Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: We have previously reported that current smoking (or having recently quit within 4 years) was associated with elevated risk of SLE, in particular anti-dsDNA+ SLE. Genetic and environmental factors, such as smoking, may interact in determining SLE risk. We investigated whether interactions between smoking and genetic risk factors may influence SLE risk.
Methods: We identified subjects with validated SLE and DNA samples within the Nurses’ Health Studies (NHS) and Partners Healthcare Biobank (PHB). 673 SLE cases were matched to 3,276 controls without SLE on age, sex and race (matched on self-report race in NHS and by 1st 3 principle components of GWAS in PHB). All subjects had data on smoking prior to SLE diagnosis date or the matched index date in controls. DNA samples were genotyped and imputed using Haplotype Reference Consortium (Michigan) and SNP2HLA for HLA. SLE risk alleles were identified from published GWAS studies (mainly from White and Asian populations): https://www.ebi.ac.uk/gwas/. After pruning for linkage disequilibrium, 86 SNPs and 10 HLA alleles with genome wide significance p ≤ 5×10-8 were included in a new weighted genetic risk score (wGRS), weighted by log OR from published GWAS. The wGRS for all markers and for HLA alleles only were studied. Smoking was classified as current/quit within 4 years at SLE diagnosis vs. past/never smoker. wGRS was dichotomized as ≤ vs. > the median value in controls. We employed conditional logistic regression models for SLE or anti-double stranded DNA antibody + SLE (dsDNA+ SLE), conditioning on matching factors and controlling for cohort. We examined additive interactions using the attributable proportion (AP) due to interaction and tested for multiplicative interactions using a 1 d.f. χ2 test, for the wGRS as well as for individual risk alleles. We repeated analyses for risk of anti-dsDNA+ SLE. We examined interactions among all subjects and among Whites only.
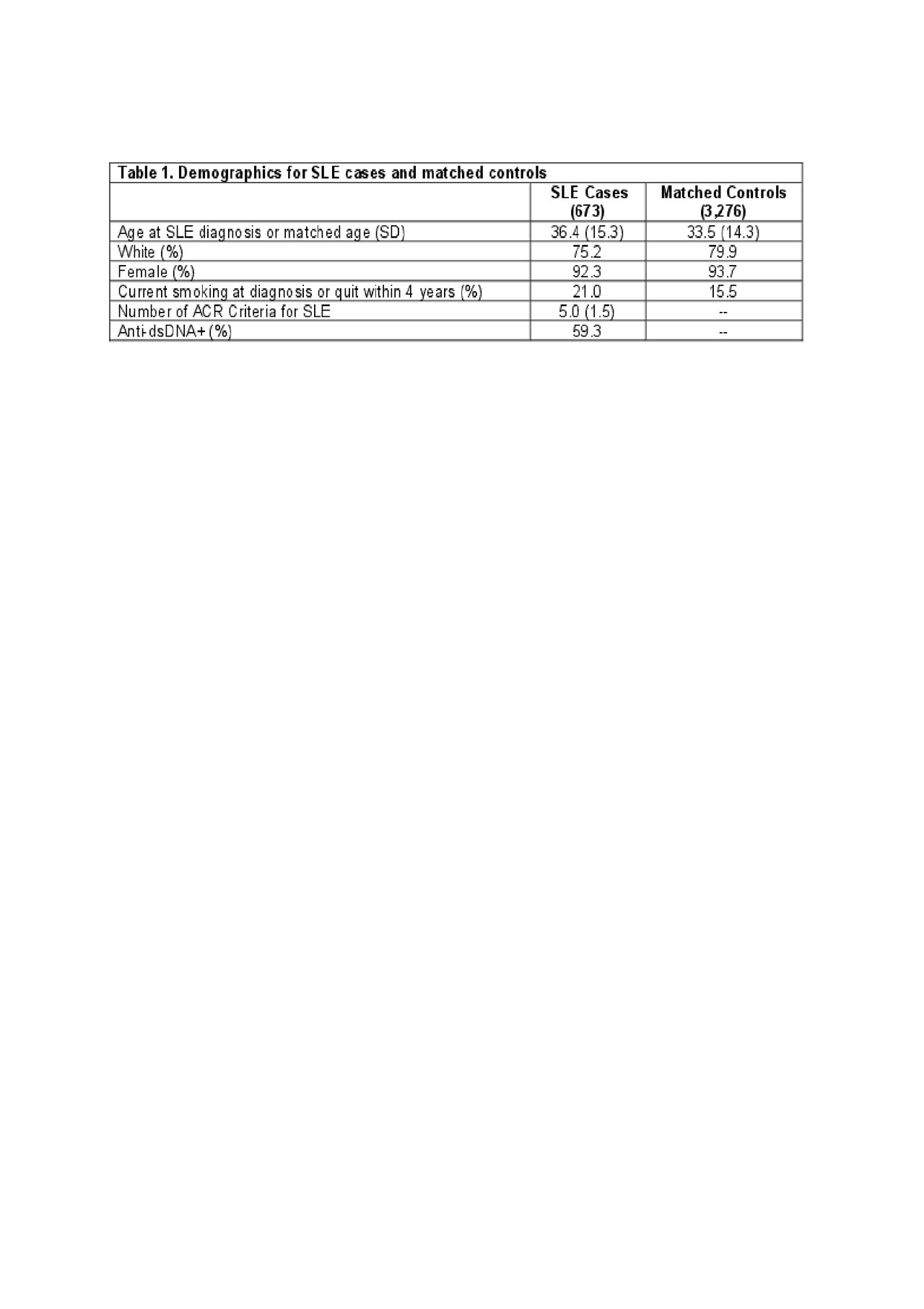
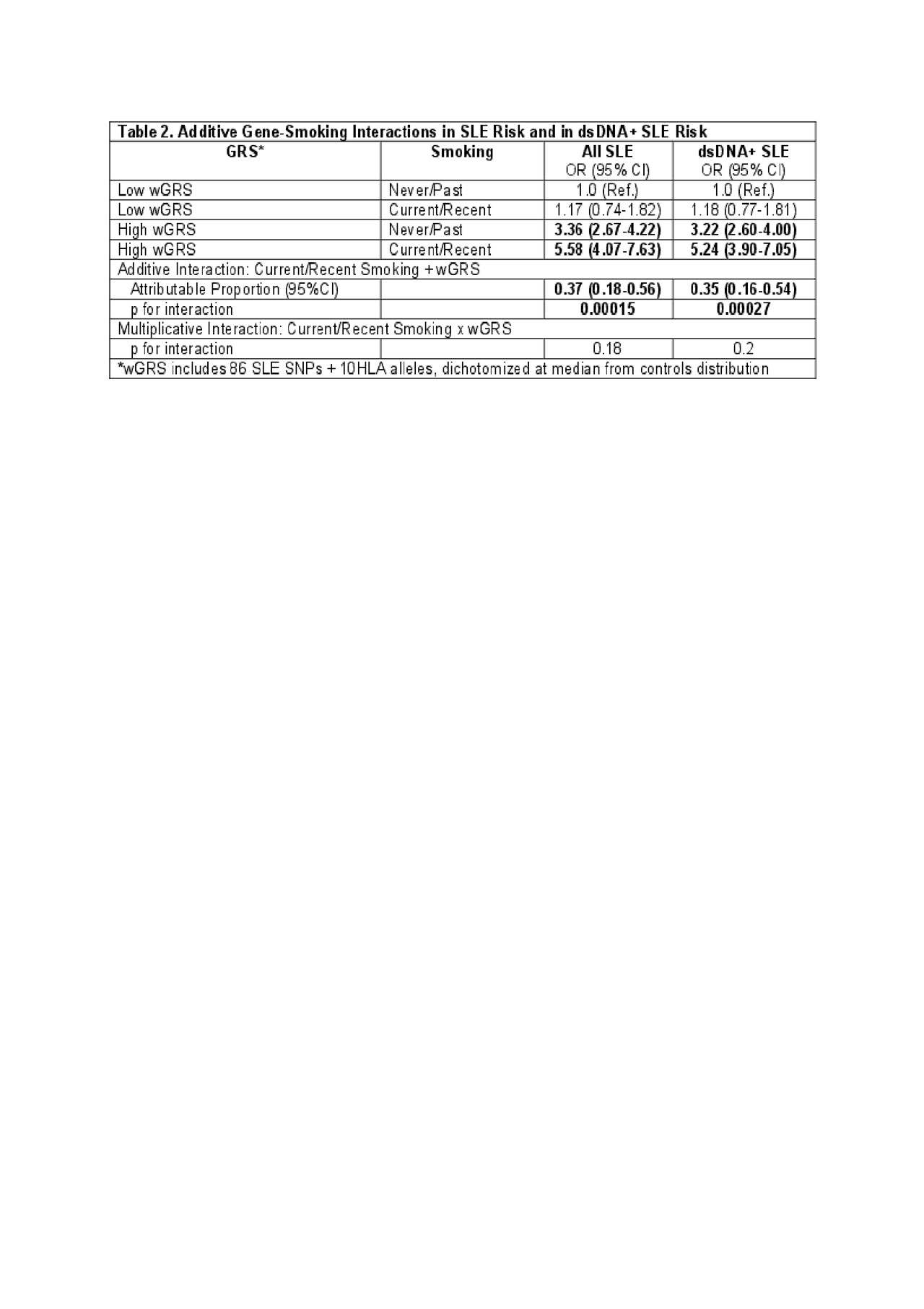
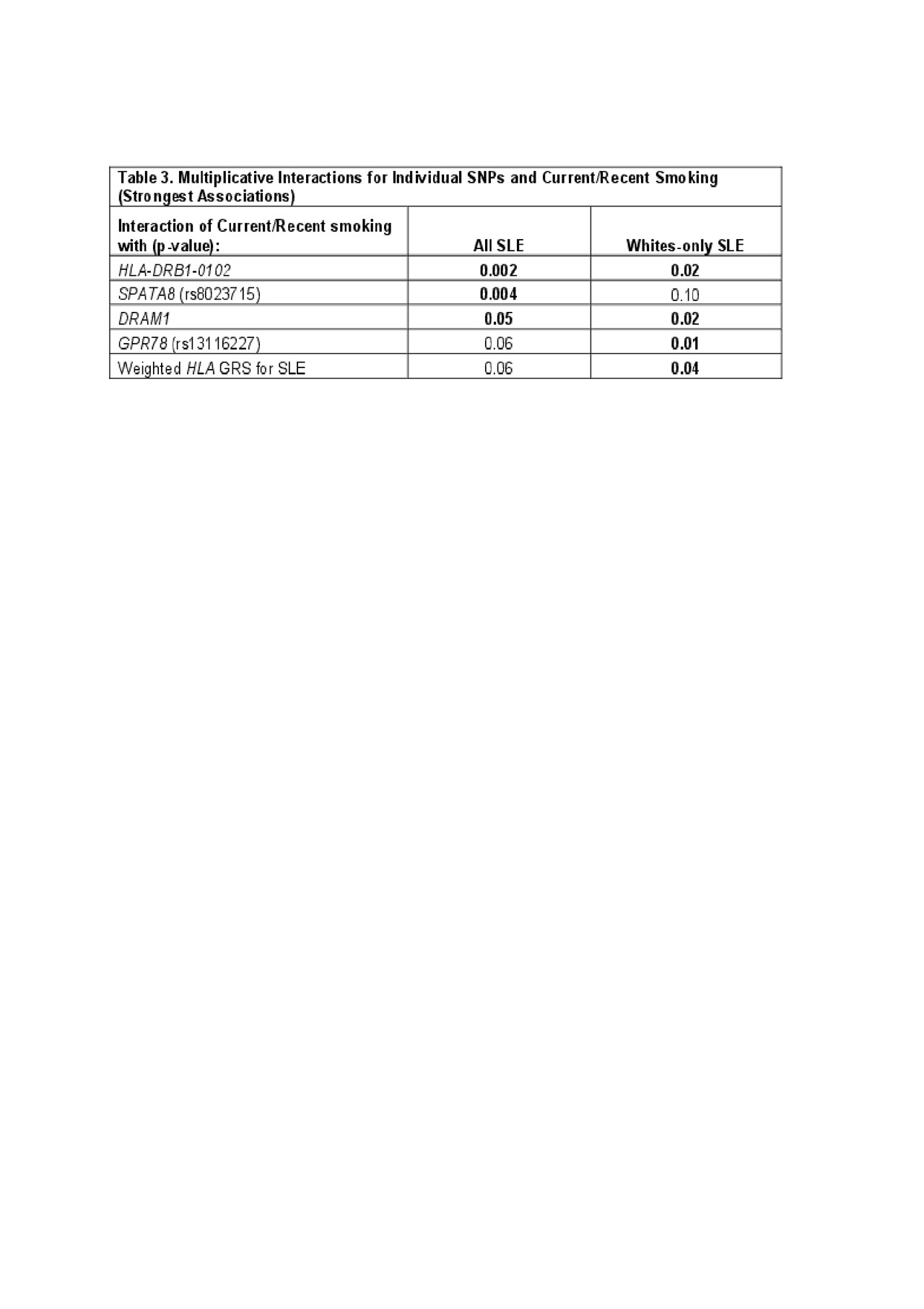
Results: Characteristics of the cases and controls are shown in Table 1. High wGRS (OR 1.4, p 5.6×10-52) and current smoking (OR 1.5, p 0.0006) were individually both strongly associated with SLE risk. SLE risk was highest in those with high wGRS and current smoking, OR 5.58 (95% CI 4.1-7.6) (Table 2). A significant additive interaction between high vs. low wGRS and current/recent vs. past/never smoking was found (AP 0.37, p 1.5×10-4). Findings were similar for interactions associated with anti-dsDNA+ SLE risk. Significant multiplicative interactions between smoking and genotypes were found with specific genotypes, including HLA-DRB1-0102 (p 0.002) (Table 3), the weighted HLA GRS for SLE, but not with overall wGRS (p 0.18). Findings were similar when limited to Whites only.
Conclusion: These findings support the hypothesis that smoking predisposes to SLE in the presence of genetic factors, with a greater than additive interaction with overall genetic risk and potentially greater than multiplicative interaction with certain genotypes. Studies should now investigate the mechanisms of these interactions and whether smoking influences the function of these genes in SLE pathogenesis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cui J, Raychaudhuri S, Speyer C, Malspeis S, Guan H, Liu X, Williams J, Davenport E, Knevel R, Karlson E, Costenbader K. Interactions Between Genome-Wide Genetic Factors and Current Smoking in Determining SLE Risk [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interactions-between-genome-wide-genetic-factors-and-current-smoking-in-determining-sle-risk/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interactions-between-genome-wide-genetic-factors-and-current-smoking-in-determining-sle-risk/