Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose
Physicians, patients, and payers may have different ideas about what constitutes successful treatment and how treatment goals should be defined for rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This analysis was designed to evaluate overlap between attained treatment goals that are important to physicians, patients, and payers after 6 months of add-on golimumab (GLM) in patients with active RA, and to determine baseline predictors of patients who achieve all 3 goals.
Methods
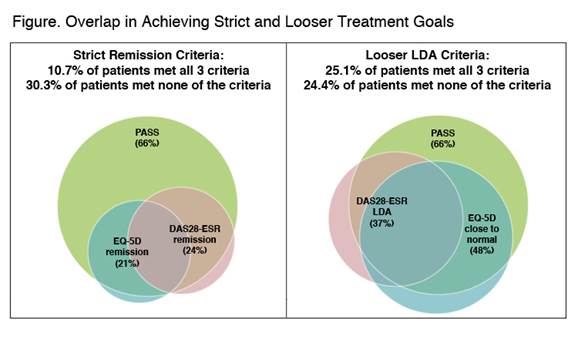
GO-MORE was an open-label, multinational, prospective study in biologic-naïve patients with active RA (28-joint disease activity score using erythrocyte sedimentation rate [DAS28-ESR] ≥3.2) despite disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) treatment. Patients received 50-mg subcutaneous (SC) GLM once monthly for 6 months. Efficacy outcomes including DAS28-ESR, patient-acceptable symptom state (PASS; 1 yes/no question of patient satisfaction with their current disease state), and EuroQol 5-dimension (EQ-5D) were evaluated at month 6. The overlap in achievement of strict remission treatment goals was evaluated (DAS28-ESR remission, normal EQ-5D [≥.8], and met PASS); looser low disease activity (LDA) goals were also evaluated (DAS28-ESR LDA, EQ-5D near normal [≥.7], and met PASS). A multivariate regression analysis identified baseline predictors of patients who achieved the intersection of the 3 criteria.
Results
In 3280 efficacy-evaluable patients, mean disease duration was 7.6 years; mean DAS28–ESR was 5.97 (SD=1.095). As previously reported, 23.9% of 3280 efficacy-evaluable patients achieved remission, and 37.4% achieved LDA (based on DAS28-ESR) at month 6.1 21% of patients achieved normal QoL, and 48% achieved close-to-normal QoL (EQ-5D ≥.7). 66.0% of patients achieved PASS. Overlap in patients who achieved each goal is shown (figure). 10.7% of patients (350/3280) met all 3 strict criteria, and 25.1% (823/3280) met all 3 looser criteria. Significant baseline predictors of achieving all 3 strict remission criteria were absence of comorbidities; lower DAS28, Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ), and swollen joint count scores; and greater anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide levels and EQ-5D Index scores. When PASS was replaced with HAQ ≤.5 (minimal or no functional impairment, achieved by 37.4% of patients) in either the set of strict or looser criteria, the percentage of patients who met all 3 criteria was similar to when PASS was used.
Conclusion
In patients with active RA who failed ≥1 DMARD and received add-on GLM for 6 months, overlap in achievement of LDA goals of physicians, patients, and payers was attained in 25.1% of patients. Overlap was smaller when strict remission goals were evaluated. Several measures of lower disease activity at baseline predicted achievement of all 3 strict remission criteria.
Reference:
1. Combe B et al. Ann Rheum Dis. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203229.
Disclosure:
B. Combe,
BMS, Lilly, Merck, Pfizer, Roche-Chugai, and UCB,
5;
D. Veale,
Abbott, Janssen, MSD, Pfizer, and Roche,
2,
MSD, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB,
5;
R. Burgos-Vargas,
Abbvie, BMS, Janssen, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB,
9;
G. Szűcs,
None;
M. Leirisalo-Repo,
MSD,
5;
R. Yao,
Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Whitehouse Station, NJ,
3;
S. Huyck,
Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Whitehouse Station, NJ,
3;
R. Lyu,
Employee of Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Whitehouse Station, NJ,
3;
M. Govoni,
MSD Italy,
3;
N. Vastesaeger,
MSD Belgium,
3;
H. Weng,
Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Whitehouse Station, NJ,
3.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/integrating-treatment-goals-of-physicians-patients-and-payers-during-treatment-with-golimumab-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/