Session Information
Date: Wednesday, November 13, 2019
Title: 6W020: Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Disease III: Novel Therapies (2900–2905)
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The protein A20, encoded by TNFAIP3, represses signaling upstream of the inflammatory transcription factor nuclear factor (NF)-kB by regulating ubiquitination. Heterozygous loss-of-function mutations in TNFAIP3 cause the systemic autoinflammatory disease Haploinsufficiency of A20 (HA20) [1]. Because no FDA-approved medications directly target NF-kB signaling, current HA20 therapies target NF-kB activating cytokines, with biological agents chosen based on clinical experience rather than mechanistic data [2].
Methods: HA20 patients were selected from NHGRI protocol 94-HG-0105 “Genetics and Pathophysiology of Autoinflammatory Disorders”. All patients had mutations in TNFAIP3 diagnosed by targeted sequencing. Functional activity was confirmed using a reporter assay. Whole blood was extracted into PAXgene tubes, RNA was extracted, and Nanostring was used to assess expression of interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs). Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated and stored in liquid nitrogen. After thawing, cells were rested in R10 media for 2 hours, then in R0 media for 30 minutes before measuring STAT phosphorylation by flow cytometry. Patients were followed every 3-6 months during tofacitinib treatment. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) were obtained by CLIA-certified clinical laboratories.
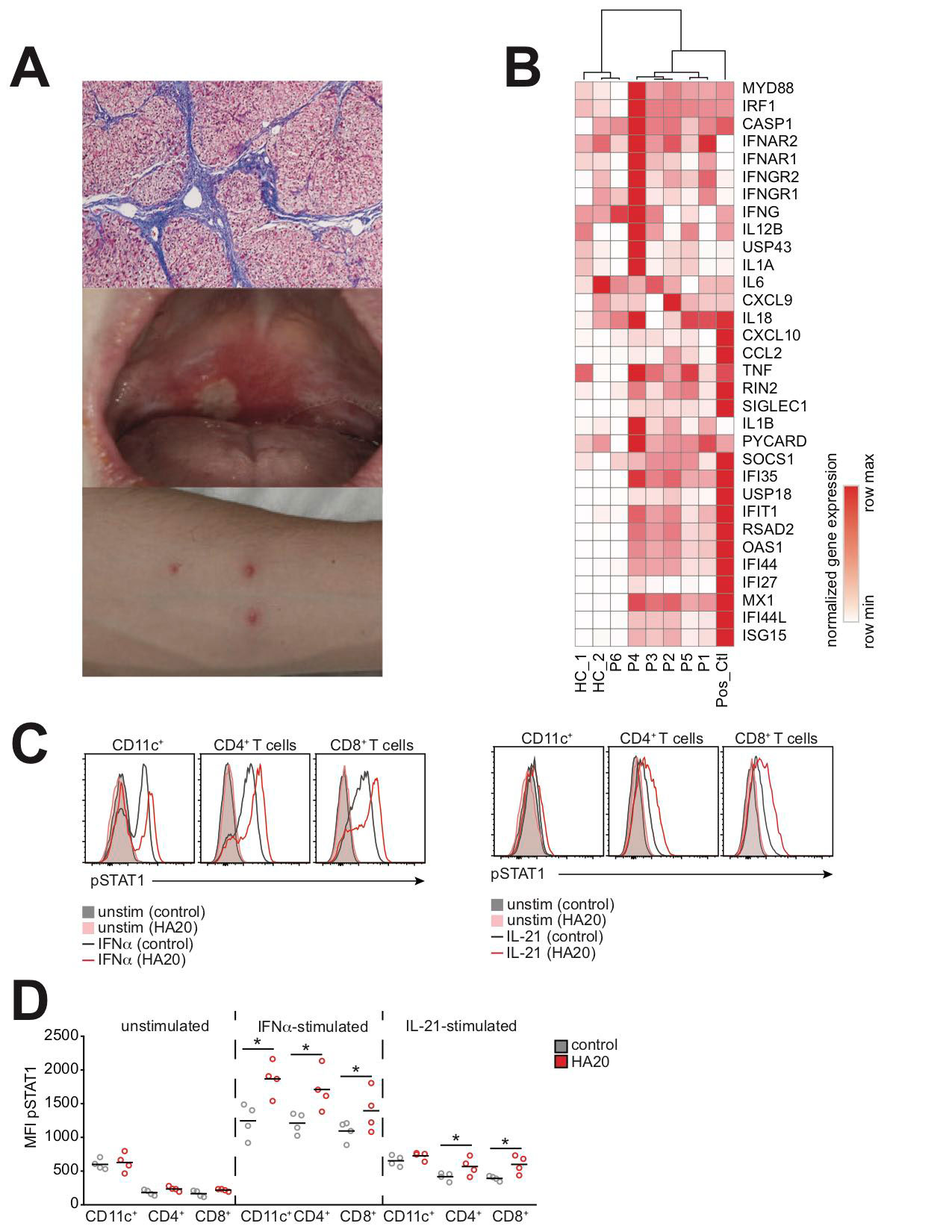
Results: ISG expression was measured on 5 patients with treatment-refractory active disease and 1 patient with inactive disease. Clinical manifestations were heterogeneous and included hepatic fibrosis, nephritis, and orogenital ulcerations (Fig 1A). All patients with active disease had increased expression of ISGs (Fig 1B). STAT1 phosphorylation was enhanced in response to both interferon (IFN)-α and Interleukin (IL)-21 (Fig 1C-D). STAT3 phosphorylation was not affected by HA20.
