Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Clinical Poster III: Treatment
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Twenty to sixty percent of patients with systemic lupus erythematous (SLE) can progress to lupus nephritis (LN) and those that do can develop end stage renal disease 15% of the time. Belatacept is a new immunosuppressive agent with 7 year post transplant outcomes showing patient/graft survival and mean estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) to be significantly higher than cyclosporine [1]. These effects have not been confirmed in LN patients who can benefit from improving strategies.
Methods:
LN patients who underwent renal transplants were identified within the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) database from 2008 to 2014 and a cohort was established based on the use of tacrolimus or cyclosporin, mycophenalate mofetil (MMF) and steroid maintenance medications. This cohort was stratified by use of Belatacept and propensity score matching was used to match non-Belatacept patients to 39 Belatacept patients based on age, gender, race, history of diabetes, status of a living donor, and year of transplant. Pre- and post-match Belatacept use was cross classified by each categorical variable and was examined with the chi-square test; the Mann-Whitney test was used to compare continuous variables. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to examine unadjusted graft failure and survival. A linear mixed model with a heterogeneous autoregressive covariance structure was used to examine follow up creatinine and eGFR values over time of the matched patients.
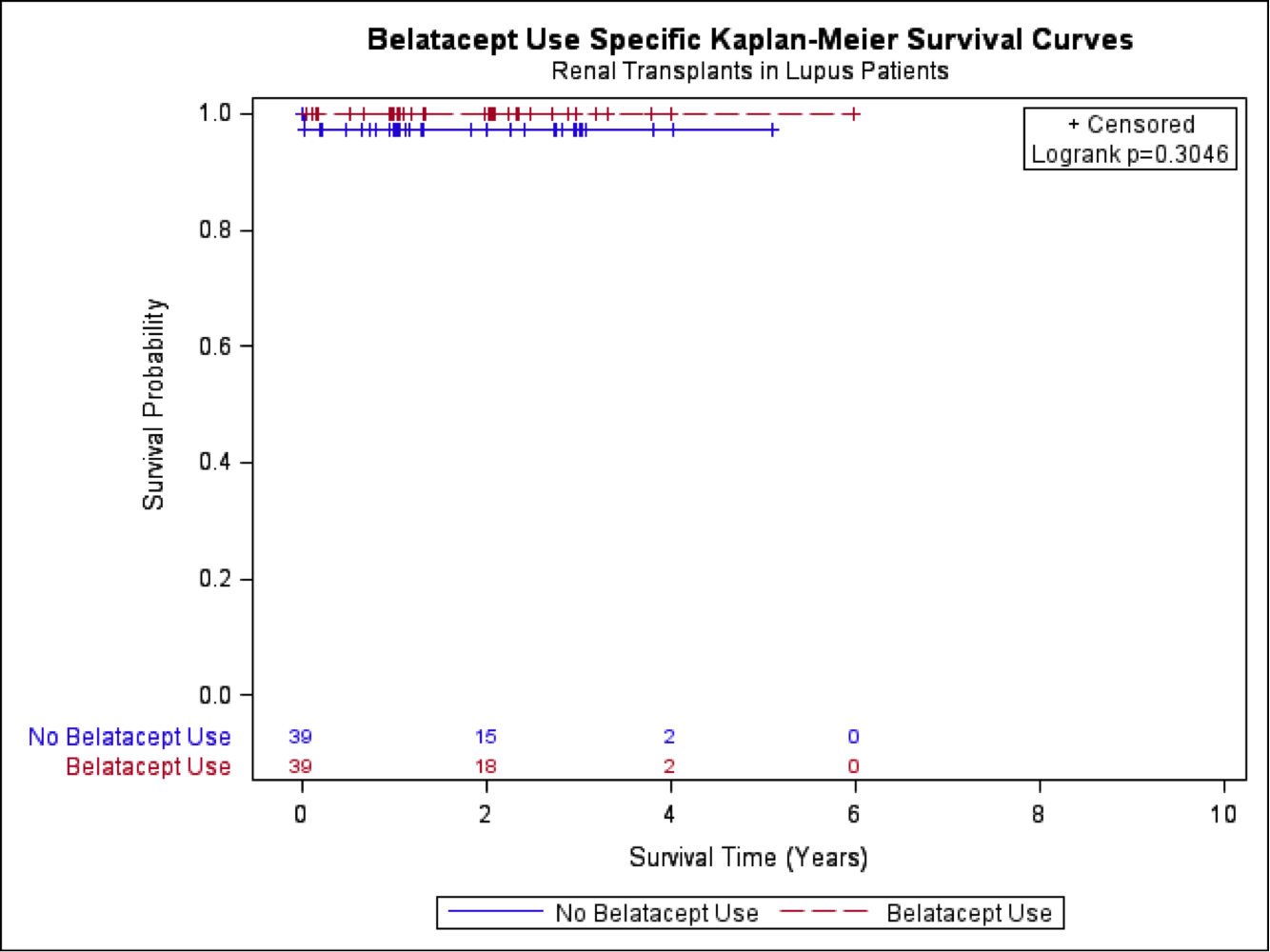
Results:
There were no graft failures or deaths within the Belatacept group and a single patient who experienced graft failure and death within the matched non-Belatacept group. Results of the linear mixed models for creatinine and GFR provided evidence of no difference between groups. For every year there was a significant increase in creatinine (0.22 mg/dL; p = 0.009) and decrease in GFR (-7.20 mL/min/1.73 m2; p < 0.001).
Conclusion:
Belatacept has been used in a limited number of patients requiring renal transplants with LN since 2008. In our study, no significant difference in graft survival, death or renal function in cohorts using standard therapy versus Belatacept was noted. No improvement in mean eGFR was seen in the Belatacept group as seen in prior work [1]. Future studies are needed to evaluate the impact of Belatacept based regimens in LN patients post-transplant.
1. Vincenti, F., Rostaing, L., Grinyo, J., Rice, K., Steinberg, S., & Gaite, L. et al. (2016). Belatacept and Long-Term Outcomes in Kidney Transplantation. New England Journal Of Medicine, 374(4), 333-343. doi: 10.1056/nejmoa1506027
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bhatty O, Aurit S, Sen R, Nahas J, Jagadesh S. Investigating Lupus Nephritis Patient Outcomes Receiving Belatacept Post Renal Transplant Using the UNOS Database [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/investigating-lupus-nephritis-patient-outcomes-receiving-belatacept-post-renal-transplant-using-the-unos-database/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/investigating-lupus-nephritis-patient-outcomes-receiving-belatacept-post-renal-transplant-using-the-unos-database/