Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Itolizumab (ITO) is a novel first-in-class monoclonal antibody (IgG1-k) specific for CD6, a co-stimulatory receptor that is highly expressed on T cells that plays an important role in their activity and trafficking. Excessive activation through CD6 has been implicated in the pathogenesis of multiple autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and lupus nephritis (LN). Consequently, ITO is being evaluated as treatment for SLE and LN. Here, we demonstrate that ITO induces cleavage of cell surface CD6, leading to decreased T cell activity, and that the levels of cell and soluble CD6 in SLE patients dosed with ITO is a pharmacodynamic marker of drug activity.
Methods: Mechanistic experiments were carried out ex vivo using PBMCs from normal donors. Samples from patients dosed with ITO, including blood, serum and urine, were collected as part of the EQUALISE trial, an open label Phase 1b 2-part study evaluating the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics (PK), pharmacodynamics (PD), and clinical activity of subcutaneous doses of ITO (0.4 to 3.2 mg/kg on Day 1 and Day 15) in patients with SLE (NCT04128579). Cell surface CD6 was assessed by flow cytometry using an anti-CD6 antibody that does not compete with the binding of ITO, while soluble CD6 in cell supernatants, serum and urine was quantified by an electrochemiluminescent assay.
Results: When PBMCs were incubated with ITO (0.01-10ug/ml), CD4 and CD8 T cell populations exhibited loss of surface CD6 in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Cell surface loss was accompanied by a concomitant increase in soluble CD6 in the supernatant (Figure 1). The resulting CD6low T cells showed reduced T-cell activity (as indicated by activation markers and cytokine production), compared to isotype-treated CD6high cells, despite removal of ITO from the system. In samples from SLE patients dosed with ITO, significant loss of cell surface CD6 on T cells was observed after the first dose. Decreases in cell surface CD6 from baseline were most pronounced at doses ≥1.6 mg/kg and were accompanied by increases in soluble CD6 in the serum and urine (Figure 2). PK/PD analysis of the relationship between ITO concentrations and cell surface CD6 levels indicated that the data were described by an Emax model, which predicted a maximal decrease in CD6 expression of approximately 78%.
Conclusion: Cell surface CD6 regulates T cell activity and ITO-induced loss of CD6 leads to inhibition of T cell activity and can be used to monitor PD activity. SLE patients in the EQUALISE trial demonstrate dose-dependent loss of CD6 with maximal loss occurring at 1.6mg/kg, suggesting that higher doses are not necessary to achieve the greatest inhibition of T cell activity.
