Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) produces joint destruction, functional deterioration, comorbidity and premature death. The best results are achieved with an early start of a treat-to-target and tight control strategy that allow to quickly and effectively control the inflammatory process. Methotrexate is the DMARDs of first choice, but only half of patients (pts) respond satisfactorily in monotherapy and often produces side effects. Studies exploring the contribution of genetic variability to the variability of the efficacy to MTX in RA and its toxicity show highly variable results. The aim was to explore the combined effect of the clinical characteristics related to the patient, the disease and the treatment, and of different genetic polymorphisms linked to the transport and metabolic pathways of MTX, on the therapeutic response of this drug, in terms of efficacy and safety, in a cohort of RA patients treated with MTX in monotherapy.
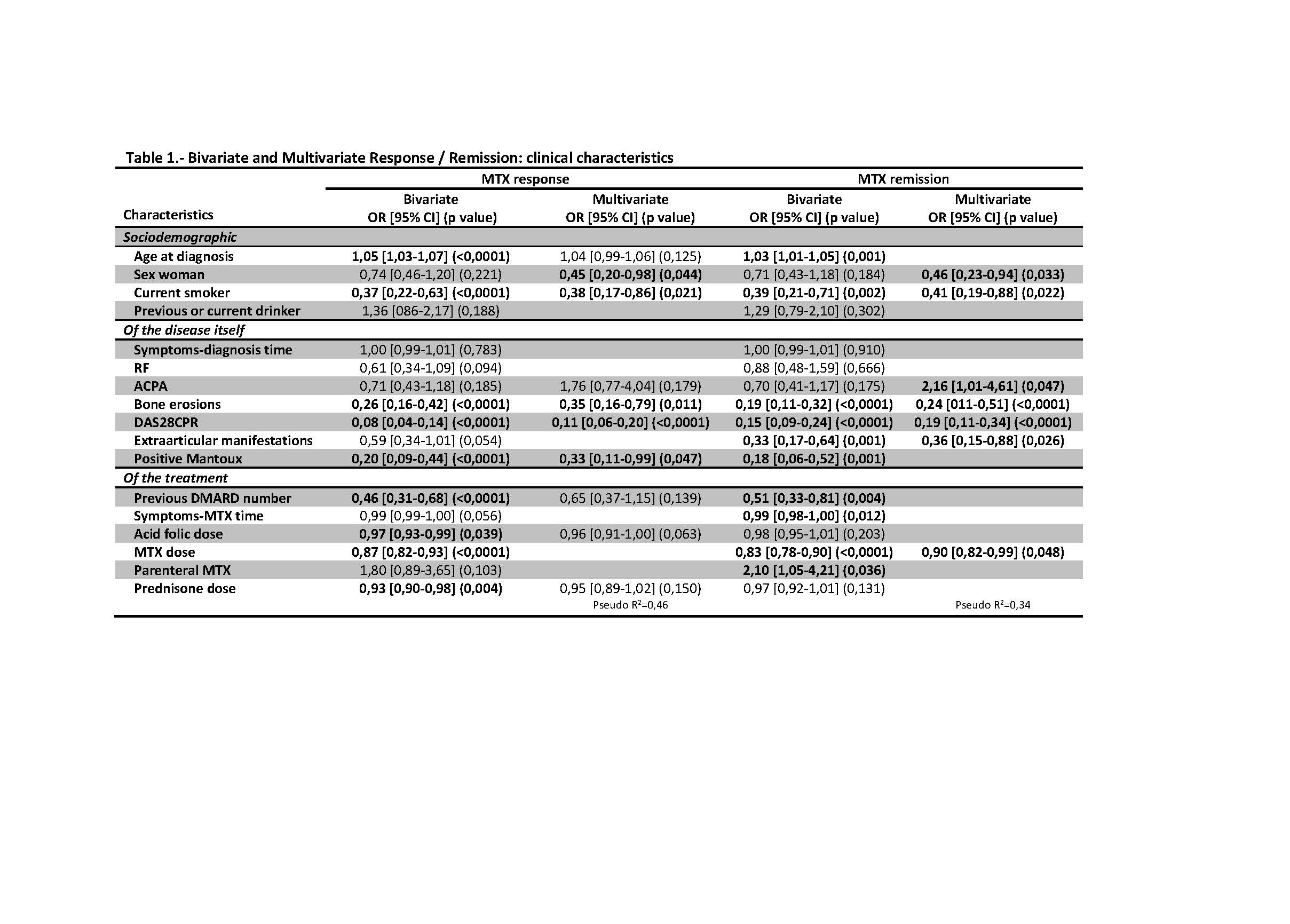
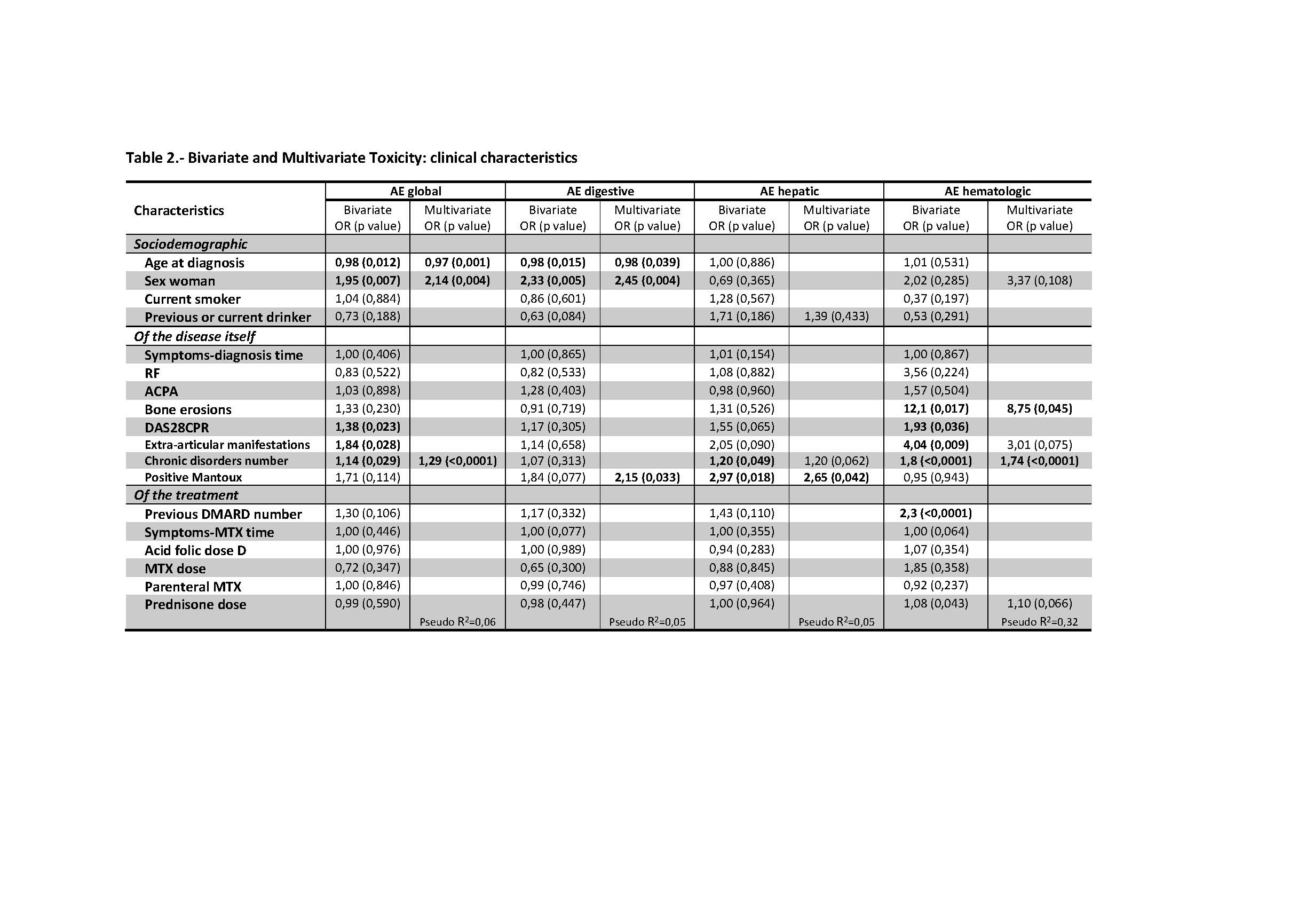
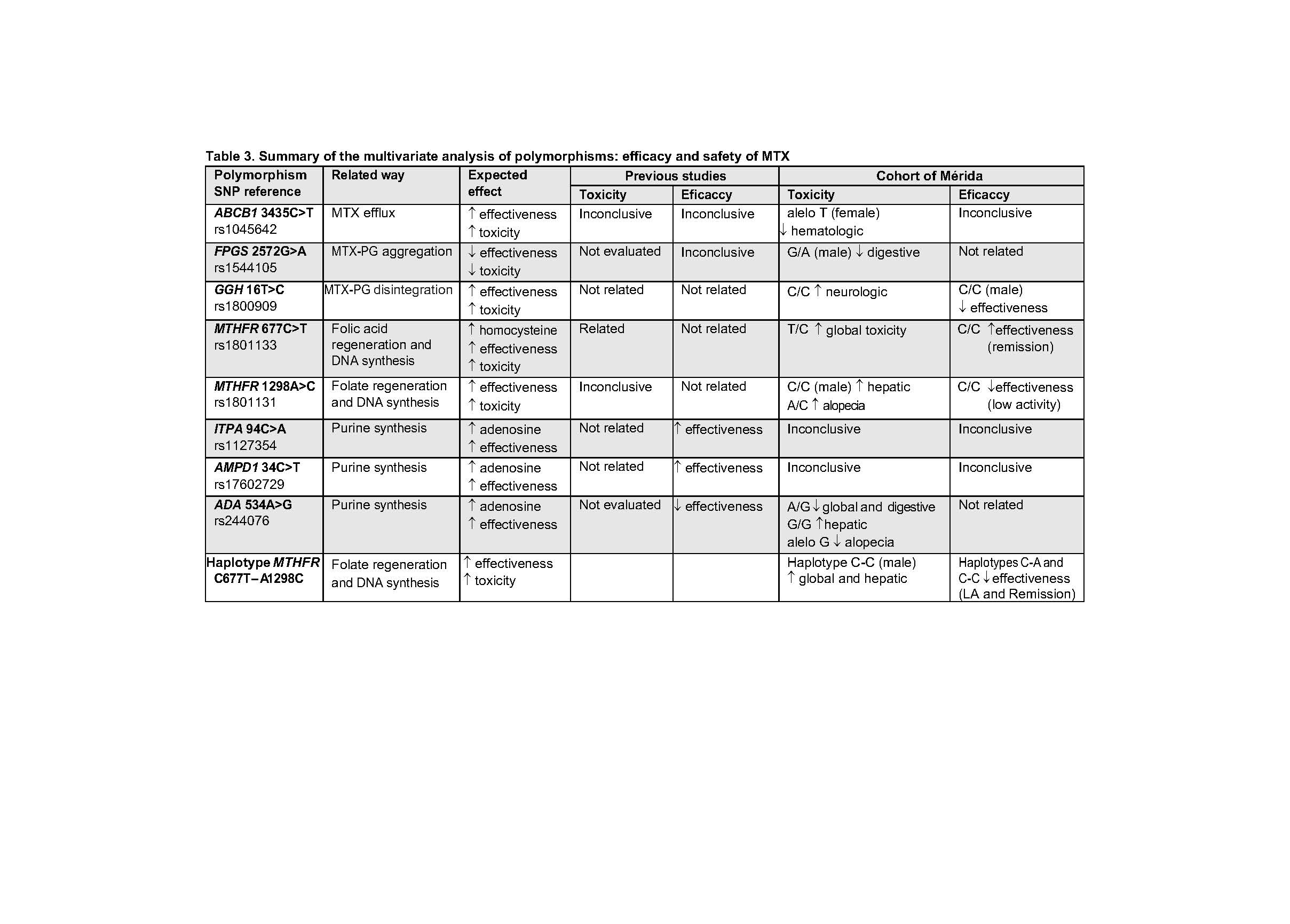
Methods: Case-control study nested in a cohort of patients with RA of the Hospital de Mérida, Spain, (2012-2015), followed-up by protocol in the monographic consultation of RA of the Rheumatology Service and treated with MTX monotherapy (since 1990). Efficacy was defined as a maintained response (low activity) and