Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The oral, selective Janus kinase-1 inhibitor filgotinib (FIL) significantly improved RA signs and symptoms in patients (pts) with MTX-naïve and MTX- and biologic-refractory RA.1–5 In 52-week (W) active controlled trials, FIL safety was comparable to adalimumab and MTX.1,2 Updated integrated analysis of FIL safety is needed.
Methods: Data were integrated from 3 phase 3 (FINCH 1–3; NCT02889796, NCT02873936, NCT02886728), 2 phase 2 (DARWIN 1, 2; NCT01668641, NCT01894516), and 2 long-term extension (DARWIN 3, NCT02065700; FINCH 4, NCT03025308) trials including up to 5.5 years (y) FIL exposure. Pts were ≥18 y with active RA per ACR criteria. DARWIN 3 and FINCH 4 data through April 26, 2019, and Sept 16, 2019, respectively, were included; other trials are complete. Placebo (PBO)-controlled analysis set included pts from 4 PBO-controlled trials receiving FIL 200 or 100 mg once-daily (QD) or PBO for 12W. Long-term as treated analysis set included all available data for pts receiving ≥1 dose FIL 200 or 100 mg QD from 7 trials, including after treatment conversion. Incidence (n [%]) and exposure-adjusted incidence rates (EAIR) per 100 pt-years exposure (PYE) of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs; onset after first dose and no later than either 30 days after last dose or new drug first dose date −1 day) and TEAEs of special interest (AESIs) are presented. EAIR and 95% confidence intervals were estimated with Poisson models with treatment and study covariates and natural log of exposure offset, unless otherwise specified for infrequent events. Positively adjudicated major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) and venous thromboembolisms (VTE) were included.
Results: In long-term as treated set, 74.2% of pts received FIL for ≥52W (Table 1). In 12W PBO-controlled set, rates of TEAEs, TEAEs Grade ≥3, serious AEs (SAEs), and TEAEs leading to discontinuation or death were comparable for both FIL doses vs PBO (Table 2). EAIR for TEAEs were lower with FIL 200 vs 100 mg in as treated set but comparable between doses for TEAEs Grade ≥3, SAEs, and TEAEs leading to discontinuation or death. All and serious infection incidences were numerically higher for FIL vs PBO in the PBO-controlled set; herpes zoster occurred in 0.1%/0.3%/0.3% receiving FIL 200 mg/100 mg/PBO (Table 3). In as treated set, EAIR of all and serious infections were numerically higher for FIL 100 vs 200 mg, and herpes zoster EAIR was numerically higher for FIL 200 vs 100 mg. In PBO-controlled set, 0/3/2 cases of MACE occurred with FIL 200 mg/100 mg/PBO. In as treated set, MACE EAIR were comparable for FIL doses. No VTE occurred in 12W PBO-controlled set. In as treated set, VTE EAIR were 0.2 and 0.0/100 PYE for FIL 200 and 100 mg, respectively. Malignancies were uncommon and comparable for FIL doses.
Conclusion: FIL was well tolerated; no consistent dose dependent effect was observed for AESIs. VTE and other AESIs were infrequent. No new safety signals were identified with FIL dosing up to 5.5 y.
References
- Westhovens. Ann Rheum Dis 2017;76:998–1008.
- Kavanaugh. Ann Rheum Dis 2017;76:1009–19.
- Combe. Ann Rheum Dis 2019;78(suppl 2):A77.
- Genovese. JAMA 2019;322(4):315–25.
- Westhovens. Ann Rhem Dis 2019;78(suppl 2):A259.
