Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Polygenic risk scores (PRS) have been constructed to summarize genetic risk but there is limited research on environment-wide analysis of risk factors for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In this study, we performed an environment-wide association study to construct an environment risk score (ERS) for SLE and compare the risk conferred by ERS and PRS.
Methods: A total of 335 incident SLE cases were identified in the UK Biobank and matched 1:10 with age, sex, and ethnic background 3350 healthy controls. We examined the association between 37 environmental factors and SLE, using a univariate followed by a multivariate analysis. We summed the natural logarithm of the odds ratios (OR) of statistically significant environmental variables in the multivariable model to derive an ERS for SLE. Model discrimination was compared by De-Long`s test. PRS was calculated using the ORs of previously reported SLE genetic risk loci.
Results: The multivariate analysis revealed the association between daily sunlight exposure, depression, sleeplessness, sex hormone binding globulin levels, and air pollution with increased risk of SLE, while moderate physical activity was a protective factor. Increasing quartiles of the newly developed ERS were associated with similar degree of risk for SLE as the PRS. Integrating PRS with environmental factors significantly improved model performance.
Conclusion: We devised an ERS for SLE that summarizes the environmental component of the disease risk. We show that ERS confers a comparable degree of SLE risk as the PRS. Combining genetic and environmental factors could improve risk prediction models in SLE.
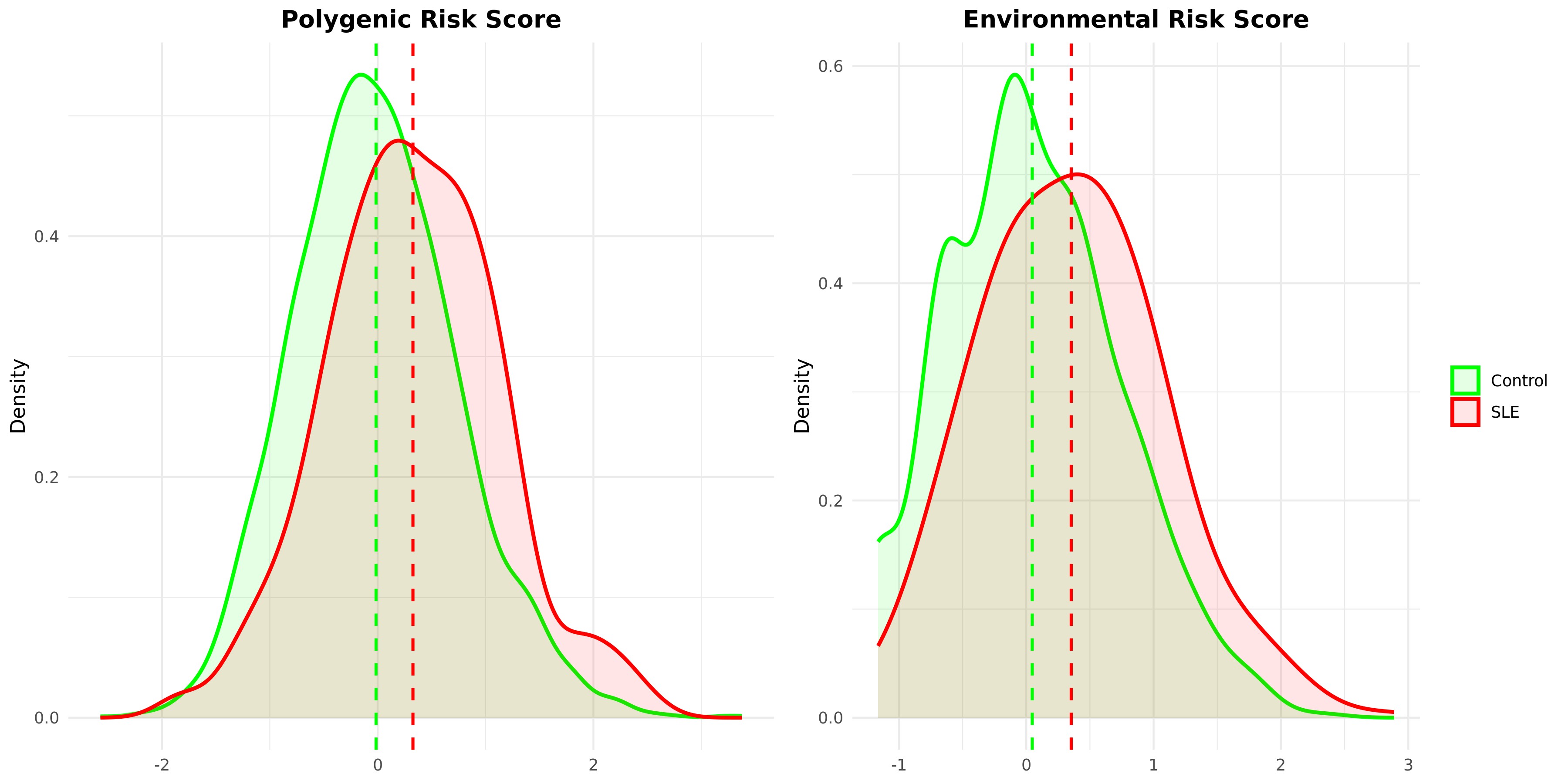 Comparison of standardized polygenic and environmental risk scores between SLE cases and matched controls. P values for the mean difference between cases and matched controls for polygenic and environmental risk score are 2.41×10-13 and 1.76×10-13, respectively.
Comparison of standardized polygenic and environmental risk scores between SLE cases and matched controls. P values for the mean difference between cases and matched controls for polygenic and environmental risk score are 2.41×10-13 and 1.76×10-13, respectively.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hocaoglu M, Sawalha A. Integrated Analysis of Polygenic and Environmental Risk Scores for Late-Onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/integrated-analysis-of-polygenic-and-environmental-risk-scores-for-late-onset-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/integrated-analysis-of-polygenic-and-environmental-risk-scores-for-late-onset-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/
