Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster I: Comorbidities
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Increased Risk of Incident Chronic Kidney Disease among Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Cohort Studies
Abstract
Background/Purpose: Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) may have a higher risk of developing chronic kidney disease (CKD) compared with general population. However, the data on this risk are still limited and not well-characterized. This systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted with the aim to comprehensively investigate the risk of incident CKD among patients with RA by reviewing all available studies.
Methods: A systematic review was performed using MEDLINE and EMBASE database from inception to April 2018 to identify all cohort studies (either retrospective or prospective) that compared the risk of incident CKD in patients with RA versus individuals without RA. Point estimates and standard errors from each study were extracted and combined together using the random effect, generic inverse variance method of DerSimonian and Laird. Visualization of funnel plot was used for evaluation for publication bias.
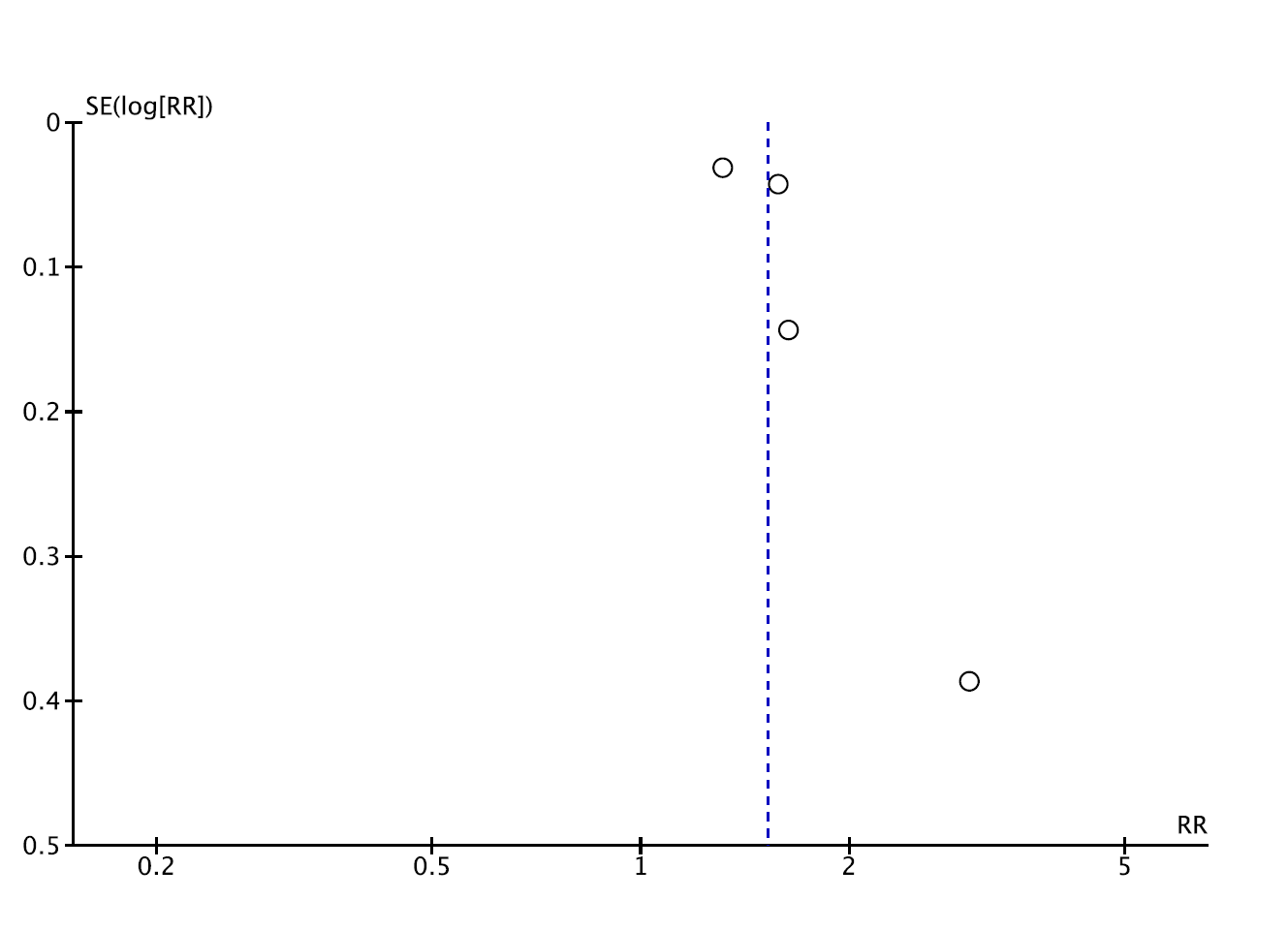
Results: Of 2,580 retrieved articles, a total of 4 retrospective cohort studies with 1,627,981 participants met the inclusion criteria and were included into the meta-analysis. The risk of incident CKD was significantly increased among patients with RA with the pooled risk ratio of 1.52 (95% CI, 1.28-1.80). The statistical heterogeneity of this study was high with an I2 of 82%. The forest plot of this systematic review and meta-analysis is shown as figure 1. The funnel plot was relatively symmetric and, thus, did not suggest the presence of publication bias in favor of positive studies (figure 2) although interpretation of the funnel plot was limited by the relatively small number of included studies.
Conclusion: A significantly increased risk of incident CKD among patients with RA compared with individuals without RA was demonstrated in this study.
Figure 1: Forest plot
Figure 2: Funnel plot
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ungprasert P, Raksasuk S. Increased Risk of Incident Chronic Kidney Disease Among Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increased-risk-of-incident-chronic-kidney-disease-among-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis-of-cohort-studies/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increased-risk-of-incident-chronic-kidney-disease-among-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis-of-cohort-studies/