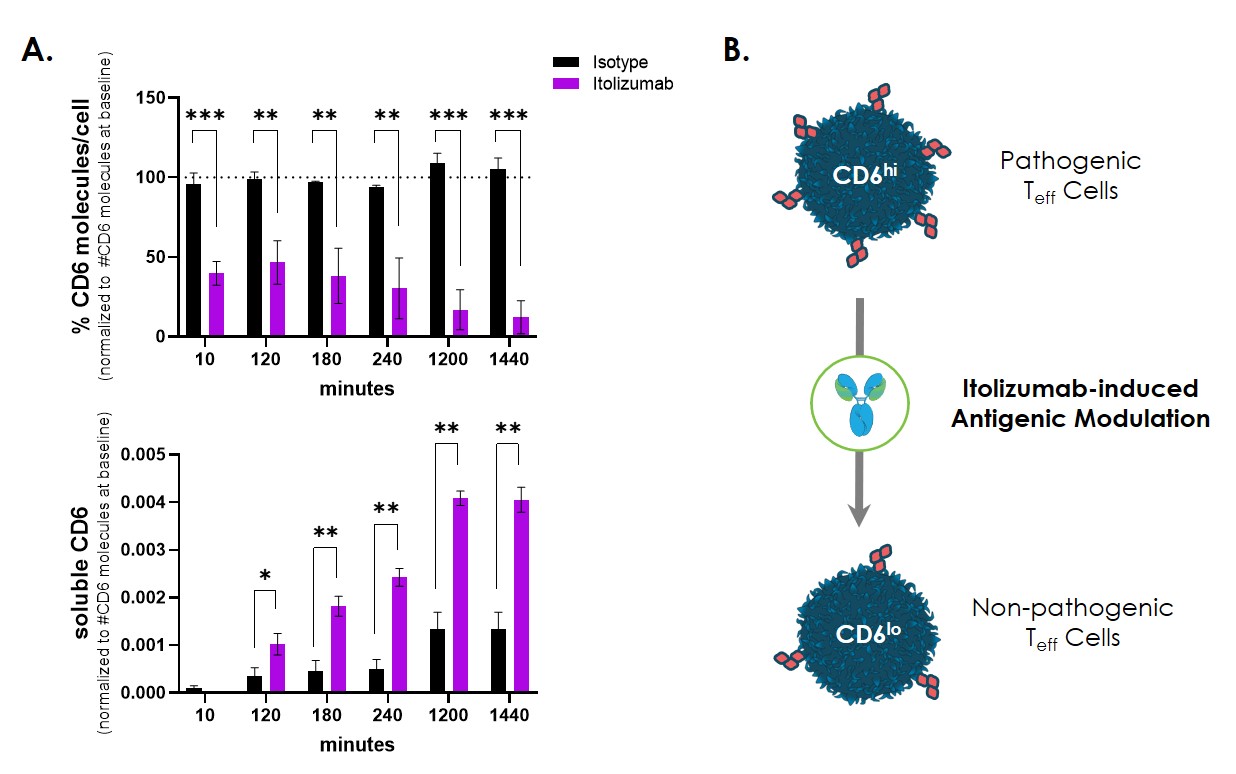 Figure 1. Itolizumab induces loss of CD6 from the T cell surface. (A) PBMCs from 3 different donors were incubated with 10ug/ml of itolizumab and cell surface expression of CD6 was assessed on CD4 T cells and soluble CD6 quantitated in the PBMC supernatant at the indicated timepoints. The calculated number of CD6 receptors on CD4 T cells at baseline as assessed by flow cytometry was used to normalize values across the 3 donors. (B) Schematic of how itolizumab-induced loss of CD6 (antigenic modulation) might affect T cell activity, transforming the cell to possess a less inflammatory phenotype. ***p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05
Figure 1. Itolizumab induces loss of CD6 from the T cell surface. (A) PBMCs from 3 different donors were incubated with 10ug/ml of itolizumab and cell surface expression of CD6 was assessed on CD4 T cells and soluble CD6 quantitated in the PBMC supernatant at the indicated timepoints. The calculated number of CD6 receptors on CD4 T cells at baseline as assessed by flow cytometry was used to normalize values across the 3 donors. (B) Schematic of how itolizumab-induced loss of CD6 (antigenic modulation) might affect T cell activity, transforming the cell to possess a less inflammatory phenotype. ***p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05
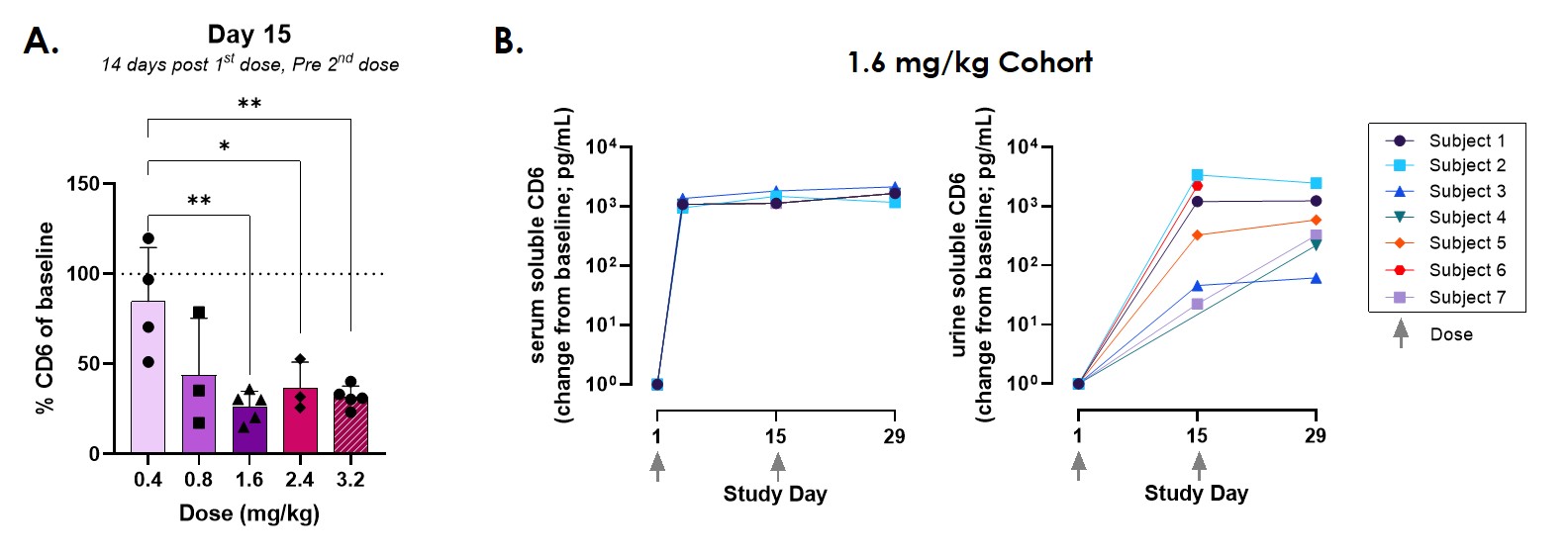 Figure 2. Changes in CD6 in EQUALISE subjects. (A) Cell surface CD6 expression on CD4 T cells decreases following first dose of itolizumab. Expression calculated as % of baseline (pre-drug) expression. (B) Levels of soluble CD6 in serum and urine increase after first dose of itolizumab. Data shown as change from baseline (pre-drug). ***p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05
Figure 2. Changes in CD6 in EQUALISE subjects. (A) Cell surface CD6 expression on CD4 T cells decreases following first dose of itolizumab. Expression calculated as % of baseline (pre-drug) expression. (B) Levels of soluble CD6 in serum and urine increase after first dose of itolizumab. Data shown as change from baseline (pre-drug). ***p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chu D, Chinn L, Ampudia J, Polu K, Rothman J, Fung M, Thomas D, Putterman C, Ng C, Connelly S. Itolizumab-induced Modulation of Cell Surface CD6 Is a Pharmacodynamic Marker of Drug Activity in SLE Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/itolizumab-induced-modulation-of-cell-surface-cd6-is-a-pharmacodynamic-marker-of-drug-activity-in-sle-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/itolizumab-induced-modulation-of-cell-surface-cd6-is-a-pharmacodynamic-marker-of-drug-activity-in-sle-patients/
