Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Adalimumab (ADA) is approved for treatment of Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC); therefore, it is postulated that new onset or flare of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a rare occurrence in ADA clinical trials for non-IBD indications. The purpose of this analysis was to determine the rates of IBD adverse events (AEs) in ADA clinical trials, particularly in spondyloarthritis (SpA) patients (pts) who are at higher risk of IBD as a feature of SpA.
Methods: The rates of IBD AEs in 73 phase 2–4 interventional ADA clinical trials in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pJIA), pediatric enthesitis-related arthritis, uveitis (non-infectious intermediate, posterior, or pan-uveitis), hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), adult and pediatric psoriasis (Ps), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), non-PsA peripheral SpA (pSpA), non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA), and ankylosing spondylitis (AS) were analyzed (trials in UC, CD, and intestinal Behcet’s disease [BD] were excluded). The search criteria for IBD events included the following standardized MedDRA queries preferred terms: inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), ulcerative colitis (UC), Crohn’s disease (CD), IBD-not otherwise specified (NOS), and ulcerative proctitis. The incidence rates (IR) for events of IBD (combined new onset and flare) in interventional clinical trials of ADA are reported as events per 100 pt-years (PY). 95% confidence intervals (CI) were based on exact Poisson confidence limits.
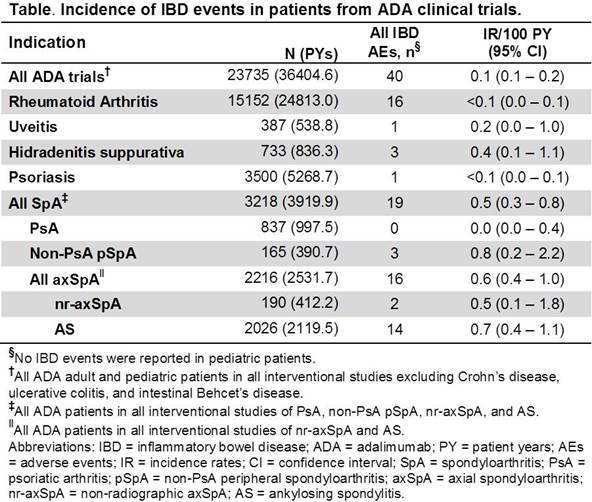
Results: ADA was administered to 23735 pts, representing 36404.6 PY of exposure. Overall, the IR for IBD events in all interventional ADA trials included in this analysis was 0.1/100PY (Table). The rates of IBD events varied across therapeutic indications from <0.1 to 0.8/100PY. There were no reports of IBD events in pediatric pts. The IR for IBD events in RA, uveitis, HS, and Ps trials were <0.1, 0.2, 0.4, and <0.1/100 PY. In SpA, the overall rates of IBD were 0.5/100 PY, while the rates were 0, 0.8, 0.5, and 0.7/100 PY in PsA, non-PsA pSpA, nr-axSpA, and AS, respectively. 2216 pts with axSpA (AS: 2026, nr-axSpA: 190) were exposed to ADA; in AS, 14 IBD events (7 new onset and 7 flares) were reported in 12 pts (7 new onset and 5 flares), while in nr-axSpA, 2 IBD events were reported in 1 pt (2 flares).
Conclusion: The rates of IBD AEs in ADA clinical trials were generally low across all indications, with all events occurring in adult pts. In AS pts, who are at increased risk of manifesting IBD, the rates of IBD for pts treated with ADA (0.7/100 PY [95% CI, 0.4–1.1]) were similar to published placebo rates pooled across multiple clinical trials (1.3/100 PY [95% CI, 0.2–4.8]).1 In pts at risk for IBD requiring biologic therapy, ADA is a reasonable therapeutic option based on the observed low IBD event rates in ADA clinical trials and its demonstrated efficacy in treating UC and CD pts. References:
- Braun, J. et al., Arthritis & Rheum, 2007; 57:639-47.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Curtis JR, Elewaut D, Chen S, Hojnik M, Naveh N, Anderson JK. Incidence of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Events in Adalimumab (HUMIRA) Clinical Trials Across Indications [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/incidence-of-inflammatory-bowel-disease-events-in-adalimumab-humira-clinical-trials-across-indications/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/incidence-of-inflammatory-bowel-disease-events-in-adalimumab-humira-clinical-trials-across-indications/