Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Spondylarthropathies Psoriatic Arthritis – Pathogenesis, Etiology - Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Aberrant activation of IL-23/IL-17 cytokine axis is a dominant pathology in the psoriatic disease. IL-23 regulates expansion/maintenance/functional maturation of Th17 cells. Th17 cells along with their signature cytokines IL-17 and IL-22 is now believed to play a critical role in the pathogenesis of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Because Tyk2 and JAK2 is recruited to IL-23 receptor it is expected that JAK-STAT mediated signaling system is important in PsA. We hypothesized- (i) JAK STAT signaling system regulates the Th17 cells in PsA and (ii) that Tofacitinib an inhibitor of Jak-1, Jak-2 and Jak-3 targets the Th17 cells by inhibiting the IL-23 induced JAK STAT signaling system.
Methods: • PBMC and synovial mononuclear cells (SFMC) from PSA patients (n=15) and PBMC from age/sex matched normal individuals (n=15) were collected • All patients had an active disease and were not on DMARDS or biologics • rIL-23 induced activated IL-17+ T cells were generated and evaluated as per our earlier reports (Raychaudhuri SP, et al. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012 ;359:419-29 ). • Cells were cultured with and without Tofacitinib (50nM) • Western blot studies were done to indentify Jak2/p-Jak2, Tyk2/p-Tyk2, stat3/p-stat3, stat4/p-stat4 in the sorted activated CD3+ T cells. • Hi-D FACS studies were done to identify the activated memory CD4+ CD11a+CD45RO+IL-17+ T cells and CD8+CD11a+CD45RO+IL-17+ T cells in SFMC/PBMC of PsA and PBMC of normal individuals.
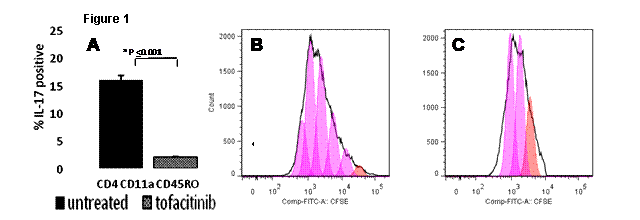
Results: In both PsA and controls sorted activated CD3+ T cells in presence of IL-23 demonstrated activation of the following JAK-STAT signaling molecules: Jak2, Tyk2, and stat3 but stat4 activation was substantially weaker. Further we noticed Tofacitinib markedly inhibited phosphorylation of Jak2 and STAT-3 the signaling proteins induced by IL-23. HiD-FACS analysis of the activated CD3+T cells in PsA patients demonstrated that IL-23 induced marked upregulation of IL-17 in the memory T cells (CD11a+CD45RO+) (Fig 1). We noticed that SFMC and PBMC treated with rIL-23 in PsA patients had 30±4.5% and 18±3.8% activated memory CD4+IL-17+ T cells respectively compared to 5± 0.7% in healthy persons (p<0.001%). Further we noticed that CD4+ CD11a+CD45RO+IL-17+ T cells were 5±2% (p<0.001%) (Fig 1) in cells treated with Tofacitinib. Tofacitinib significantly inhibited proliferation of these CD4+CD11a+CD45RO+IL-17+ T cells (p<0.01%) (Fig 1).
Conclusion: · In PsA the key immune response that is the generation of the pathologic CD4+ CD11a+CD45RO+IL-17+ T cells and their proliferation is regulated by the JAK-STAT signaling system. · JAK STAT signaling regulates the Th17 cells in PsA and this may be one of the mechanisms of action of Tofacitinib. These observations provide new insight about the disease process of PsA and its management.
Figure 1. A. HiD FACS studies of the PBMC from active ankylosing spondylitis patients demonstrated that- (i) rIL-23 induced marked upregulation of IL-17 in the memory T cells (CD11a+CD45RO+) and that (ii) rIL-23 induced IL-17 expression could be markedly inhibited by Tofacitinib (p<0.001). B and C. CFSE dilution study demonstrated less number of generations and less numbers of CD4+ CD11a+CD45RO+IL-17+ T cells on day 5 in PBMC cultured with tofacitinib (C) compared to cells cultured without Tofacitinib (B).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Raychaudhuri SP, Raychaudhuri SK. JAK STAT Kinase Cascade Regulates the IL-23/IL-17 Cytokine Axis in Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/jak-stat-kinase-cascade-regulates-the-il-23il-17-cytokine-axis-in-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/jak-stat-kinase-cascade-regulates-the-il-23il-17-cytokine-axis-in-psoriatic-arthritis/