Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: RA Treatments & Their Safety (1674–1710)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Previous clinical trial and real-world data suggest that risk of serious infection events (SIEs) and opportunistic infections (OIs) is similar with tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily (BID; recommended dosage for RA) vs TNFi,1,2 while herpes zoster (HZ) rates are higher with tofacitinib.2 Here, we characterized infections in ORAL Surveillance (NCT02092467).
Methods: ORAL Surveillance was a long-term, randomized, open-label, non‑inferiority, Phase 3b/4 safety endpoint study of tofacitinib vs TNFi in patients (pts) aged ≥ 50 yrs with active RA despite MTX treatment and ≥ 1 additional cardiovascular (CV) risk factor. Pts were randomized 1:1:1 to receive open-label tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg BID or a TNFi (adalimumab 40 mg every other week [North America]; etanercept 50 mg every week [rest of the world]) with stable background MTX. Incidence of all infections regardless of severity (any adverse event in the infections and infestations System Organ Class), HZ (non-serious/serious), and SIEs were analyzed overall and by age (50 – < 65 yrs; ≥ 65 yrs). Overall OI and tuberculosis (TB) incidence were also analyzed. Incidence rates (IRs; pts with events per 100 pt-yrs [PY]), hazard ratios (HRs), and Number Needed to Harm (NNH; number of PY of exposure needed for a treatment to have 1 more SIE vs reference) were calculated. First infection events occurring ≤ 28 days after the last dose or up to the last contact date were considered.
