Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The purpose of this study is to explore new biomarkers for early diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). For better discrimination power, we especially investigated the samples of early RA (eRA) patients with the onset of RA less than 2 year.
Methods: Gene expression profiles of peripheral mononuclear cells (PBMC) and CD4+ T cells obtained patients with eRA, advanced RA (aRA, disease duration more than 2 year) and osteoarthritis (OA) were investigated using microarray. PBMC from 11 patients with eRA and CD4+ T cells from 10 patients with eRA were analyzed compared to patients from aRA and OA. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was performed to verify the results of microarray. The concentrations of representative cytokines were measured with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits.
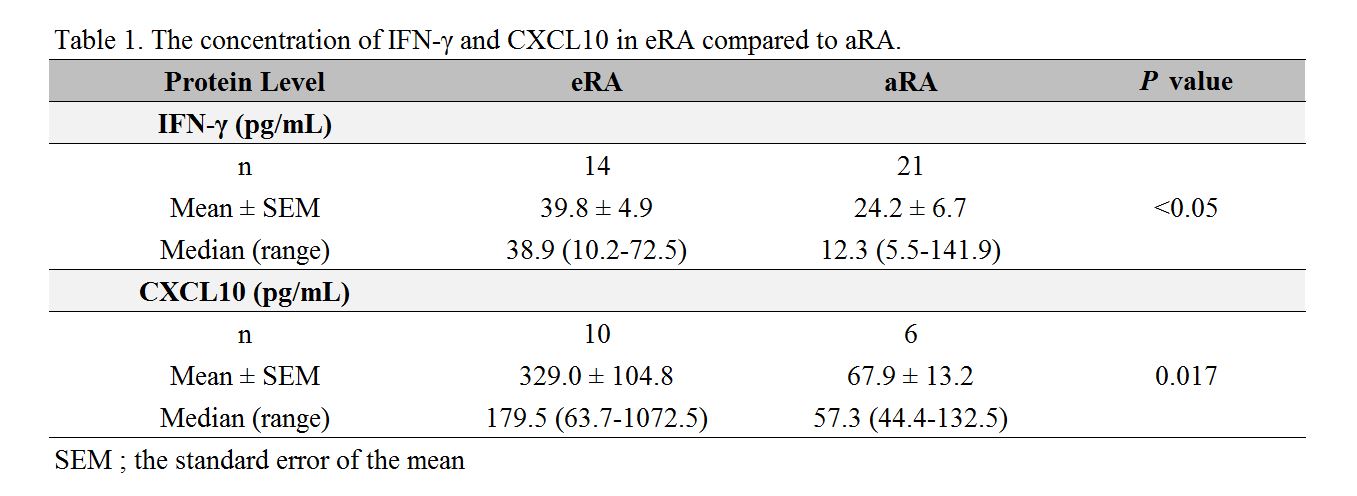
Results: We identified 52 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) with more than 1.5-fold higher expression values and 27 DEGs with lower expression on microarray of PBMC of eRA patients compared to OA (p < 0.05). 29 genes were highly upregulated in CD4+ T cells of patients with eRA compared to aRA and OA (3-fold, p < 0.05). The top 10 genes were mainly interferon signature genes and related chemokine including CXCL10 (chemokine C-X-C motif ligand 10; 225-fold, p = 0.004), IFIT3 (interferon-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 3; 85-fold, p = 0.0002), IFIT1 (interferon-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 1; 33-fold, p = 0.002), RSAD2 (radical S-adenosyl methionine domain containing 2; 23-fold, p = 0.001), TNFAIP6 (tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 6; 15-fold, p = 0.005), SLAMF7 (SLAM family member 7; 14-fold, p = 0.008), IFI44 (interferon-induced protein 44; 14-fold, p = 0.0003), IFIH1 (interferon induced with helicase C domain 1; 13-fold, p = 0.0002), OASL (2-5-oligoadenylate synthetase-like; 11-fold, p = 0.0002), HERC5 (HECT and RLD domain containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 5; 11-fold, p = 0.0003). The differentially expressed genes were verified using qRT-PCR. Elevated levels of IFN-¥ã and CXCL10 were demonstrated in patients with eRA. The concentration of IFN-¥ã and CXCL10 was significantly higher in eRA than aRA (Table 1).
Conclusion: Our study defined that IFN-¥ã signature genes in CD4+ T cells and level of IFN-¥ã in serum were highly presented in the early stages of rheumatoid arthritis. In addition, we found CXCL10, which supposed to be stimulated by IFN-¥ã, was significantly increased not only in the gene level but also in the protein level of peripheral blood from eRA. IFN-¥ã signature as well as CXCL10 could be useful as biomarkers in patients with the early stage of rheumatoid arthritis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lee K, Lee J, Min HK, Kim HR, Lee SH, Park SH, Ju JH, Kim H. Interferon Gamma Signature Genes and CXCL10 As New Biomarkers in Early Stage of Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interferon-gamma-signature-genes-and-cxcl10-as-new-biomarkers-in-early-stage-of-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interferon-gamma-signature-genes-and-cxcl10-as-new-biomarkers-in-early-stage-of-rheumatoid-arthritis/