Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Filgotinib (FIL) is an oral Janus kinase 1 preferential inhibitor, approved for the treatment of moderate to severe active rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In previous analyses, comparable incidence of selected adverse events (AEs) occurred in FIL 200 mg (FIL200) and 100 mg (FIL100) dose groups, except for herpes zoster.1 This analysis aimed to provide an update on FIL selected AEs up to a median (max) exposure of 3.8 (8.3) years.
Methods: Integrated FIL RA data from 7 clinical trials are reported: Phase 2 (NCT01888874, NCT01894516), Phase 3 (NCT02889796, NCT02873936, NCT02886728), and the long-term extension studies DARWIN 3 Phase 2 (NCT02065700) and FINCH 4 Phase 3 (NCT03025308). Exposure-adjusted incidence rates (EAIRs)/100 patient-years of exposure (PYE), censored at time of first event, were determined for major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE), venous thromboembolism (VTE), arterial systemic thromboembolism, nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC), malignancies excluding NMSC, herpes zoster, serious infections and deaths. Data were as of May 2, 2022 (DARWIN 3) and May 6, 2022 (FINCH 4). MACE and VTE only include positively adjudicated events with a data cutoff of April 3, 2022.
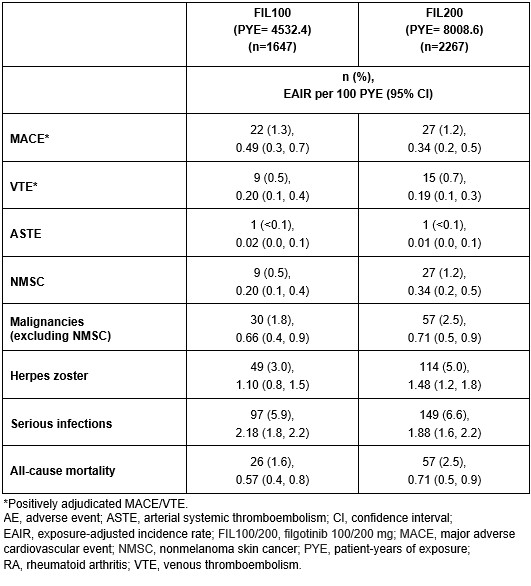
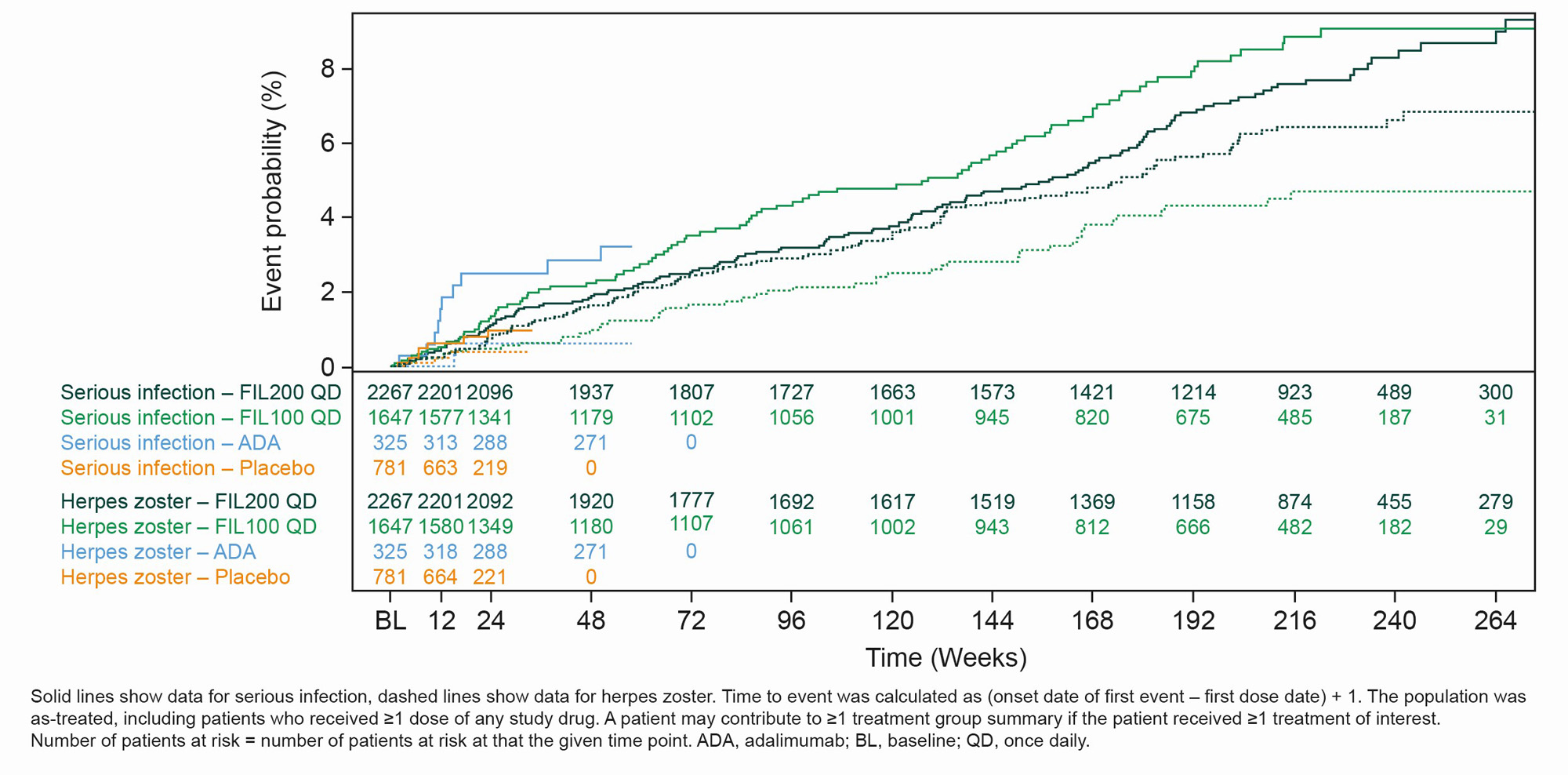
Results: The as-treated population included 3691 patients with 12,541 PYE. Median (max) exposure was 3.8 (8.3) in the pooled FIL group; 3.8 (8.3) years for FIL200 and 3.3 (7.8) years for FIL100. Baseline demographics and disease characteristics were balanced between groups.2 Small numerical differences were observed between FIL doses for EAIRs of selected AEs. Numerically higher incidences of NMSC, herpes