Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Treating to target is routine in rheumatoid arthritis, but no comparable standard has been defined for SLE. In 2015, the definition of Lupus Low Disease Activity State (LLDAS) was generated by Asia-Pacific Lupus Collaboration, and the preliminary validation demonstrated its attainment to be associated with improved outcomes in SLE. A SLEDAI-2K score lower than 4 is the main criteria for LLDAS. SSDM is an interactive mobile disease management application, including application systems for both the doctors and patients. The patients can perform self-assessment, including SLEDAI-2K, 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36), and medical records entry (including medication and laboratory test results) through the mobile application. The data is synchronized to the SSDM of authorized rheumatologists and stored in cloud database. Based on the patients’ data, rheumatologists will provide medical advices to the patients.
The objective of this study is to evaluate the patterns of T2T and related influential factors among SLE patients after applying SSDM in real world.
Methods: Patients were trained to master SSDM by rheumatologists or nurses in clinics. The first assessment for SLEDAI-2K was performed as the baseline. Patients were required to perform repeated assessments after leaving the clinics.
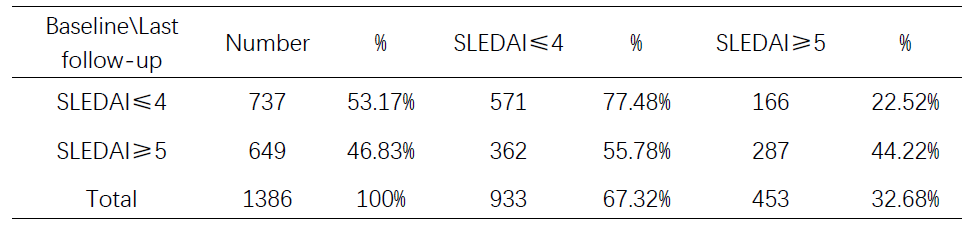
Results: From July 2015 to May 2019, 24,531 SLE patients enrolled in SSDM and mean age is 34.39±13.21(14-80) years old. And median disease duration is 3.29 years. The most commonly used drugs are hydroxychloroquine, glucocorticoids, leflunomide, mycophenolate mofetil, cyclophosphamide, methotrexate and cyclosporine A. Among them 1,386 SLE patients from 191 hospitals across China were followed up for more than 12 months through SSDM, and the results were summarized in Table 1.
The ratio of T2T achievers was 53.17% (737/1,386) at the baseline and improved significantly to 67.32% (933/1,386) after a 12-month follow-up, p< 0.01. Among T2T achievers at baseline, 77.48% (571/737) maintained T2T, and 22.52% (166/737) relapsed. Of patients who didn’t achieve T2T at baseline, 55.78% (362/649) of the patients achieve T2T after 12-month follow-up.
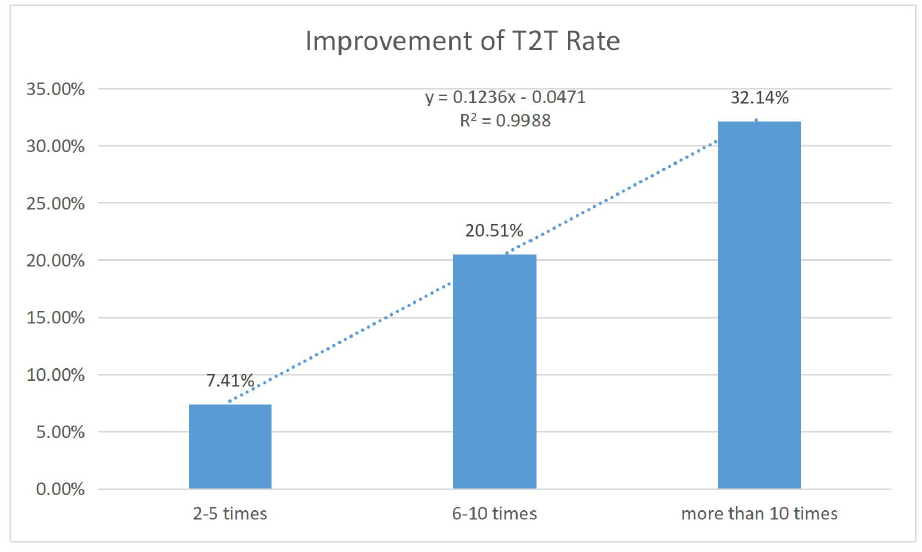
The impact of the times of self-assessment for SLEDAI-2K on T2T has been analyzed. The more frequent of the self-assessments being conducted by patients, the higher improvement of T2T rate will be. We performed linear regression analysis of variables in statistics and parameter estimation by least square method. The improvement of T2T rate(y) was positively correlated with times of self-assessment for SLEDAI-2K(x) independently. The regression equation as “y = 0.1236x – 0.0471 R2 = 0.9988”, p< 0.01. (Figure 1)
Conclusion: After proactive disease management via SSDM for more than 12 months, the rate of T2T in SLE patients increased significantly. Patients with SLEDAI-2K≤4 score at baseline had a significantly higher retention rate of disease activity. The patients who performed more self-assessments through SSDM had lower probability of relapse and higher rate of T2T maintaining and achievement. SSDM is a valuable tool for long term SLE follow-up through empowering patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Huang J, Wang Y, Wei H, Yang J, Xie T, Wang H, Wang X, Zhang Y, Zhao C, Zou J, He F, Ru J, Wu H, Wang G, Sun L, Xu S, Hao Y, Li X, Li Z, Wu B, Jia Y, Liu Y, Xiao H, Xiao F, Bao C. Influential Factors in Promoting Treat-to-Target for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus via Empowering Patients: A Cohort Study from China by Smart System of Disease Management (SSDM) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/influential-factors-in-promoting-treat-to-target-for-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-via-empowering-patients-a-cohort-study-from-china-by-smart-system-of-disease-management-ssdm/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/influential-factors-in-promoting-treat-to-target-for-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-via-empowering-patients-a-cohort-study-from-china-by-smart-system-of-disease-management-ssdm/