remission during follow-up, according to DAS28-PCR, and toxicity, as any adverse event related to MTX at any time during treatment. The SNPs ABCB1_C3435T, GGH_T16C, FPG_G2782A, MTHFR_C677T, MTHFR_A1298C, AMPD1_C34T, ITPA_C94A and ADA_A534G, and variables related to the pts, the disease and the treatment were studied.
Results: A total of 301 pts were included (mean age at diagnosis 50 years, 67% women, mean baseline value of DAS28-PCR of 4.5, baseline deterioration of physical function in 75%, early bone erosions in 55% and extraarticular involvement in 24%), representative of a severe RA. MTX monotherapy failed in half of the pts, generally due to lack of efficacy, and half had adverse events related to MTX, most frequently gastrointestinal, neurological and hepatic, which caused the suspension of MTX in a third of the cases and an 18 % of the total. The probability of MTX response was lower in women, active smokers and patients with more severe disease (higher baseline activity, early erosions and extra-articular manifestations), and independently of the clinical determinants, in homozygotes for the mutated allele (C/C genotype) of the MTHFR_A1298C SNP and in the carriers of the CC haplotype of C677T-A1298C of MTHFR (28.2%). T/T genotype of MTHFR_677CTc was associated with a higher probability of remission (OR = 4.07). The overall toxicity was more frequent in women and younger pts and C/T genotype