Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: RA – Treatments Poster II: Comparative Effectiveness, Biosimilars, Adherence & the Real World
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patients with RA who have received multiple biologics or targeted therapies over time tend to have more refractory and more severe disease, which may lead to worse clinical response to treatment. We examined characteristics of sarilumab-treated patients with RA in order to evaluate the hypothesis that disease severity was greater in those who received sarilumab shortly after its Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval (May 2017) than in subsequent time periods.
Methods: Patients with RA who initiated sarilumab treatment from May 2017 to June 2019 were identified in the American College of Rheumatology’s Rheumatology Informatics System for Effectiveness (RISE) registry. They were divided into 3 cohorts based on time since FDA approval, with the overall period divided into tertiles rounded to the nearest calendar quarter (Cohort 1: May 2017 to March 2018; Cohort 2: April 2018 to December 2018; Cohort 3: January 2019 to June 2019). Patient characteristics reflecting demographics, RA-related features, and comorbidities (measured based on prescriptions, using the RxRisk score) were evaluated using all available data prior to sarilumab initiation. Between-cohort comparisons were made using chi-square test for categorical variables and a nonparametric test for continuous variables.
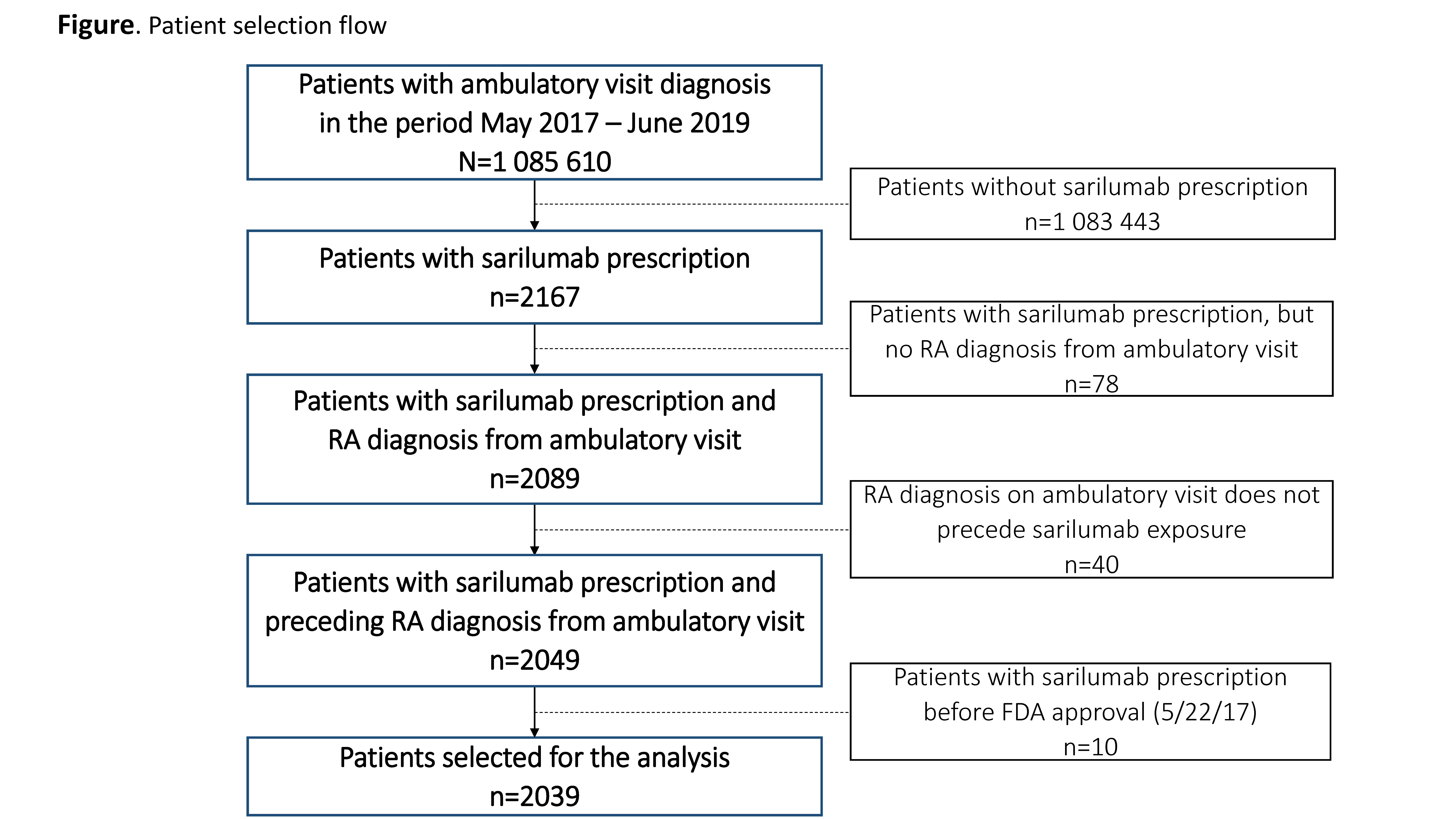
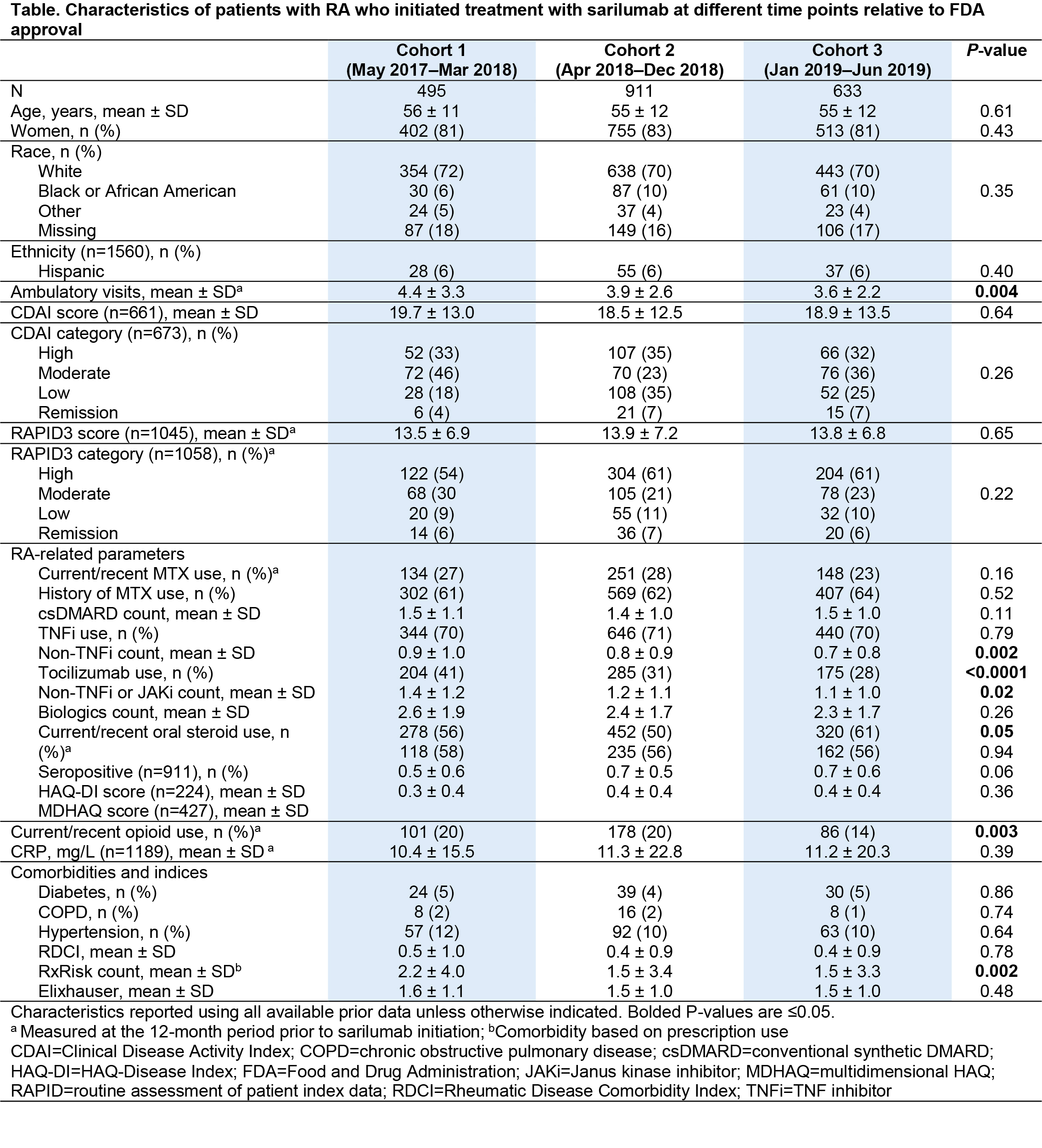