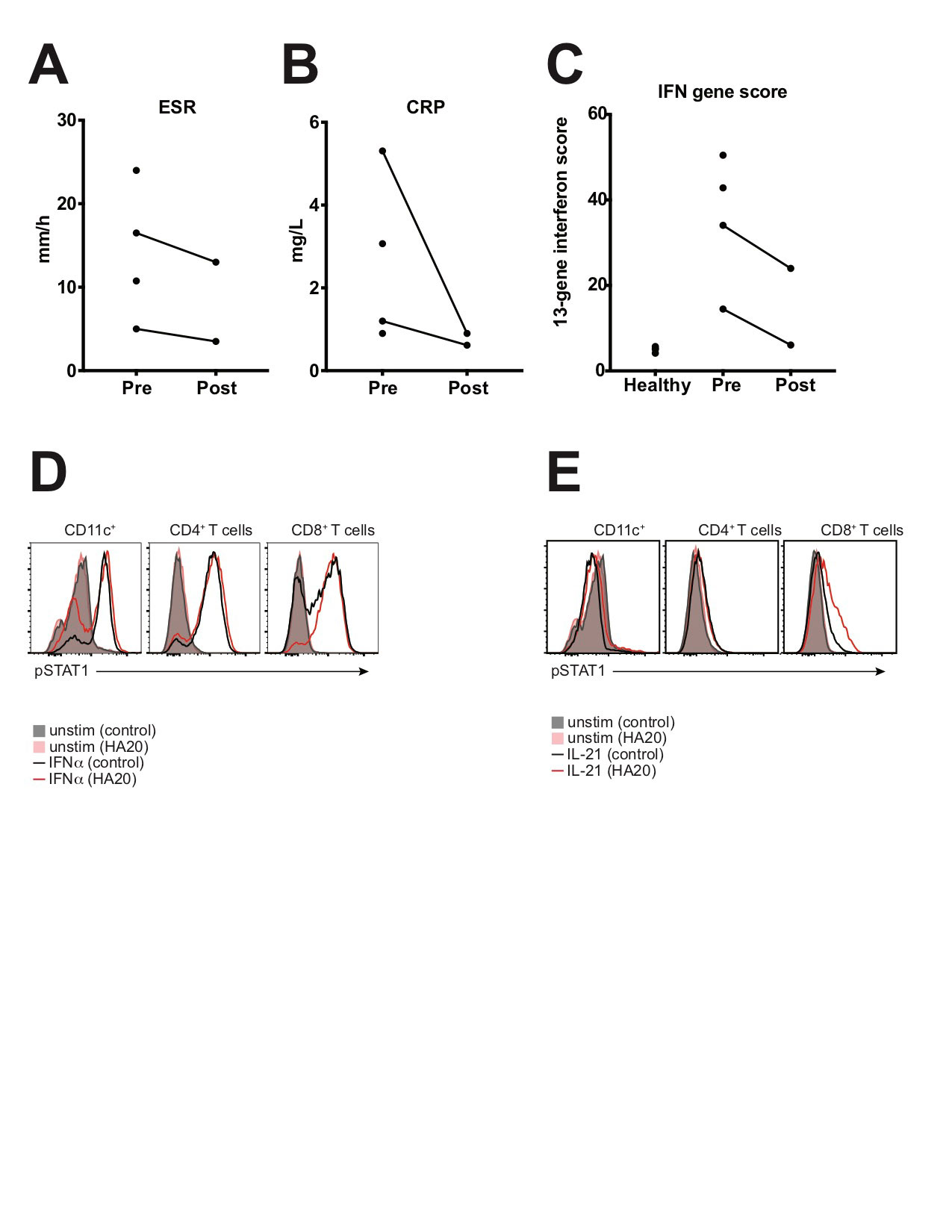
To date, 4 patients have undergone treatment with the JAK inhibitor tofacitinib, with treatment planned for the 5th patient. Treatment duration was 3-18 months at the time of analysis. All 4 patients reported improvements in clinical disease activity, and post-treatment data were available for 2 patients. Reduction in ESR, CRP, IFN gene score, and STAT1 phosphorylation were seen after treatment with tofacitinib (Fig 2). Tofacitinib was well-tolerated with no major adverse effects.
Conclusion: A group of treatment-refractory HA20 patients had increased expression of ISGs and enhanced STAT1 phosphorylation. Treatment with tofacitinib led to a clinical and immunological response. These results indicate that STAT1 signaling contributes to HA20 pathology, and that IFN signature predicts response to tofacitinib.
References
- Zhou Q, Wang H, Schwartz DM, Stoffels M, Park YH, Zhang Y, Yang D, Demirkaya E, Takeuchi M, Tsai WL et al: Loss-of-function mutations in TNFAIP3 leading to A20 haploinsufficiency cause an early-onset autoinflammatory disease. Nat Genet 2016, 48(1):67-73.
- Aeschlimann FA, Batu ED, Canna SW, Go E, Gul A, Hoffmann P, Leavis HL, Ozen S, Schwartz DM, Stone DL et al: A20 haploinsufficiency (HA20): clinical phenotypes and disease course of patients with a newly recognised NF-kB-mediated autoinflammatory disease. Ann Rheum Dis 2018, 77(5):728-735.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Blackstone S, Schwartz D, Sampaio Moura N, Stone D, Waldman M, Hoffmann P, Jones A, Romeo T, Barron K, Milner J, Kastner D, Ombrello A. Interferon Signature Predicts Response to Tofacitinib in Haploinsufficiency of A20 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interferon-signature-predicts-response-to-tofacitinib-in-haploinsufficiency-of-a20/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interferon-signature-predicts-response-to-tofacitinib-in-haploinsufficiency-of-a20/