Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster I: Axial Spondyloarthritis (0908–0939)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Ixekizumab (IXE) demonstrated rapid efficacy in patients (pts) with AS at week (W) 16 in the absence of elevated inflammation as measured by baseline serum CRP values or spinal MRI Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) score.1 This analysis evaluated the improvement in pain with IXE based on longitudinal status of objective measures of inflammation by MRI, CRP value, and BASDAI 5/6 over 16W.
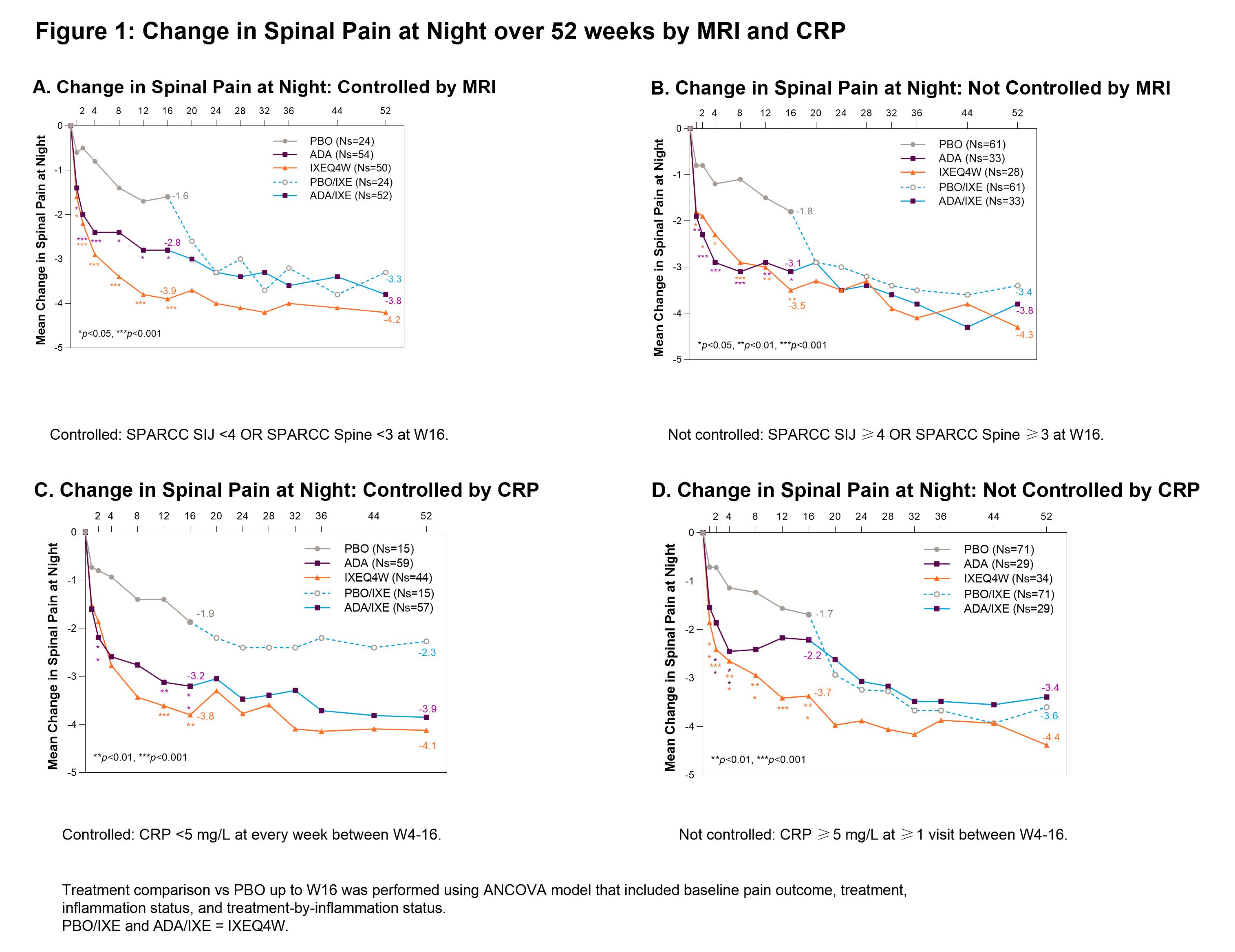
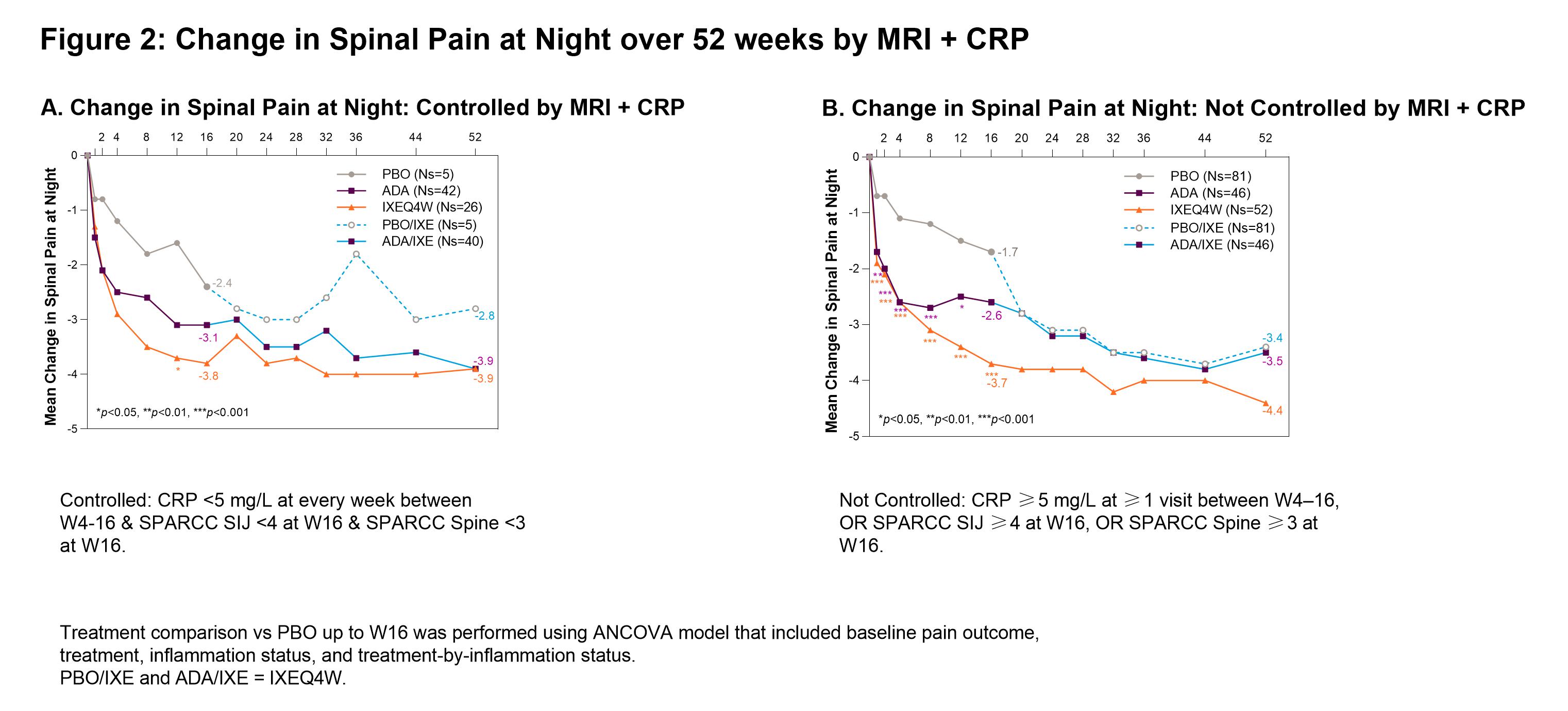
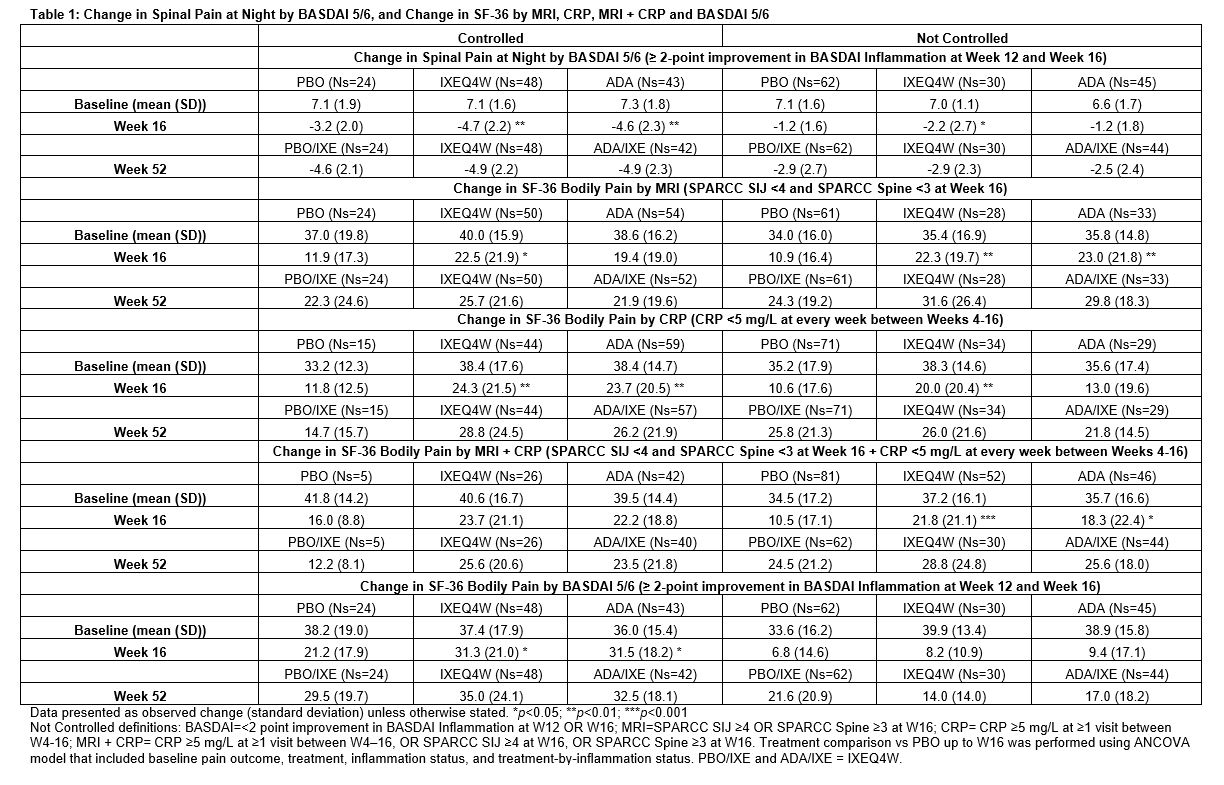
Methods: The Phase III COAST-V (NCT02696785) 52W, multi-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo (PBO)-controlled study examined the efficacy of IXE in pts with active AS. Adalimumab (ADA) was used as an active reference arm for the first 16W. Pts originally assigned to PBO or ADA were re-randomized to IXE at W16. Change in spinal pain at night (SP-N) and Short Form 36 Health Survey Questionnaire (SF-36) Bodily Pain were measured during study visits and analyzed while controlling for inflammation status using MRI, CRP levels and mean of BASDAI 5/6 (Q5: Duration, Q6: Intensity of morning