of MTHFR_C677T. Hepatic toxicity was more frequent with positive Mantoux, G/G genotype of ADA_A534G and males, but no females, with C/C genotype of MTHFR_A1298C. Some SNPs showed a protective effect for toxicity. Sex behaved as a modifying factor.
Conclusion: Most of the SNPs studied have been associated with some measure of outcome, although the size of the effect is small. Genetic association studies should take into account the sex of patients and other clinical variables. Young patients and women had a worse response. Smoking is the main modifiable risk factor of poor response to MTX in RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chamizo Carmona E, carrasco-Cubero C, Rojas Herrera S, Gonzalez Naranjo M, Aznar Sanchez J, Veroz Gonzalez R, Dorado P, LLerena Ruiz A. Influence of the Clinical Characteristics and Different Genetic Polymorphisms Related to MTX, on the Efficacy and Safety in Patients with RA Treated with MTX in Monotherapy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/influence-of-the-clinical-characteristics-and-different-genetic-polymorphisms-related-to-mtx-on-the-efficacy-and-safety-in-patients-with-ra-treated-with-mtx-in-monotherapy/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/influence-of-the-clinical-characteristics-and-different-genetic-polymorphisms-related-to-mtx-on-the-efficacy-and-safety-in-patients-with-ra-treated-with-mtx-in-monotherapy/