Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I: Risk Factors, Predictors, & Prognosis
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) level of disease activity, cannot be evaluated by a single clinical or laboratory measurement. Hence, composite indices have been created via factor analysis (FA). FA uncovers the fact that multiple observed variables have similar patterns of responses because they are all associated with a latent, not directly observable, variable. Yet, only one directly patient-reported outcome (PRO), the patient’s global (PaGH), has been included in the composite indices. The PaGH answers a very general question of “Considering all the ways your RA has affected you how would you say your health is?”, making it easy to apply but hard to interpret. Lately, more specific PROs have been proven to add valuable and unique information on the patient’s disease state. We wanted to see if this is the case in early RA.
Methods: In the Care in early rheumatoid arthritis (CareRA) trial, patients with early RA (≤1 year) (n=379) naïve to DMARDs were randomized to one of four remission induction treatment schemes and followed up over 2 years (Verschueren et al, 2015). Key clinical variables such as swollen (SJC) and tender joint count (TJC), patient (PaGH) and physician (PrGH) global health assessment, CRP or ESR; along with pain, fatigue and physical function (Health Assessment Questionnaire-HAQ) were recorded at every consultation. Exploratory factor analysis (EFA) was performed for all observations and per time point as well on (1) key set variables only and (2) when also including other PROs. Pearson correlations of all variables were calculated. Firstly, missing data was handled using multiple imputation resulting in 15 complete datasets. Next, clustering was removed by performing multiple outputation 1000 times on the 15 datasets. Each of the 15 000 datasets was analyzed by EFA with oblimin rotation. The analyses were combined after re-ordering the factors by maximizing factor congruence.
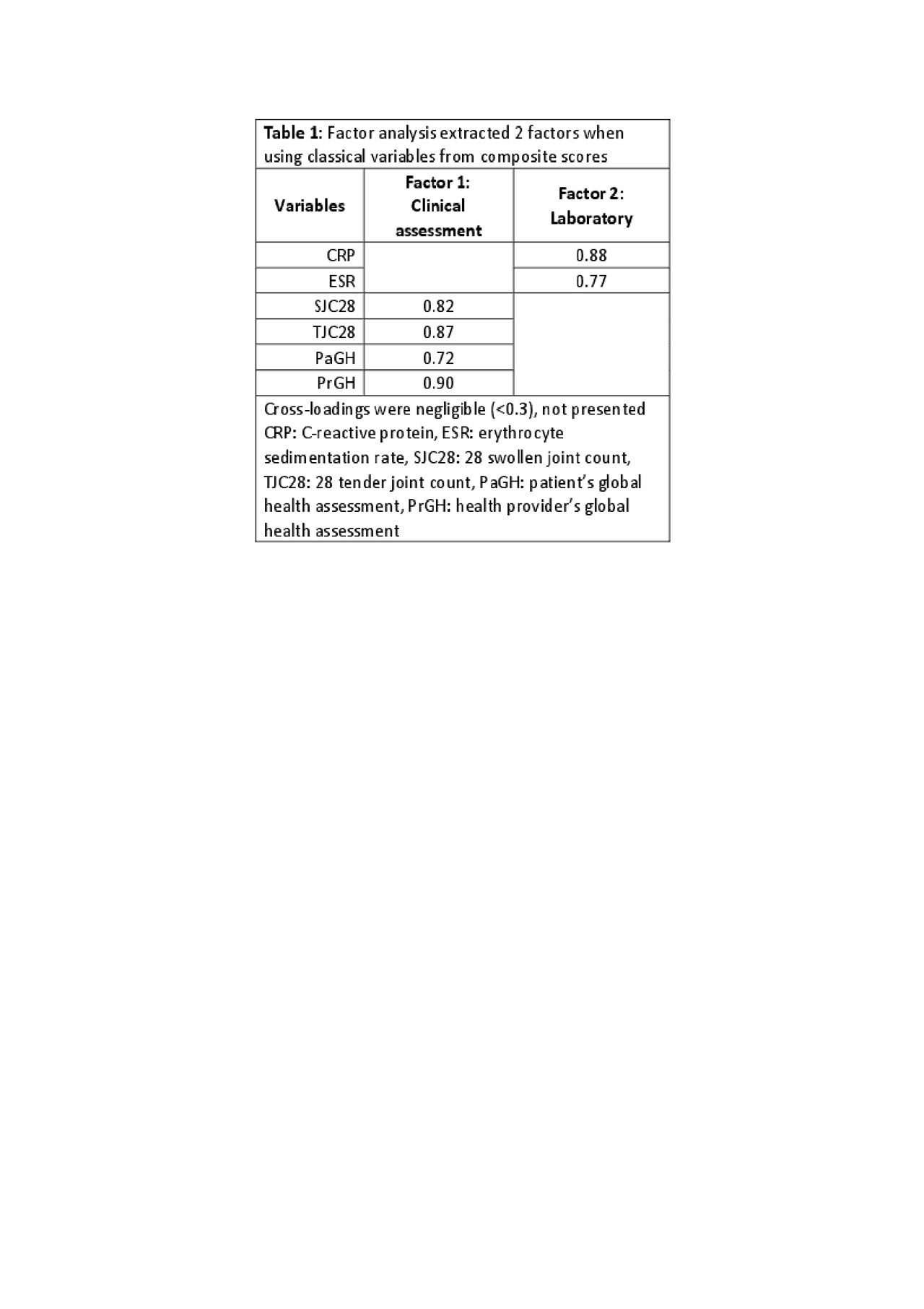
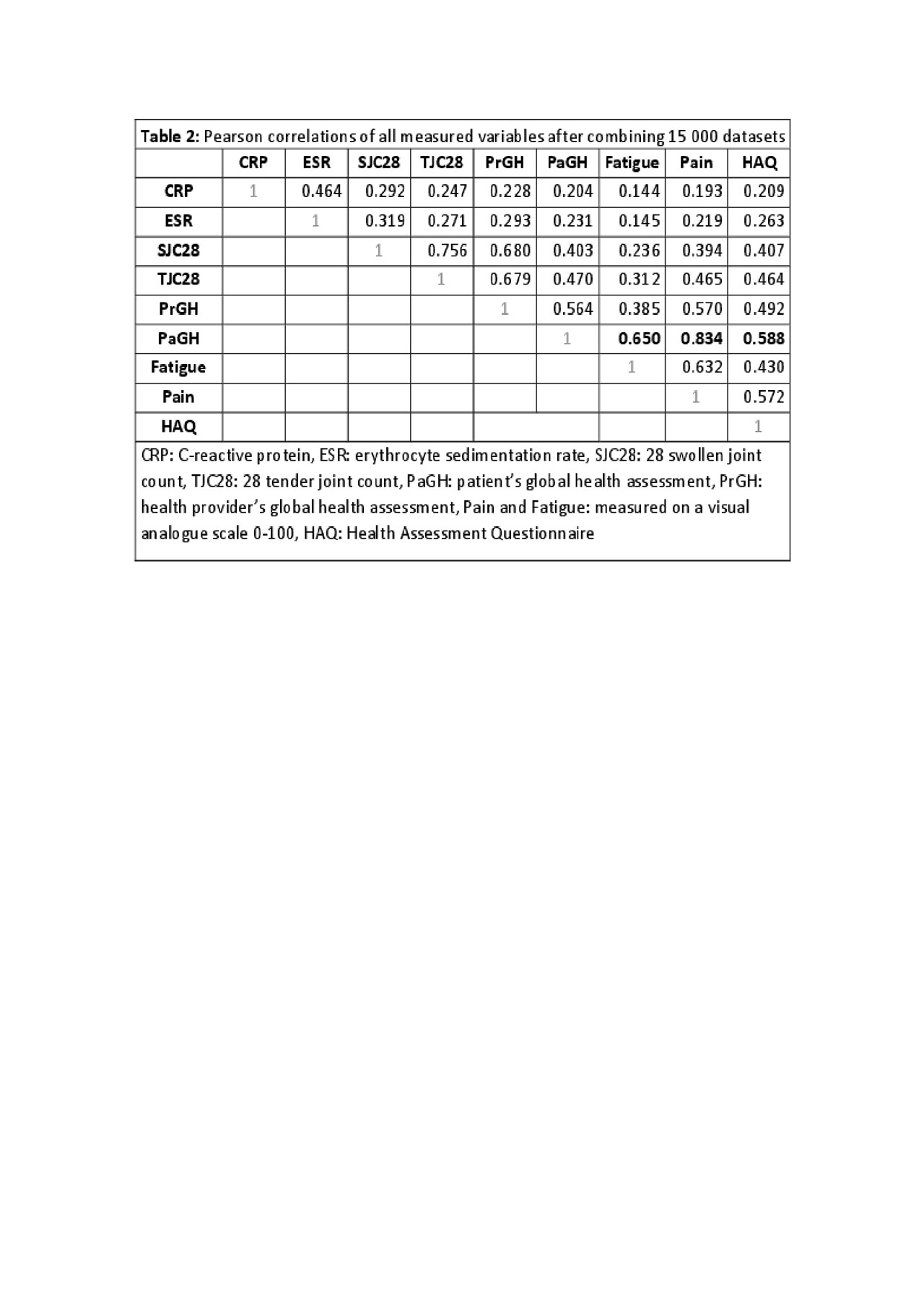
