Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: Pediatric Rheumatology – ePoster II: SLE, Juvenile Dermatomyositis, & Scleroderma
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Children with systemic lupus erythematosus(cSLE) have more severe disease as compared to adults. Additionally, Asians in their geographic area have high burden of infections as well. There is paucity of data on infections & mortality in cSLE from India. We are a pediatric rheumatology referral center & have studied infections and mortality in cSLE at our unit.
Purpose:
- To study spectrum of infections in cSLE.
- To study mortality in cSLE.
- To compare infections & mortality with other centers.
Methods: Records of cSLE patients(onset < 18) from Jan09-Mar19 were reviewed. Data on infections & death collated. Patients who did not attend clinic for ≥1 year were considered lost to follow up & contacted via telephone. Serious infections:leading to hospitalization/ death/ required iv. therapy. Chi square test was applied as needed.
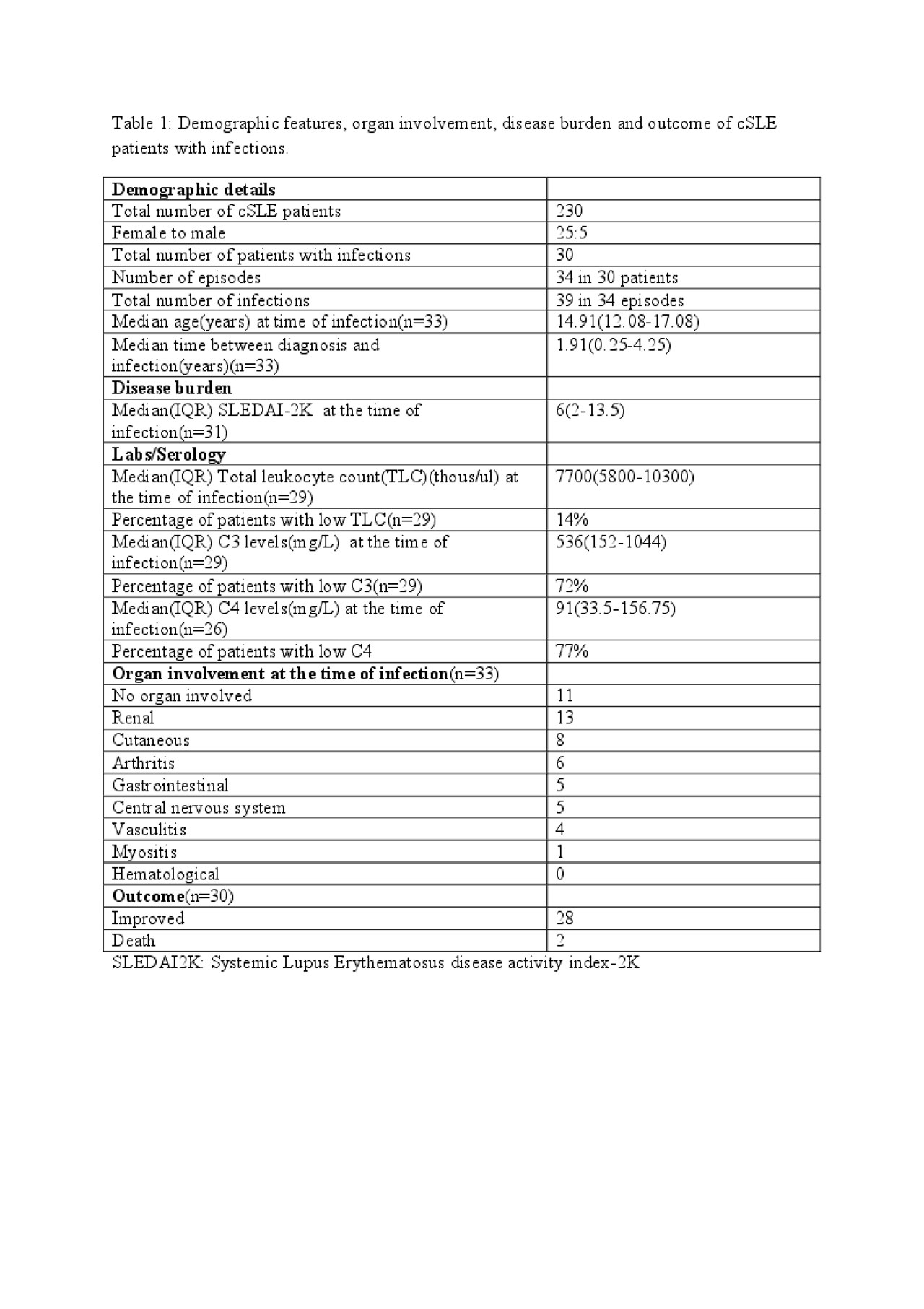
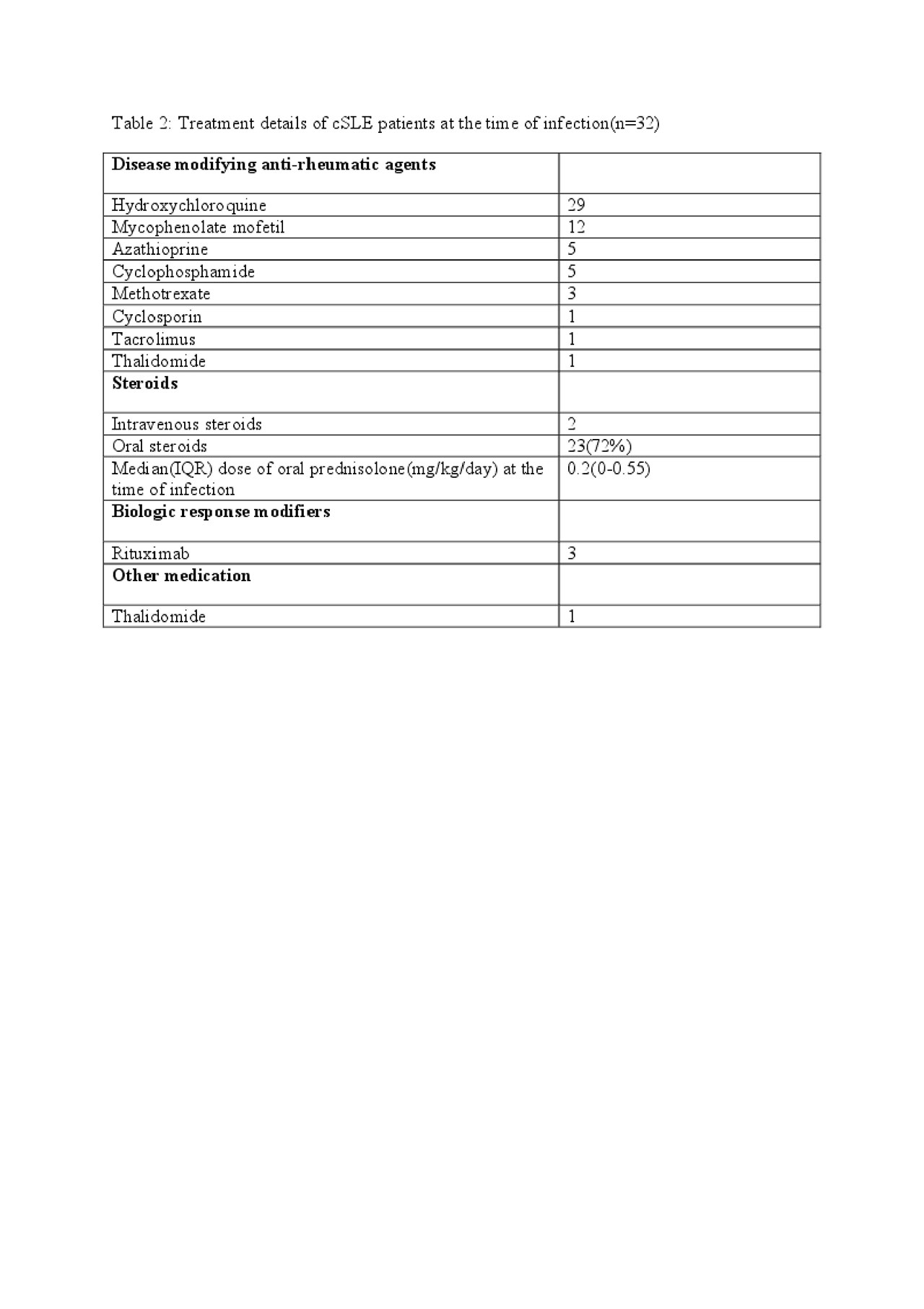
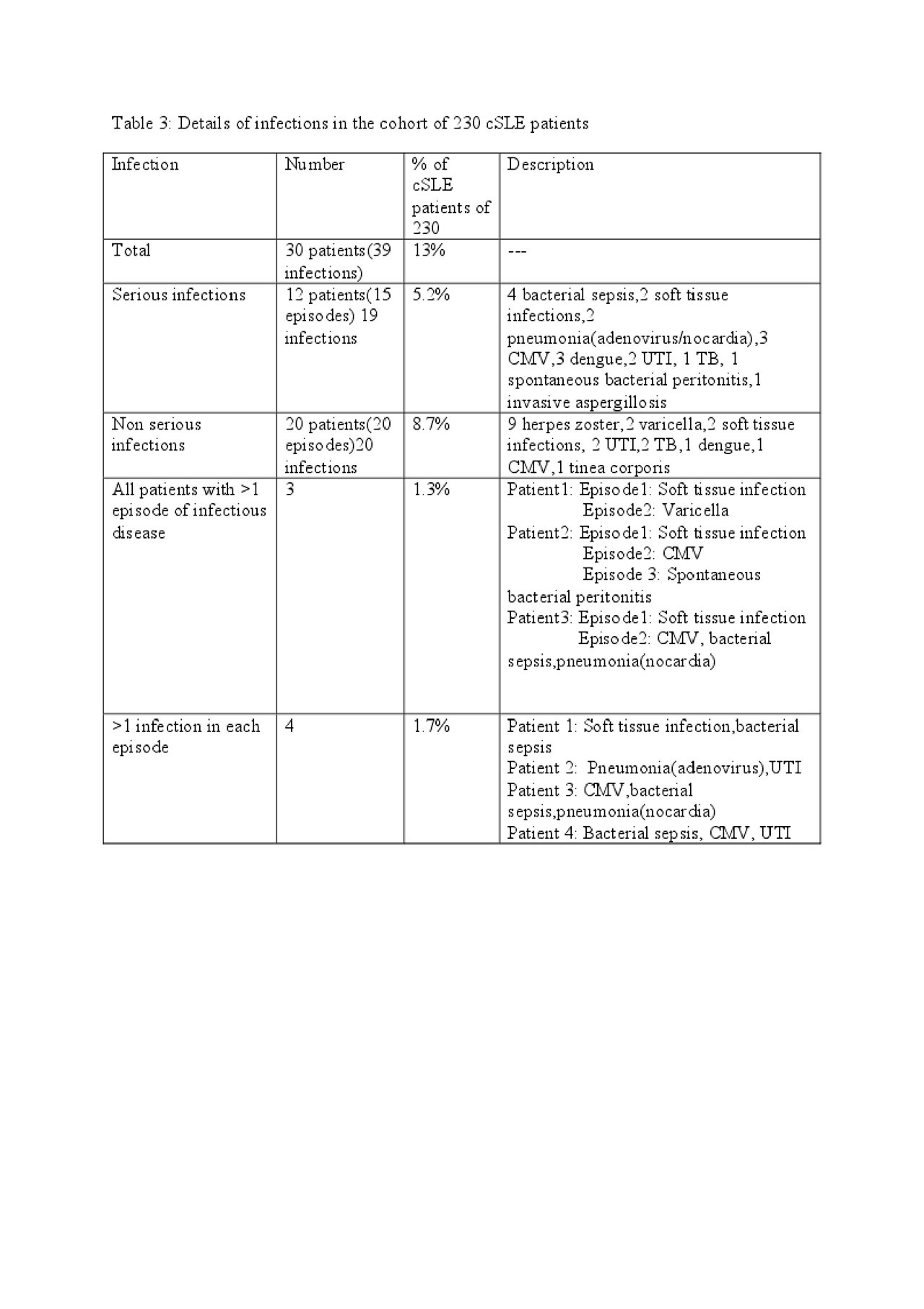
Results: 230 cSLE seen over 10 yrs. Thirty(13 %) infections: 25 girls, 5 boys. Median time to infections from diagnosis: 1.91 yrs. Median SLEDAI-2K at the time of infection:6. Eighty three percent of children