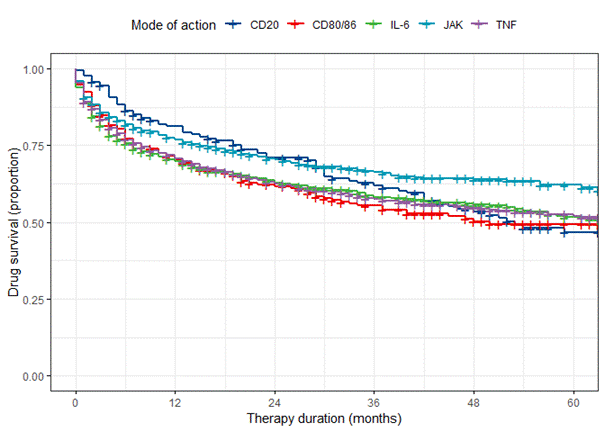
Results: During the analysis period, 4678 treatments with bDMARDs (TNFi: 2237, IL-6 inhibitors: 640, Abatacept: 262, Rituximab: 165) or JAKi (1374)) were started. After 5 years, the survival rate was highest in the JAKi group (68.3%) compared to patients receiving TNFi (58.6%), IL-6 inhibitors (58.6%), abatacept (55.0%) or rituximab (53.3%). The adjusted Cox regression analysis revealed a significantly higher probability of treatment discontinuation in patients receiving rituximab (HR 1.36 [95% CI 1.06-1.74], p=0.015), abatacept (HR 1.46 [95% CI 1.18-1. 80], p< 0.001), IL-6 inhibitors (HR 1.20 [95% CI 1.02-1.42], p=0.026) or TNFi (HR 1.29 [95% CI 1.15-1.46], p< 0.001) compared to the reference group JAKi. No significant differences were found between the bDMARDs. Notably the persistence on JAKi and rituximab after two years was comparably high but then the curve of rituximab dropped (figure 1) between 24 and 36 months of therapy. 60% of the corresponding treatment discontinuations occurred between March 2020 and July 2022.
Conclusion: Persistence on JAKi after 5 years was significantly higher than on bDMARDs. An association between the lower persistence on rituximab and the COVID-19 pandemic seems likely, with increased treatment discontinuations between March 2020 and July 2022.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Risser L, Witte T, Englbrecht M, Strunz P, Froehlich M, Schmalzing M, Gernert M, Bartz-Bazzanella P, von Der Decken C, Karberg K, Gauler G, Spaethling-Mestekemper S, Kuhn C, Vorbrueggen W, Welcker M, Kleinert S. Janus Kinase Inhibitors Persist Longer Than Biologics in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Retrospective Analysis of Real-world Outpatient Data from the German Rhadar Database [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/janus-kinase-inhibitors-persist-longer-than-biologics-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-retrospective-analysis-of-real-world-outpatient-data-from-the-german-rhadar-database/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/janus-kinase-inhibitors-persist-longer-than-biologics-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-retrospective-analysis-of-real-world-outpatient-data-from-the-german-rhadar-database/