Results: The different factor analyses (FAs) based on the classical components of disease activity scores, supported the traditional approach of composite indices extracting 2 factors that are stable over time, meaning no substantial cross-loadings between factors (Table 1). Still, pain (0.83), fatigue (0.65) and HAQ (0.59) were strongly correlated with PaGH in our cohort (Table 2). When rerunning the FA including also these variables, the 2-factor model was no longer stable with variables changing the factors in which they loaded over time. However, when a 3-factor model was extracted, there were large positive loadings on Factor 1 describing the patient’s personal assessment, Factor 2 clinical assessment and Factor 3 laboratory (Table 3).
Conclusion: The classical FA with the key variables gives a 2-factor model that bundles everything in one, except for acute phase reactants (CRP and ESR). However, PaGH seems to be associated with pain, fatigue, and functionality. By including these variables, a third factor dedicated to the patient’s perceptions is extracted and a very clear factor structure showing three latent factors is present. This could indicate that these patient’s assessments should be added to the standard measurements of disease state.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pazmino S, Lovik A, Boonen A, De Cock D, Stouten V, Joly J, Van der Elst K, Bertrand D, Westhovens R, Verschueren P. Including Pain, Fatigue and Functionality Regularly in the Assessment of Patients with Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Separately Adds to the Evaluation of Disease Status [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/including-pain-fatigue-and-functionality-regularly-in-the-assessment-of-patients-with-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-separately-adds-to-the-evaluation-of-disease-status/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/including-pain-fatigue-and-functionality-regularly-in-the-assessment-of-patients-with-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-separately-adds-to-the-evaluation-of-disease-status/