Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2015
Title: Imaging of Rheumatic Diseases Poster II: X-ray, MRI, PET and CT
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: To
evaluate synovial inflammation on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) before
treatment and changes after treatment with intra-articular (i.a.) infliximab
(IFX) or methylprednisolone (MP) injections in relation to clinical response in
chronic or recurrent gonarthritis patients.
Methods: In
the RIA study (Remicade Intra Articularly), a prospective double-blind trial in
chronic or recurrent gonarthritis patients randomized to i.a. IFZ or MP. T1
contrast enhanced MRI of the affected knee before and 4 weeks after treatment
were scored for Hoffa synovitis using the MRI Osteoarthritis Knee Score
(MOAKS), and for joint effusion using the Knee Osteoarthritis Scoring System
(KOSS). Outcomes of MRIs were compared between the randomization groups. Associations
between MRI outcomes pre- and post-treatment and baseline characteristics were
analysed by logistic regression analysis.
Results:
19 patients had baseline MRIs available. Baseline MRI outcomes were not
associated with baseline characteristics. 18 patients (20 knees; 14 IFX and 12
MP) had 2 consecutive MRIs. Hoffa synovitis scores pre- and post-treatment were
not associated with patient characteristics. Pre-treatment effusion scores were
associated with number of previous i.a. corticosteroid injections (OR (95% CI)
0.74 (0.55;0.99)); post-treatment no associations were found. At baseline, MRI
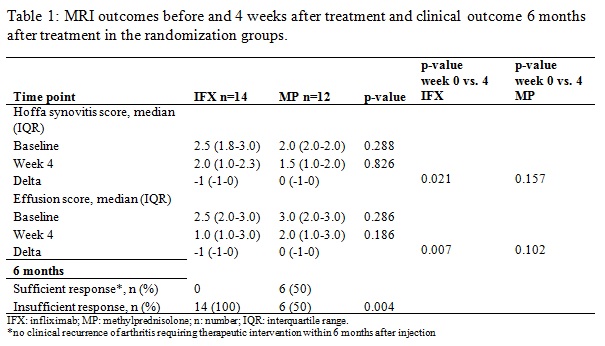
scores were
similar in the randomization groups (table 2). After four weeks, Hoffa
synovitis scores and effusion scores had decreased significantly in IFX
injected knees (delta Hoffa synovitis score -1 (-1;0), p=0.021 and delta
effusion score 0 (-1;0), p=0.007, respectively), but not in MP injected knees
(p=0.157 and p=0.102, respectively). After 6 months, a recurrence of arthritis occurred
in all IFX treated knees, and in 50% of MP treated knees. Median (IQR) Hoffa
synovitis scores and effusion scores before injection were similar in MP treated
patients with or without recurrence 2.0 (2.0;3.0) and 2.0 (1.0;2.0), p=0.080 in
patients with recurrence, and 3.0 (3.0;3.0) and 2.5 (1.8;3.0), p=0.617 in
patients without recurrence, respectively. MP treated patients with or without
recurrence also showed no difference in improvement in Hoffa synovitis scores
and effusion scores (delta Hoffa synovitis score 0.0 (-1.5;0.5), p=0.414 and 0
(-1;0), p=0.157, delta effusion score 0.0 (-1.0;0.0), p=0.157 and 0.0 (-0.5;0.0),
p=0.317, respectively.
Conclusion:
An apparent statistically significant decrease in Hoffa synovitis and effusion
scores on MRIs was seen in chronic or recurrent gonarthritis patients treated
with IFX injections, but not after MP injections. This apparent reaction to treatment
on MRI, however, appears not to be related to clinical outcome after 6 months:
a recurrence of arthritis occurred in all IFX treated knees and in 50% of MP
treated knees.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Akdemir G, van der Bijl AE, de Lange-Brokaar BJE, Huizinga TWJ, Allaart CF, Kloppenburg M. Inflammation Signs on Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Chronic or Recurrent Gonarthritis Treated with Intra-Articular Infliximab or Corticosteroids [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/inflammation-signs-on-magnetic-resonance-imaging-in-chronic-or-recurrent-gonarthritis-treated-with-intra-articular-infliximab-or-corticosteroids/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/inflammation-signs-on-magnetic-resonance-imaging-in-chronic-or-recurrent-gonarthritis-treated-with-intra-articular-infliximab-or-corticosteroids/