Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Morphea, also known as localized scleroderma, encompasses a group of idiopathic sclerotic skin diseases. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a large family of highly conserved noncoding genes that play a fundamental role in biological processes by controlling protein expression by binding to protein-coding messenger RNAs, resulting in translational repression or mRNA degradation [REF]. Besides intracellulary, miRNAs are also found in several biological fluids, including serum. We aimed to investigate serum levels of miRNAs in morphea. Methods:
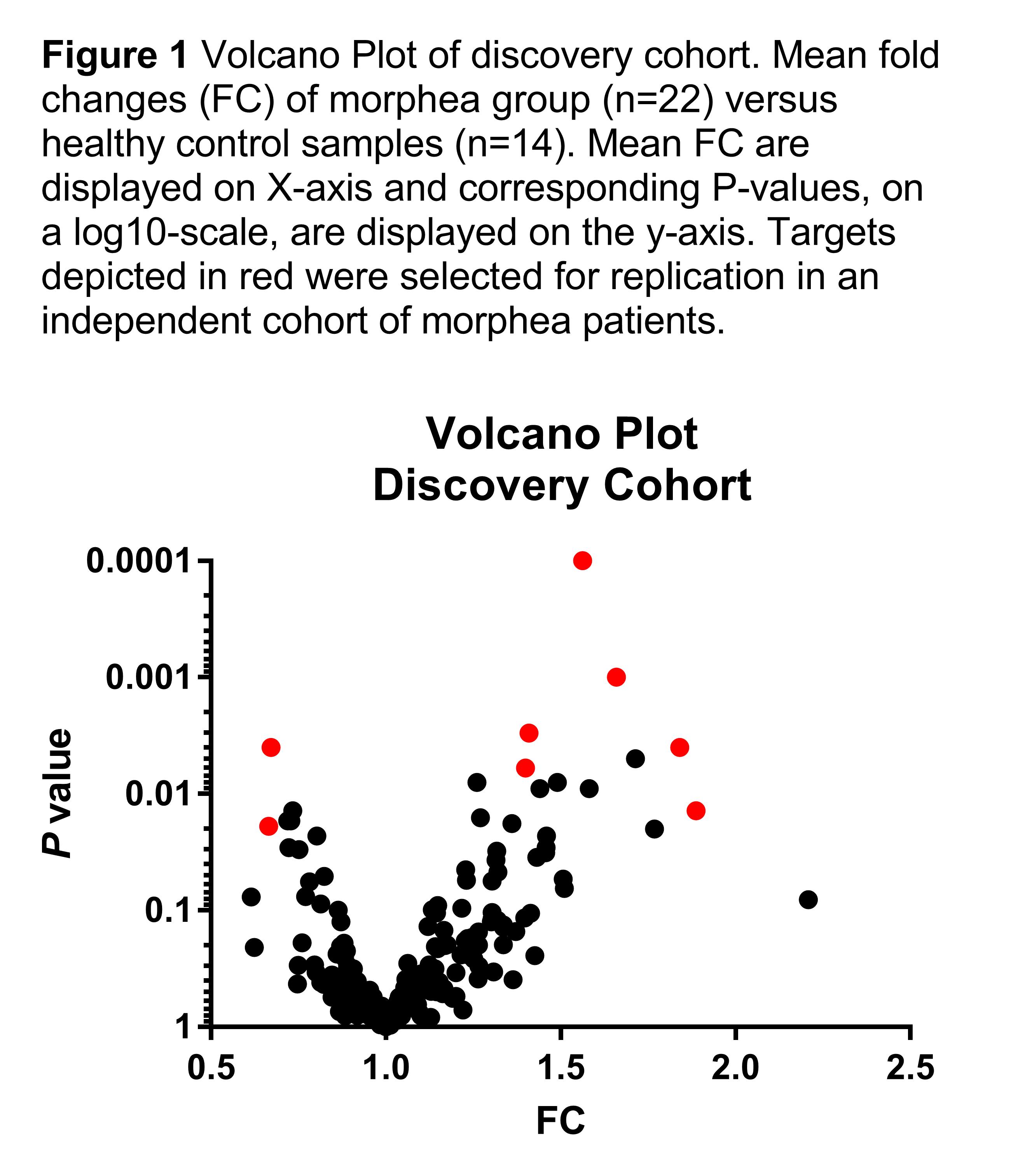
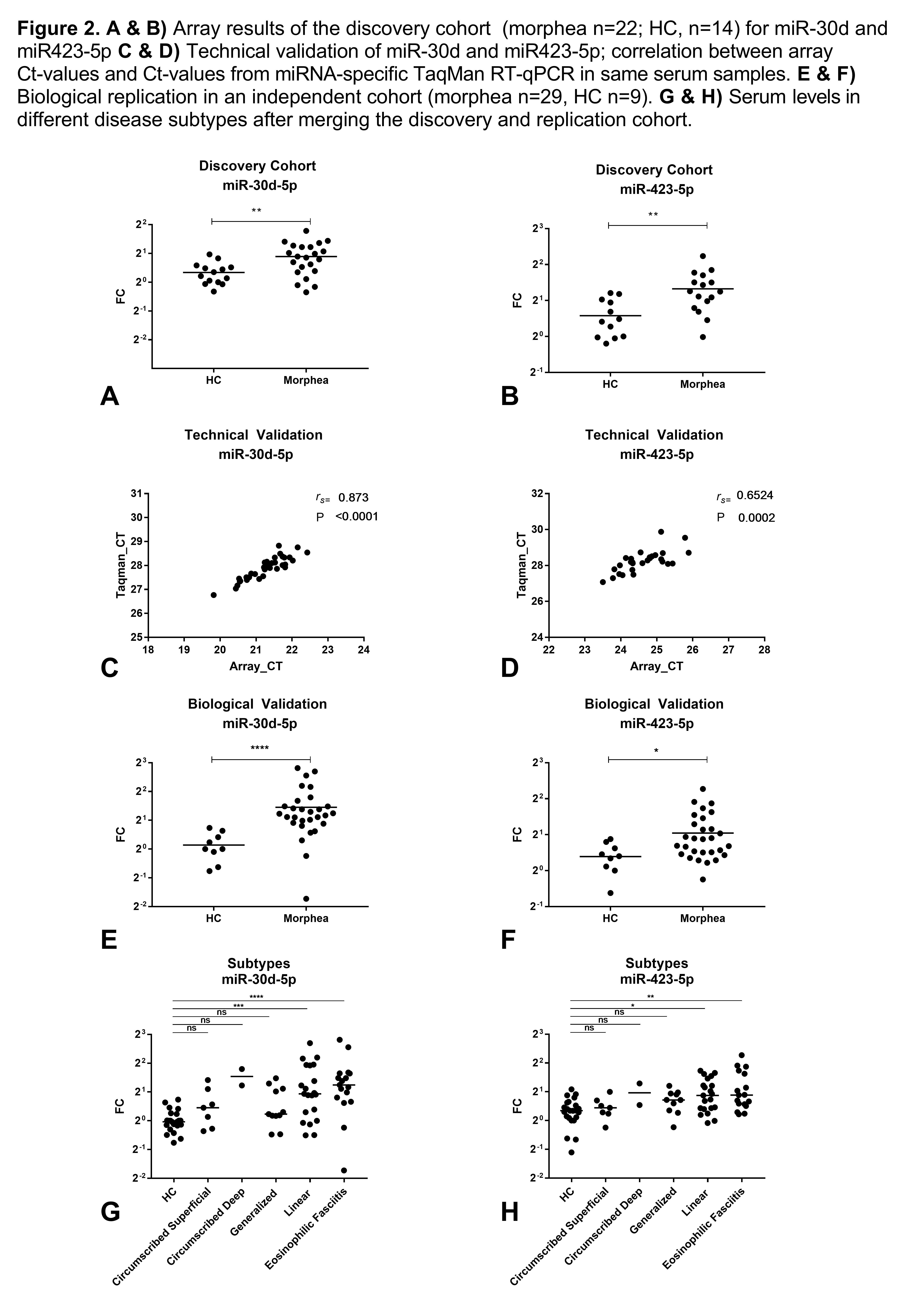
Serum was collected from patients affected by morphea. Disease subtypes were classified according to Zulian and Laxer, with the addition of Eosinophilic Fasciitis (EF) as a distinct subtype. Two independent cohorts of patients were established. A discovery cohort, consisting of 22 morphea patients and 14 healthy controls (HCs), was used for miRNA profiling in serum, by TaqMan Real-time quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR) on an OpenArray, which allowed simultaneous analysis of 758 miRNAs. The mean relative fold change (FC) was calculated for the group of morphea patients and HC, and compared between the two groups via Student’s t-test. A selection of 8 miRNAs were found to be differentially expressed between the patients and healthy controls (P<0.05; selection based on lowest P-values). These targets were selected for technical and biological validation, by miRNA-specific TaqMan RT-qPCR, in an independent cohort of 29 morphea patients and 9 HCs. Results :