Results: A total of 2039 patients, treated by 585 rheumatologists, initiated sarilumab treatment in the period May 2017–June 2019 (Figure). Cohort comparison showed relative similarity over the 3 time periods in terms of patients’ age, sex, race, and most clinical characteristics (Table). However, patients receiving sarilumab shortly after FDA approval (Cohort 1) had more ambulatory visits, a greater number of previously used non-TNF inhibitor (TNFi) biologics (particularly tocilizumab), a higher comorbidity burden, and were more likely to be current users of glucocorticoids or opioids than patients in Cohorts 2 and 3. Ongoing work is evaluating comparative response to therapy in the 3 cohorts.
Conclusion: We observed modest evidence for channeling of patients with greater RA severity and greater prior exposure to non-TNFi biologics to a newly introduced biologic, although disease activity at time of initiation was comparable over the 3 time periods. For real-world evidence generation, considerations should include cohort effects related to the timing of new drug approval in order to make valid inferences resulting from comparative effectiveness research.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fiore S, Chen L, Clinton C, Yun H, Praestgaard A, Ford K, Curtis J. Is Disease Severity Greater Among Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Who Receive a Newly Approved Biologic? Real-world US Experience with Sarilumab from the ACR RISE Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/is-disease-severity-greater-among-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-who-receive-a-newly-approved-biologic-real-world-us-experience-with-sarilumab-from-the-acr-rise-registry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/is-disease-severity-greater-among-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-who-receive-a-newly-approved-biologic-real-world-us-experience-with-sarilumab-from-the-acr-rise-registry/