Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: There is heightened interest in the use of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. There are a number of reports of efficacy of MSCs with minimal safety concerns in lupus and rheumatoid arthritis. There are, however, only a very limited number of controlled trials to assess true efficacy and safety of MSCs in rheumatic diseases. There are no controlled trials of MSCs in lupus, while there are a number of uncontrolled trials, primarily from one center in China, reporting over 60% efficacy of MSCs in refractory lupus patients. The MSC in systemic lupus erythematosus trial (MiSLE) is the first double blind placebo controlled multi-center trial of MSCs as a treatment for refractory lupus.
Methods: The MiSLE trial is a two-cohort dose escalation trial at 9 centers in the United States. A total of 81 patients will be randomized. Cohort one is complete, consisting of 41 patients receiving either 1×106 MSCs/kg or placebo in a 2/1 ratio. The MSCs are allogenic MSCs derived from umbilical cords of women undergoing elective C sections. They were prepared using standard ISCT protocols at our Clean Cell Facility. The blind is being maintained for cohort 1 through the completion of cohort 2. The second cohort of 40 patients, enrolling now, will receive 5×106 MSCs/kg. Patients had a SLEDAI of 6 or greater at screening, had failed at least one immunosuppressant, and were on 0.5mg/kg prednisone or less. Clinical response was measured as a primary outcome using the SRI4 at 24 weeks post the single MSC infusion. Due to COVID, some of the followup visits were performed by Telehealth, using investigator judgement as to what parts of the SLEDAI and BILAG could be reliably scored.
Results: Forty-one patients were enrolled into cohort one of the MiSLE trial. Due to COVID, no new patients were enrolled from March 2020 through August 2020. The cohort consists of 90% women, 49% Caucasian, 39% African American and 12% other. Average age was 38. All 7 sites active in Cohort 1 enrolled patients. The organ systems involved were 41.5% mucocutaneous, and 78.1% musculoskeletal. 14.6% had renal involvement. Mean SLEDAI score was 10.3 and 71% of patients were anti-dsDNA positive. 66% of patients were on prednisone. There were no deaths, no significant infusion reactions nor any SAEs attributed to the Investigational Product. Fifteen SAEs were reported in 10/41 participants. 10 BILAG A flares occurred in 5 patients. As expected, a number of the AEs and SAEs were infections, though MSCs are not believed to enhance infection risks. Notably a few patients contributed to most of the SAEs and lupus flares. The major issue arising due to the pandemic was delayed data entry and data inconsistency due to remote work and video visits.
Conclusion: The first cohort of patients in the MiSLE trial are infused and nearing completion of 52 weeks. There were a number of SAEs reported, but there was not a safety signal by DSMB review. Changes in data management and reporting are being instituted to improve prompt and accurate data entry. Overall, the safety data confirm that there are almost no infusion reactions with MSCs and the safety profile is sufficient to proceed to the higher dose cohort.
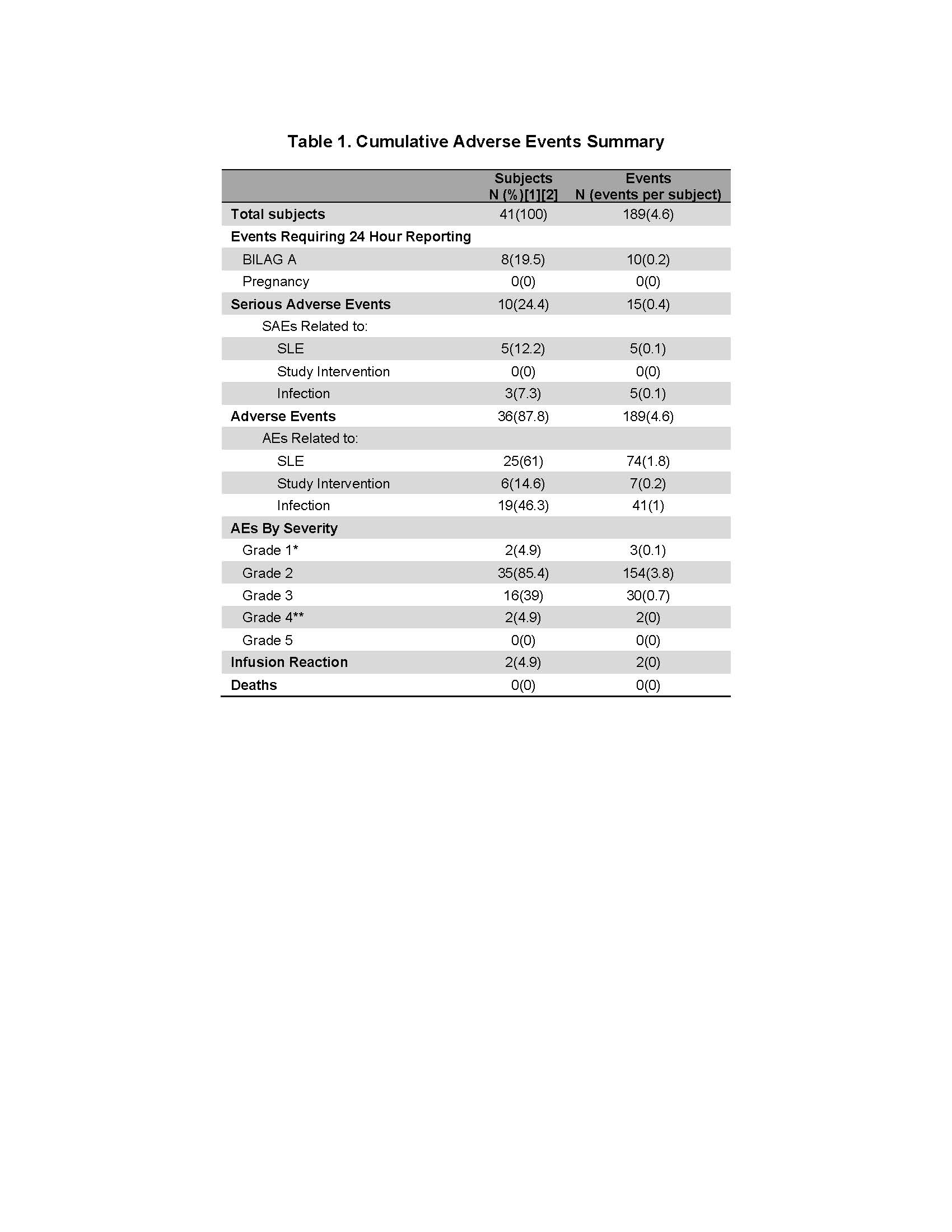 Adverse events in Cohort 1 of the MiSLE trial
Adverse events in Cohort 1 of the MiSLE trial
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gilkeson G, Kamen D, Lim S, Ramsey-Goldman R, Kalunian K, Sheikh S, Ishimori M, Wallace D. Interim Analysis of Cohort 1 in the Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Trial in Systemic Lupus Erythematosis: Safety and Data Management During the Pandemic [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interim-analysis-of-cohort-1-in-the-mesenchymal-stromal-cell-trial-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosis-safety-and-data-management-during-the-pandemic/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interim-analysis-of-cohort-1-in-the-mesenchymal-stromal-cell-trial-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosis-safety-and-data-management-during-the-pandemic/