The mean FC of the individual miRNAs from the discovery cohort are displayed in figure 1. Technical validation was achieved for all selected 8 miRNAs; supporting the array results. Serum levels of miR-30d and miR-423-5p were significantly elevated in patients, compared to healthy controls in both the discovery cohort [miR-30d: mean FC 1.4, P 0.003; miR-423-5p: mean FC 1.659, p 0.001] and the independent validation cohort [miR-30d: mean FC 2.28, P < 0.001; miR-423-5p: mean FC 1.500, p 0.0103] (Figure 2). The remaining 6 targets did not show significantly altered levels in the validation cohort. Most interesting, both miR-30d and miR-423-5p were especially increased in patients affected by more severe subtypes, such as linear morphea and eosinophilic fasciitis. Conclusion :
Serum levels of miR-30d and miR-423-5p were significantly higher in morphea compared to healthy controls in 2 independent cohorts. In addition, more severe subtypes such as linear morphea and EF showed increased levels of these 2 targets, as compared to milder subtypes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mertens JS, Marut W, Bekker CPJ, de Jong EMGJ, Radstake TRDJ. Increased Serum Levels of Micro-RNA 30d and Micro-RNA 423-5p in 2 Independent Cohorts of Patients with Morphea [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increased-serum-levels-of-micro-rna-30d-and-micro-rna-423-5p-in-2-independent-cohorts-of-patients-with-morphea/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increased-serum-levels-of-micro-rna-30d-and-micro-rna-423-5p-in-2-independent-cohorts-of-patients-with-morphea/