Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis and Myopathies Poster III: Treatment and Classification Criteria
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
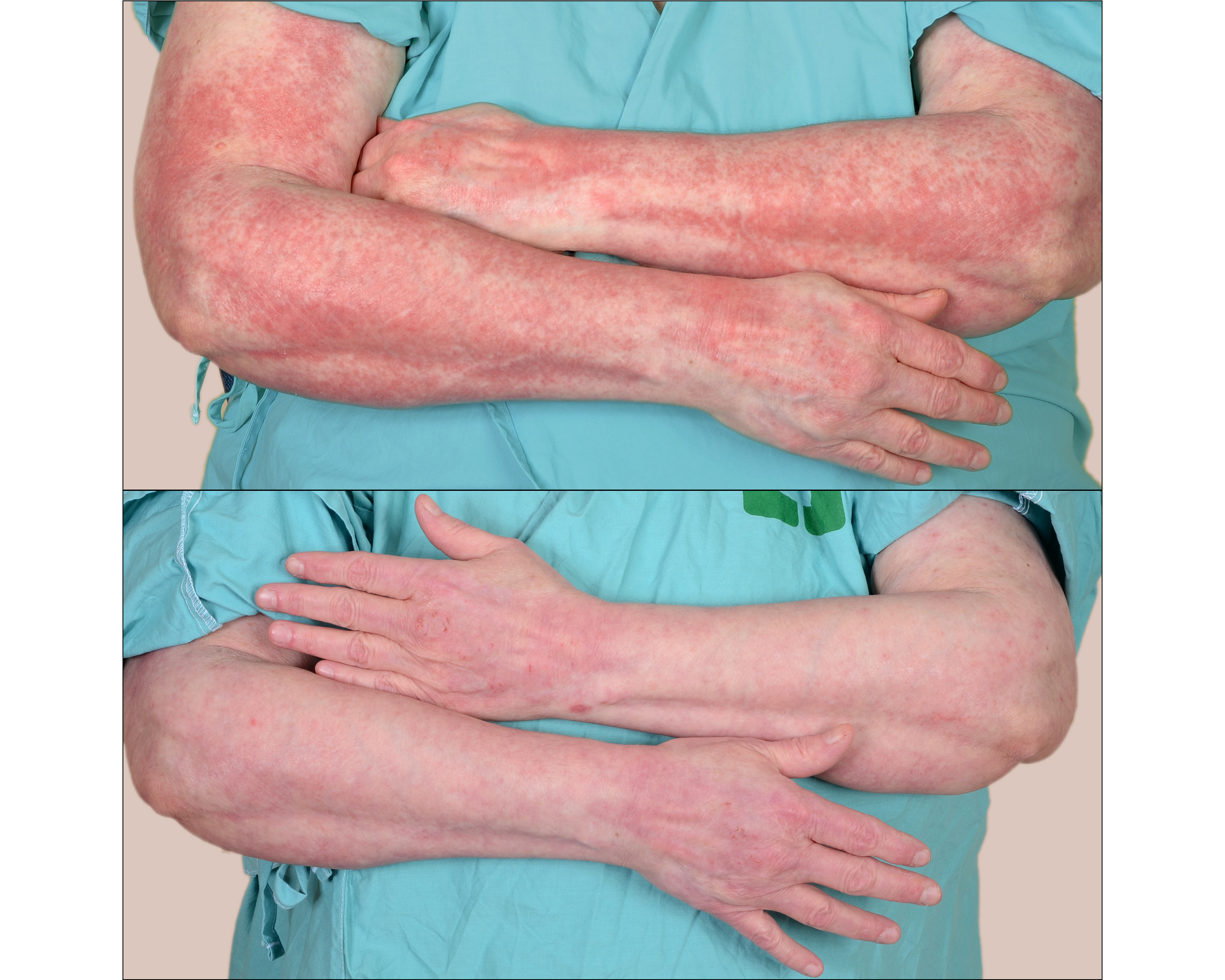
Background/Purpose: Cutaneous dermatomyositis (DM) is often refractory to multiple medications, suggesting better treatments are needed. Adrenocorticotropic hormone gel is a repository corticotropin injection that is FDA-approved for DM, but little is known about its safety and efficacy for cutaneous DM manifestations. We are conducting an open-label study to assess efficacy and safety of repository corticotropin injection for treatment of refractory cutaneous DM. Here, interim results of this clinical trial are reported. Methods: DM patients with ≥ mild active cutaneous disease despite prior treatment with ≥2 systemic agents were eligible for inclusion. Pts were initiated on 80u repository corticotropin injection twice weekly for 24 weeks (6 months (mo)), with clinical evaluations at baseline, 1 mo, 3 mo, and 6 mo. Primary outcomes include decreases in Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index (CDASI) activity and Physician’s Global Assessment (PGA) activity scores. Results: Nine adults (8 females, 1 male) with DM (8 classic, 1 amyopathic), have been enrolled (average (avg) age 53.6 years (yrs)). On average, patients carried a diagnosis of DM for 5.2 yrs (median (med) 4 yrs) at time of study enrollment. Patients had been treated with an avg of 4.6 systemic medications (med 4) prior to study entry, and were being treated with an avg of 2.3 systemic medications (med 2) at time of study entry. Avg baseline CDASI activity score was 20.8 (med 19) and avg PGA activity score was 6/10 (med 6). In terms of patient assessments, baseline patient global skin (PGS) scores averaged 3.3/10 (med 3) and patient global itch (PGI) scores averaged 6.4/10 (med 6). Six patients had a positive ANA (titer range= 1:160 to 1:1280, all speckled pattern). Eight patients had detectable myositis-associated autoantibodies (7 anti-transcriptional intermediary factor 1 gamma (TIF1γ), 1 anti-small ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme (SAE) antibodies). All 9 patients completed ≥3 mos of treatment and 7 patients completed 6 mos of treatment at time of interim data analysis. At 3 mos, 7/9 patients had improved CDASI activity scores (average 15.3; med=13) and 8/9 had improved PGA activity scores (avg 7.7; med 8) (Figure 1). Additionally, 8/9 patients had improved PGS scores (avg 6.33; med 7) and PGI scores (avg 3.22; med 3) at 3 mos. At 6 mos, 7/7 patients had improved CDASI activity scores (avg decrease from baseline = 13.4) and PGA activity scores (avg improvement from baseline of 2.4 points). Furthermore, PGS scores improved in 6/7 patients and PGI scores improved in 5/7 patients at 6 mos. Adverse effects were mild in severity and no patient discontinued medication during the study period. Conclusion: Our interim results suggest repository corticotropin injection is an effective, safe, and well-tolerated treatment for refractory cutaneous manifestations of dermatomyositis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fernandez A. Interim Results of an Open-Label Study Assessing Efficacy and Safety of Adrenocorticotropic Hormone Gel for Treatment of Refractory Cutaneous Manifestations of Dermatomyositis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interim-results-of-an-open-label-study-assessing-efficacy-and-safety-of-adrenocorticotropic-hormone-gel-for-treatment-of-refractory-cutaneous-manifestations-of-dermatomyositis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interim-results-of-an-open-label-study-assessing-efficacy-and-safety-of-adrenocorticotropic-hormone-gel-for-treatment-of-refractory-cutaneous-manifestations-of-dermatomyositis/