Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2022
Title: RA – Treatment Poster IV
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib and baricitinib are the first and second approved JAK inhibitors for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. Although their clinical efficacy has been well established, there were concerns about the risk of adverse event such as herpes zoster virus (HZ). Recently, Ytterberg et al. revealed the higher risk of malignancies in RA patients with tofacitinib compared with a TNF inhibitor in randomized, open-label, postauthorization, noninferiority trial because the noninferiority of tofacitinib could not be shown (1). However, there are few publish data of these adverse events and comparison between tofacitinib and baricitinib in clinical settings.
Methods: We retrospectively evaluated 297 RA patients treated with tofacitinib (n=192) and baricitinib (n=104). We evaluated the incidence rate (IR) of infectious disease and HZ, the standardized incidence rate ratio (SIR) of malignancies, and the factor related to incidence of infectious disease by performing univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses. Finally, we compared the incidence between tofacitinib and baricitinib. To adjust for the imbalance in clinical characteristics, the propensity scores were weighted to estimate the standard error of regression coefficient of duration for incidence of malignancies, and infectious disease using Cox proportional hazard model.
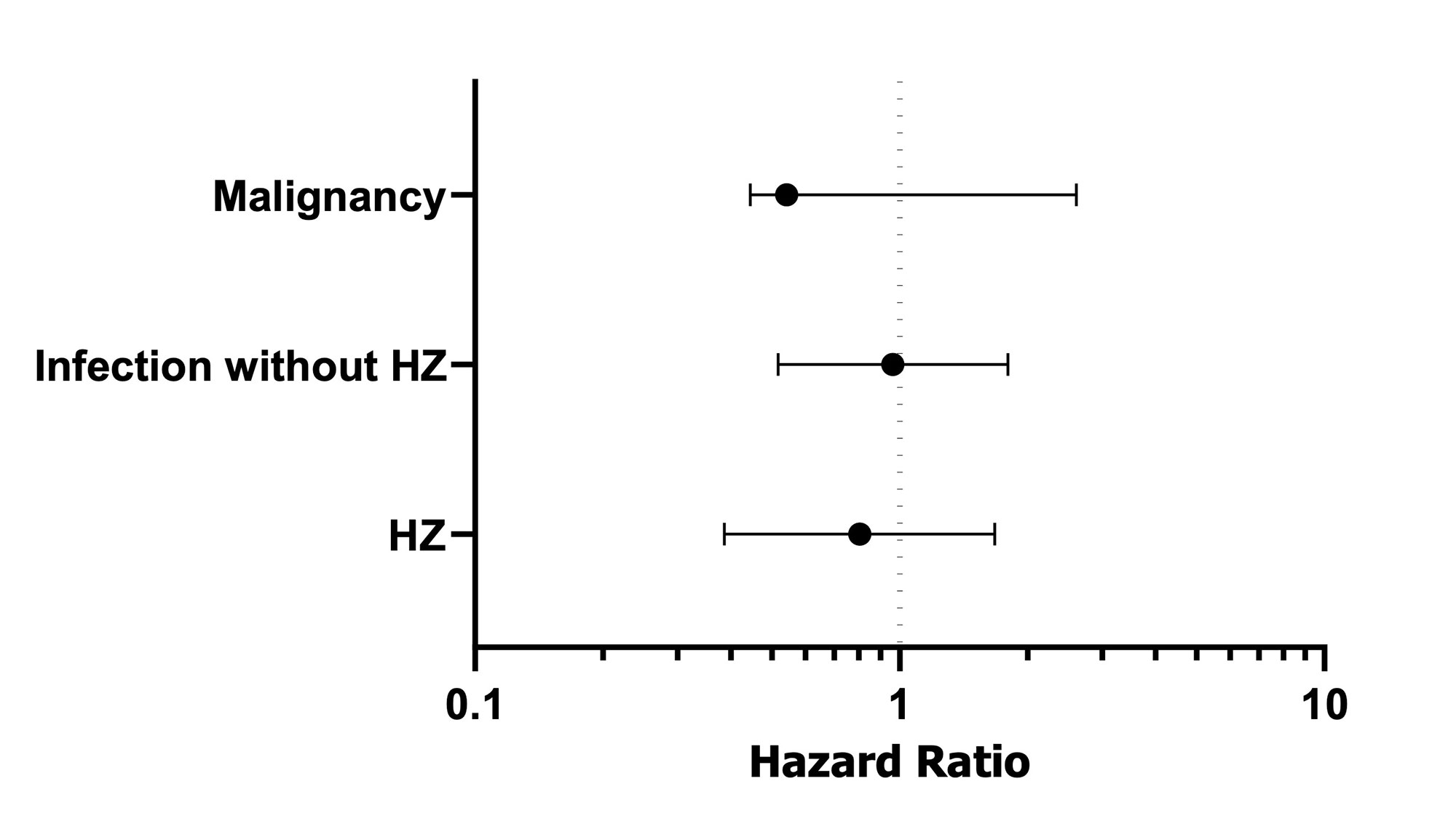
Results: The IR of infectious disease without HZ was 15.63 per 100PY, and serious infection was 8.36 per 100PY. Glucocorticoid (GC) dose was independently associated with events of infectious diseases except for HZ. The IR of HZ was13.00 per 100PY, and older age was independently risk factor of HZ. Only two cases of MACE were occurred. 11 cases of malignancies were identified. The SIR for overall malignancies in our cohort of total patients compared with the general Japanese population was 1.59 (95% CI: 0.79-2.85, p=0.173). There was no significant difference in the incidence of these adverse events of the baricitinib-treated patients and the tofacitinib-treated patients. The adjusted hazard ratio (baricitinib vs tofacitinib) estimated by weighted Cox proportional hazard model is shown in Figure 1.
Conclusion: Our present study demonstrated that the IR of malignancies was comparable between tofacitinib and baricitinib in daily clinical practice.
Reference
1. Ytterberg SR, Bhatt DL, Mikuls TR, Koch GG, Fleischmann R, Rivas JL, et al. Cardiovascular and Cancer Risk with Tofacitinib in Rheumatoid Arthritis. N Engl J Med 2022;386:316-26.
T. Uchida, None; N. Iwamoto, None; S. Fukui, None; F. Shomura, None; K. Aratake, None; T. Aramaki, None; Y. Ueki, None; A. Kawakami, None.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Uchida T, Iwamoto N, Fukui S, Shomura F, Aratake K, Aramaki T, Ueki Y, Kawakami A. JAK Selectivity Did Not Affect to the Incidence of Malignancies in the Real-World Setting: Data from a Multicenter Observational Study in Japan [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/jak-selectivity-did-not-affect-to-the-incidence-of-malignancies-in-the-real-world-setting-data-from-a-multicenter-observational-study-in-japan/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/jak-selectivity-did-not-affect-to-the-incidence-of-malignancies-in-the-real-world-setting-data-from-a-multicenter-observational-study-in-japan/