Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Title: Osteoarthritis – Clinical Aspects Poster I: Clinical Trials and Interventions
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
There is a draught of available effective treatments of knee osteoarthritis (OA) and tests of new therapies are needed. Polyacrylamide hydrogel (PAAG) is a non-toxic, non-degradable synthetic product, used for years in the augmentation of soft tissues. Animal studies have shown that intra-articular (IA) PAAG significantly alleviates lameness and joint effusion over 2 years among horses with OA. Thus, IA injection of PAAG may be a promising treatment for knee OA in humans, albeit with a need for scientific evaluation of efficacy and safety. The present study has been conducted to establish an initial estimate of effectiveness of IA injection of PAAG for the symptomatic treatment of knee OA.
Methods:
Patients with OA of the knee were invited into a prospective open-label cohort study. The patients received IA injection of 3 ml of PAAG (a proprietary 2.5% cross-linked PAAG manufactured by Contura International A/S) twice within 1 month. The WOMAC questionnaire was used to estimate efficacy, and was collected at baseline and after 4, 7 and 13 months. Efficacy was mainly estimated as a change from baseline for the WOMAC pain subscale after 4 months (Normalised to 0-100 points; 100 worst). WOMAC stiffness and WOMAC physical function were measured as secondary estimates of efficacy. The efficacy variables were analyzed using a mixed-effect model repeated measure approach without imputation of missing data. Sensitivity analyses were done using baseline observation carried forward imputation.
Results:
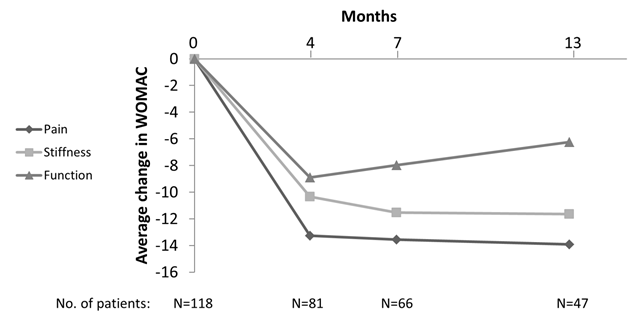
118 patients (62 females) received IA PAAG. Of these there were WOMAC data available from 81 after 4 months, 66 after 7 months, and 47 after 13 months. At baseline the mean WOMAC pain score was 43.7 (SD17.5). There were statistically significant reductions in WOMAC pain after 4 months (mean change -13.3 points [95% CI: -17.3 to -9.3]; P<.0001), which exceeds established minimal clinically important improvements margins of 9 points. Similar results were found in WOMAC stiffness and physical function (figure 1). The improvement was sustained throughout the observation period. In the sensitivity analyses the estimates were generally lower caused by the non-responder imputation approach (table 1).
Conclusion:
These results suggest beneficial effects of IA injection of a 2.5% PAAG on knee OA symptoms, even in the long term (1 year). This is promising but efficacy needs to be confirmed in a randomized study with adequate measures taken to reduce risk of bias.
Figure 1. Changes from baseline in WOMAC. No imputation of missing data.
Table 1. Sensitivity analyses of changes from baseline in WOMAC. Missing data imputed using BOCF technique.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Henriksen M, Overgaard A, Bliddal H. Initial Estimates of Efficacy of Intra-Articular 2.5% Polyacrylamide Hydrogel for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: An Observational Proof-of-Concept Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/initial-estimates-of-efficacy-of-intra-articular-2-5-polyacrylamide-hydrogel-for-the-treatment-of-knee-osteoarthritis-an-observational-proof-of-concept-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/initial-estimates-of-efficacy-of-intra-articular-2-5-polyacrylamide-hydrogel-for-the-treatment-of-knee-osteoarthritis-an-observational-proof-of-concept-study/