Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatments Poster III: Biosimilars and New Compounds
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Upadacitinib is an oral, selective inhibitor of Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) which is currently being evaluated for the treatment of several autoimmune disorders, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Upadacitinib demonstrated favorable efficacy and acceptable safety in two Phase 2b studies in subjects with moderate to severely active RA who had inadequate response to anti-TNF therapies (BALANCE I) or to methotrexate (BALANCE II). The presented analyses were conducted to characterize the relationships between upadacitinib plasma exposures and various efficacy endpoints, as well as effects on select laboratory parameters of interest to support the selection of doses to evaluate in Phase 3.
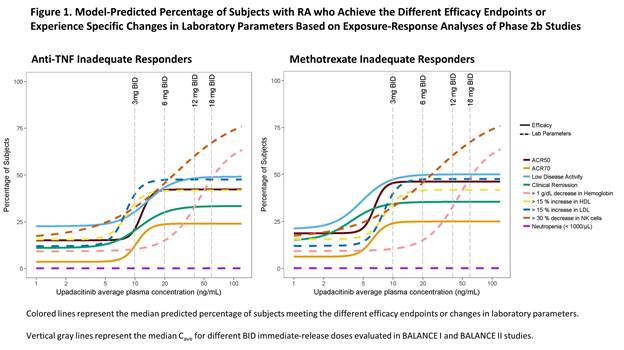
Methods: The analyses included data from 574 patients who had completed BALANCE I and II studies. Logistic regression analyses were conducted for the relationship between upadacitinib average plasma concentration during a dosing interval (Cave) and the probability of achieving various efficacy endpoints (ACR50, ACR70, low disease activity and clinical remission based on DAS28CRP) or experiencing a certain degree of change in select laboratory parameters (hemoglobin, NK cells, LDL-C, HDL-C, neutrophils). Data from BALANCE I and II were analyzed separately for efficacy, and data from both studies were pooled for the laboratory parameters analyses.
Results: The percentage of subjects achieving ACR50, ACR70, low disease activity, and clinical remission increased with increasing upadacitinib plasma exposures. With increasing upadacitinib plasma exposures, there was also an increase in the percentage of subjects experiencing decreases in hemoglobin and NK cells and increases in HDL-C and LDL-C from baseline to Week12. There was no relationship between upadacitinib plasma exposures and neutropenia (< 1000 cells/L). The model-predicted percentage of subjects who achieve various efficacy endpoints or experience specific changes in laboratory parameters is shown in Figure 1.
Conclusion: Upadacitinib plasma exposures associated with 6 mg BID to 12 mg BID using the immediate-release formulation (equivalent to15 mg QD to 30 mg QD using the extended-release formulation, respectively) are predicted to achieve near maximum efficacy in RA patients while having limited effects on NK cells, hemoglobin, LDL-C, and HDL-C. Exposures higher than 12 mg BID are not predicted to result in additional efficacy benefits in subjects with RA, but they have the potential for greater effects on laboratory parameters. Results from these analyses supported the evaluation of extended-release formulation 15 mg and 30 mg QD in Phase 3 trials in RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mohamed ME, Winzenborg I, Doelger E, Noertersheuser P, Camp HS, Meerwein S, Othman AA. Integrated Exposure-Response Analyses for Upadacitinib Efficacy and Effects on Laboratory Parameters in Rheumatoid Arthritis – Analyses of Phase 2b Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/integrated-exposure-response-analyses-for-upadacitinib-efficacy-and-effects-on-laboratory-parameters-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-analyses-of-phase-2b-studies/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/integrated-exposure-response-analyses-for-upadacitinib-efficacy-and-effects-on-laboratory-parameters-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-analyses-of-phase-2b-studies/