with serious infection had SLEDAI >4 whereas 16.7% had SLEDAI < 4 (p=0.009). Patient details-table 1 Medications at the time of infection: 78% on steroids(low dose).Therapy details Table 2. INFECTIONS: Thirty(13%) children had 34 infectious episodes with 39 infections.Twelve (40%) had serious infection in 15 episodes. Ten improved & 2(16.6%) died-one with septicemia, second, invasive aspergillosis(pulmonary).Twenty patients had non-serious infections, commonest herpes zoster(30%).Details in Table 3. MORTALITY: Of 230 cSLE patients,156 were on regular follow up & 74 lost to follow up. Ten(4.3%) deaths in this cohort. Three of 156 patients(2%) who were on regular follow up died: mean follow up 1.91 yrs (0.5-4.25 yrs). Cause of death infections in 2, non infectious in one: Patient 1. Invasive aspergillosis(pulmonary),Patient 2. Adenoviremia with refractory septic shock(defaulted treatment 9 mths). Patient 3. Probable thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Seven(9.4%) of 74 patients who were lost to follow up died: cause not known. Infectious complications(13%) & mortality(4.3%) in this cohort are far superior than those reported from other centers in the subcontinent(infections25%,mortality5-20%)(1,2). Mortality rates at this centre are comparable to other cohorts across the world(1.4-30%)(3-8).
REFERENCES
- Aggarwal et al. Lupus 2018
- Abujam et al. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2016
- Lopes SRM et al.Lupus 2017
- Abdel-Hafez MA et al. Lupus 2015
- Fonseca et al. Reumatol Clin. 2016
- Tan JHT et al.Lupus 2015
- Pattaragarn A.et al. J Med Assoc Thai. 2005
- Ramírez Gómez LA et al. Lupus 2008
Conclusion: Infections in cSLE occurred in 13%, 40% serious infections,6.6 % mortality. Of non serious infections, herpes zoster was most common. Infections occurred predominantly in patients with active disease ( SLEDAI >4).Overall mortality was 4.3%. In addition to infections, irregular follow up was major contributor to death. Patients on regular follow up had a lower mortality(2%) when compared to those that were lost to follow up(9.4%). Mortality at this centre is comparable to the west and infection rate is lower than other centers in the region(1).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mittal S, Agarwal M, Sawhney S. Infections and Mortality in 230 Childhood Lupus Patients: A Single Center Experience from North India [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/infections-and-mortality-in-230-childhood-lupus-patients-a-single-center-experience-from-north-india/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/infections-and-mortality-in-230-childhood-lupus-patients-a-single-center-experience-from-north-india/