stiffness). Observed data analyses are presented for each group stratified by treatment arm. Initial analysis: ‘controlled inflammation’ is defined as MRI SPARCC SI joint <4 and MRI SPARCC Spine <32 at W16, CRP < 5mg/L at every visit W4-16, or BASDAI 5/6 improvement of ≥2 points W12 and W16. ‘Not Controlled’ are noted in figure legends. Second analysis: control is defined as CRP < 5 mg/L at every week between W4-16 and MRI SPARCC SI joint <4 at W16 and MRI SPARCC Spine <3 at W16.
Results: When inflammation is controlled per MRI, pts treated (tx) with IXEQ4W (-3.9 p < 0.001) and ADA (-2.8 p=0.02) experienced significant reduction in SP-N vs PBO (-1.6) at W16, further improvements were experienced in pts rerandomized to IXE by W52 (Fig1A). When inflammation was not controlled per MRI, IXEQ4W (-3.5 p < 0.01) and ADA (-3.1 p=0.02) experienced significant reduction in SP-N at W16, all IXE tx pts had further reductions at W52 (Fig1B). When inflammation was controlled per MRI+CRP, IXEQ4W (-3.8 p=0.2) and ADA (-3.1 p=0.4) had reduction in SP-N at W16 vs PBO (-2.4), all IXE groups had further improvements at W52 (Fig2A). When inflammation was not controlled as measured by MRI+CRP, IXEQ4W (-3.7 p < 0.001) had significant reduction in SP-N vs PBO (-1.7), whereas improvement with ADA (-2.6 p=0.06) was not significant, all IXE tx pts had further reduction by W52 (Fig1B). For SF-36 bodily pain, improvements were observed at W16 and W52 whether inflammation was controlled or not controlled per MRI, CRP, MRI+CRP, or BASDAI 5/6 (Table 1).
Conclusion: This analysis adds support to the hypothesis that IXE improves pain in pts with and without measurable inflammation.
References
1. Maksymowych et al. ACR. 2021.
2. Maksymowych et al. Rheumatology (in press) doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keab099.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
de Vlam K, Conaghan P, Mease P, Rahman P, Krishnan V, Bolce R, Sandoval Calderon D, Park S, Gallo G, Maksymowych W. Ixekizumab Shows a Distinct Pattern of Pain Improvement Beyond Measurable Inflammation as Assessed by MRI or CRP or BASDAI Questions 5 & 6 in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ixekizumab-shows-a-distinct-pattern-of-pain-improvement-beyond-measurable-inflammation-as-assessed-by-mri-or-crp-or-basdai-questions-5-6-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ixekizumab-shows-a-distinct-pattern-of-pain-improvement-beyond-measurable-inflammation-as-assessed-by-mri-or-crp-or-basdai-questions-5-6-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis/