Session Information
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: ultrasonography (US) has been implemented recently as a possible diagnostic method for CPPD[1]. However, data on the reliability of US in CPPD diagnosis are lacking. Aim of the study was to assess the inter-reader and intra-reader reliability of US on detecting CPP deposition in fibrocartilage(FC), hyaline cartilage (HC), tendons (T) and synovial fluid (SF)
Methods: the OMERACT “US in CPPD” group defined firstly the US CPPD identification criteria following the methods adopted by OMERACT and described at the OMERACT handbook (http://www.omeract.org/omeract_publications.html). After a systematic literature review and a Delphi survey the set of US criteria for identification of CPPD by were defined (table 1).
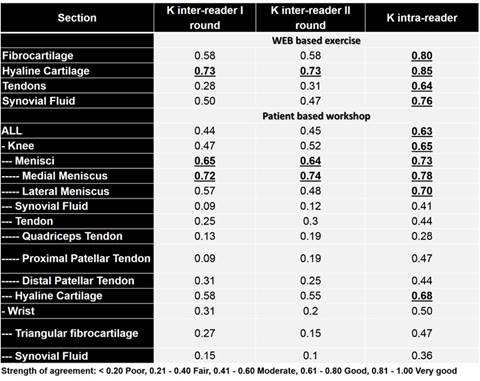
Subsequently, a two steps procedure for the assessment of the reliability has been followed. Firstly, the panel gave a dichotomous score on the presence absence of CPPD in 150 photos of FC, HC, T and SF equally distributed, on a web based platform. The assessment has been carried out twice in order to calculate both inter and intra-reader reliability. In the second step, the experts met for a real life-patient based assessment of CPPD in a workshop organised in Siena-Italy. In that occasion, FC/HC/T/SF of the right knee and FC and SF of the right wrist of 8 patients were assessed twice in a day by all experts giving again a dichotomous score for CPPD. 8 US scanners (ESAOTE mylab seven) equipped with the same probe and the same preset (made ad hoc before the meeting), have been used for the workshop.
Results: Reliability values of the web based exercise and of the workshop are presented in table 2. Tendons and synovial fluid analysis did not reach sufficient strength of agreement neither on the web based nor in the patient based exercise regarding the inter-reader kappa and independently of the site. However, in the static exercise, both tendons and SF reached a good intra-reader reliability meaning that scanning technique of these structures is very important for CPPD identification. On the other hand, menisci (but not triangular FC of the wrist) and HC reached good kappa values for inter-reader and intra-reader agreement both on static and web-based exercise.
Conclusion: Knee cartilage and fibrocartilage structures resulted to be reliable enough for identification of CPPD. On the other hand, CPPD identification in tendons and synovial fluid is challenging and the actual OMERACT criteria for these sites do not ensure a safe classification of patients. OMERACT US criteria for CPPD identification in knee menisci and HC allow a reliable classification of patients and should be used when CPPD is suspected. References:
1 Zhang W, Doherty M, Bardin T, et al. European League Against Rheumatism recommendations for calcium pyrophosphate deposition. Part I: terminology and diagnosis. Ann Rheum Dis 2011;70:563–70. doi:10.1136/ard.2010.139105
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Filippou G, Scirè CA, Damjanov N, Adinolfi A, Carrara G, Picerno V, Toscano C, Bruyn GAW, D'Agostino MA, Delle Sedie A, Filippucci E, Gutierrez M, Micu MC, Moller I, Naredo E, Zufferey P, Pineda C, Porta F, Schmidt WA, Terslev L, Vlad V, Frediani B, Iagnocco A. Inter-Reader and Intra-Reader Reliability of the New Omeract Ultrasonographic Criteria for the Diagnosis of Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/inter-reader-and-intra-reader-reliability-of-the-new-omeract-ultrasonographic-criteria-for-the-diagnosis-of-calcium-pyrophosphate-deposition-disease/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/inter-reader-and-intra-reader-reliability-of-the-new-omeract-ultrasonographic-criteria-for-the-diagnosis-of-calcium-pyrophosphate-deposition-disease/