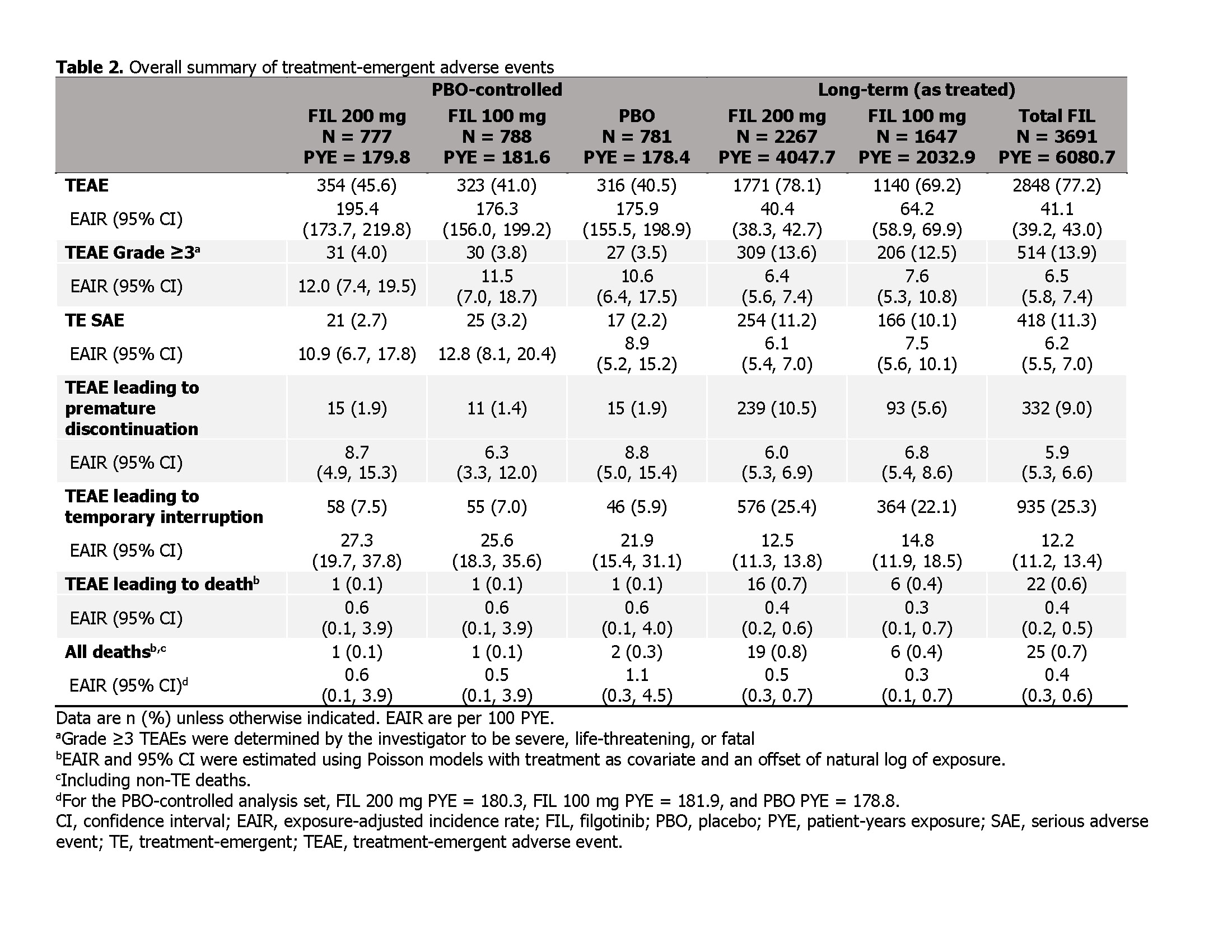 Table 2. Overall summary of treatment-emergent adverse events
Table 2. Overall summary of treatment-emergent adverse events
 Table 3. Treatment-emergent adverse events of special interest
Table 3. Treatment-emergent adverse events of special interest
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Winthrop K, Tanaka Y, Takeuchi T, Kivitz A, Matzkies F, Genovese M, Jiang D, Chen K, Bartok B, Jahreis A, Besuyen R, Burmester G, Gottenberg J. Integrated Safety of Filgotinib in Patients with Moderately or Severely Active Rheumatoid Arthritis Receiving Treatment for up to 5.5 Years [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/integrated-safety-of-filgotinib-in-patients-with-moderately-or-severely-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-receiving-treatment-for-up-to-5-5-years/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/integrated-safety-of-filgotinib-in-patients-with-moderately-or-severely-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-receiving-treatment-for-up-to-5-5-years/

