Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Inhibition of Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase IV Suppresses the Autoimmunity in Lupus-Prone Mice.
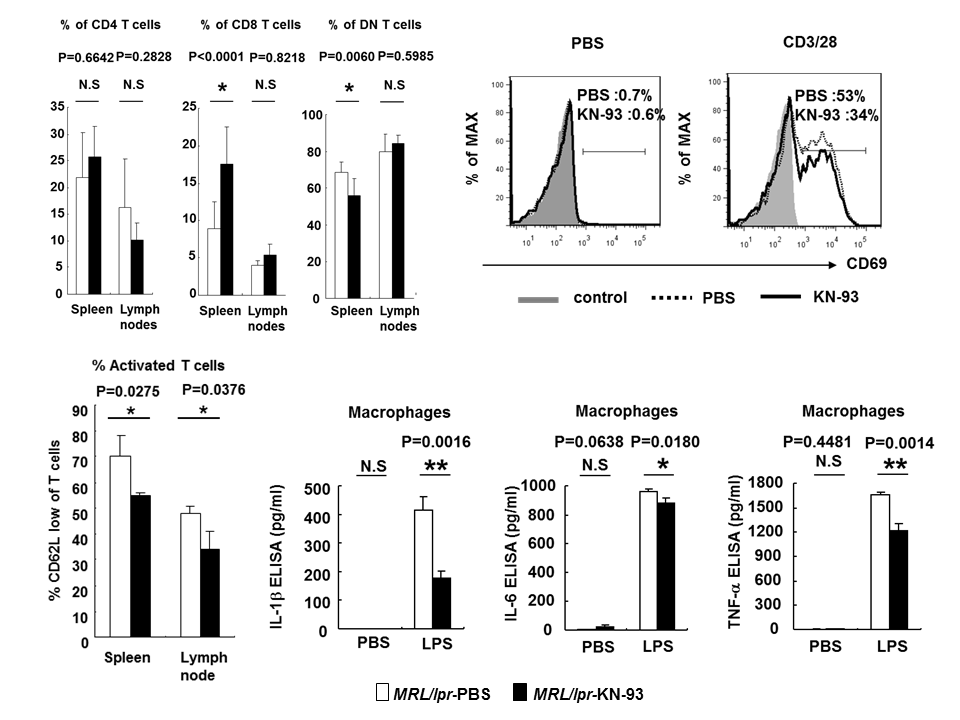
Background/Purpose: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic inflammatory disease associated with abnormal immune cell function.SLE T cells express high levels of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV (CaMKIV). We have shown previously that pharmacologic (Arthritis Rheum. 2011) or genetic silencing of Camkiv (J Immunol. 2011) suppresses lupus nephritis in lupus-prone mice. The purpose of this study was to determine whether pharmacologic inhibition of CaMKIV would improve immune function abnormalities. Methods: We treated MRL/lpr mice with KN-93, a CaMKIV inhibitor. The agent was administered by intraperitoneal injections at a dosage of 2.67 ug/gm of body weight per mouse 3 times a week, starting at week 8 of age through week 16. We evaluated the presence of CD4+, CD8+, CD3+CD4-CD8- (double negative, DN) and CD62L low T cells and proinflammatory cytokine production. We also determined the effect of inhibition or silencing of CaMKIV on proinflammatory cytokine production by human T cells and macrophages. Results: CaMKIV inhibition in MRL/lpr mice resulted in significant suppression of DN and CD62L low of T cells population and IFN-g production by T cells. In human activated T cells and macrophages, pharmacologic inhibition of CaMKIV resulted in suppression of IFN-g production and CD69 expression by T cells and IL-1b, IL-6 and TNF-a by macrophages. Silencing of CaMKIV in human activated T cells showed increased expression of FoxP3 mRNA level and decreased IL-17A mRNA level. Conclusion: We conclude that pharmacologic inhibition of CaMKIV suppresses cell activation and cytokine production in lupus-prone mice. Our data justify the development of small-molecule CaMKIV inhibitors or silencing CaMKIV for the treatment of patients with SLE.
Disclosure:
K. Ichinose,
None;
A. Kawakami,
None;
G. C. Tsokos,
None.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/inhibition-of-calciumcalmodulin-dependent-protein-kinase-iv-suppresses-the-autoimmunity-in-lupus-prone-mice/