zoster and all-cause mortality were reported with FIL200 vs FIL100; incidences of MACE and serious infections were numerically lower with FIL200 vs FIL100, with overlapping confidence intervals (Table). Over 240 weeks, the risks of MACE and VTE were comparable for FIL100 vs FIL200; low event numbers make interpretation difficult. The risk of herpes zoster was higher with FIL200 vs FIL100, and generally similar for serious infection or all-cause mortality (Figure).
Conclusion: Over a maximum of 8.3 years, FIL200 and FIL100 continued to show small numerical differences in EAIRs of selected AEs between dose groups in the overall RA population. Slightly higher incidence rates for NMSC, herpes zoster and all-cause mortality were reported in the FIL200 than FIL100 group, with a higher incidence of MACE and serious infections with the lower dose; confidence intervals overlapped between the dose groups.
References:
1. Winthrop KL, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2022;74(S9): abstract 0273
2. Winthrop KL, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2022;81:184–92
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Withrop K, Aletaha D, Caporali R, Tanaka Y, Takeuchi T, Van Hoek P, Stiers P, Rajendran V, Van Beneden K, Gottenberg J, Burmester G. Integrated Safety Analysis of Filgotinib in Patients with Moderate to Severe Active Rheumatoid Arthritis with a Maximum Exposure of 8.3 Years [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/integrated-safety-analysis-of-filgotinib-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-with-a-maximum-exposure-of-8-3-years/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/integrated-safety-analysis-of-filgotinib-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-with-a-maximum-exposure-of-8-3-years/