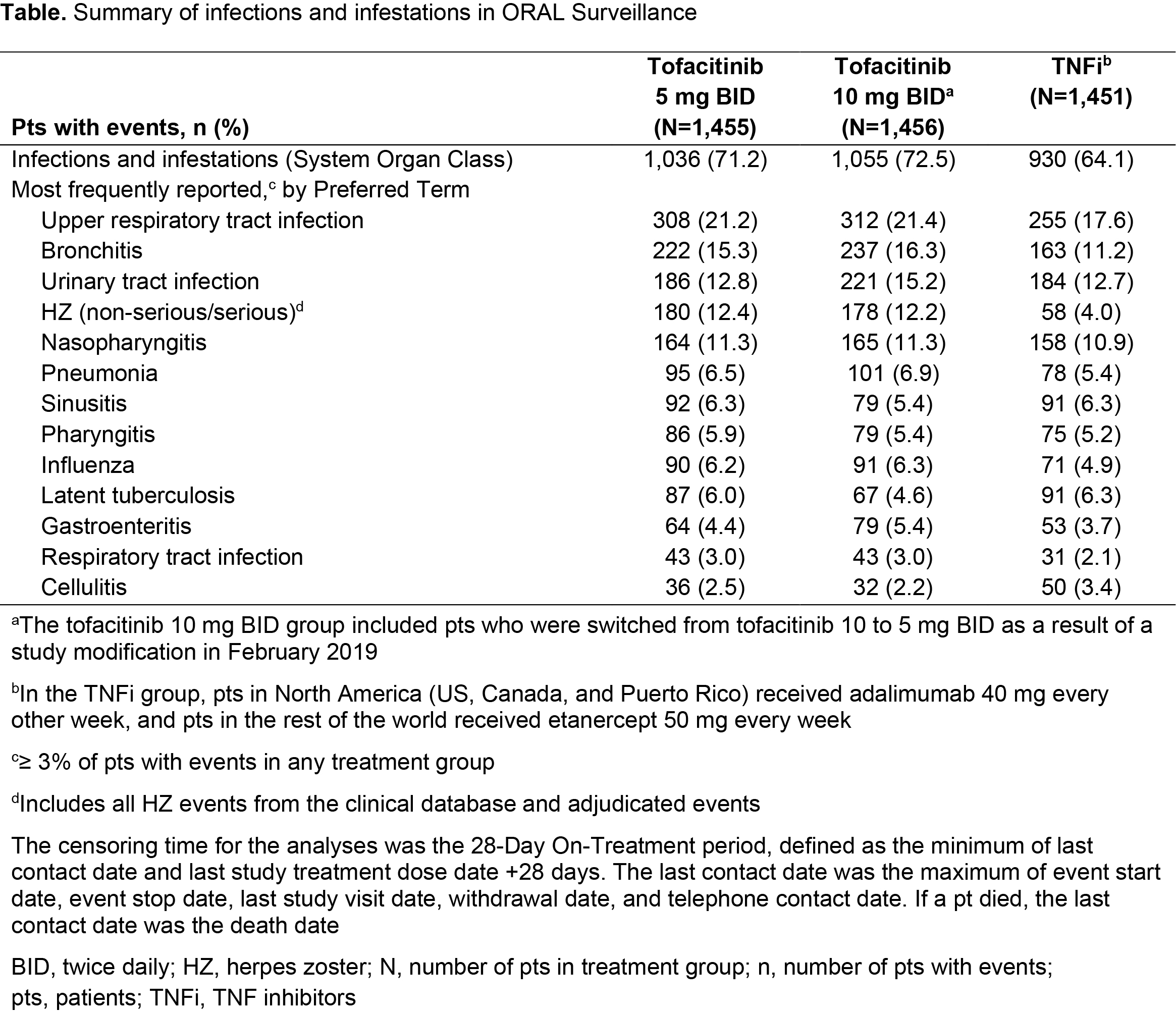
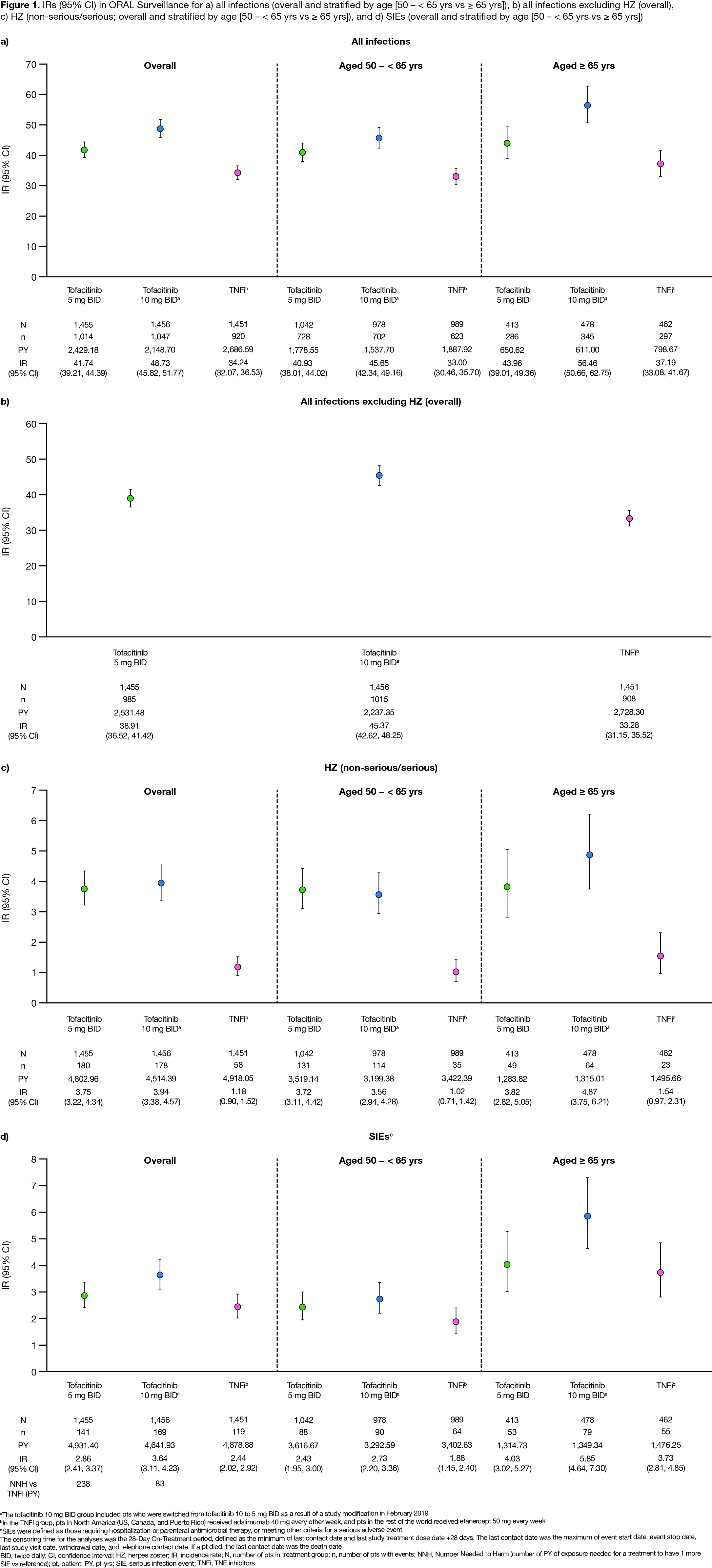
Results: Of 4,362 treated pts, 3,009 (69%) were aged 50 – < 65 yrs and 1,353 (31%) were aged ≥ 65 yrs. At baseline, mean age was 61.2 yrs, mean RA duration was 10.4 yrs, and pts had active disease (mean Clinical Disease Activity Index 39.8). Across treatment groups, 5.3–5.9% of pts were reported to have been vaccinated for HZ prior to or during the study. Respiratory infections, urinary tract infections, and HZ were the most common infections with tofacitinib (Table). Incidence of all infections was higher for tofacitinib vs TNFi, with notably higher HZ incidence for tofacitinib (Figure 1a–c, Figure 2a–c). Across treatments, > 90% of HZ cases were non-serious, and > 92% were mild/moderate in severity. IRs of all infections, HZ, and SIEs were generally higher in pts aged ≥ 65 vs 50 – < 65 yrs (Figure 1). For SIEs, IRs were numerically higher for tofacitinib vs TNFi (Figure 1d). HRs for SIEs were > 1 for tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg BID vs TNFi and tofacitinib 10 vs 5 mg BID; for tofacitinib 10 mg BID vs TNFi, 95% CIs were > 1 (Figure 2d). NNH for SIEs were 238 PY and 83 PY for tofacitinib 5 and 10 mg BID vs TNFi, respectively (Figure 1d). OI IRs were numerically higher for tofacitinib vs TNFi, due to HZ OI (adjudicated; data not shown). TB IRs were: tofacitinib 5 mg BID, 0.02; tofacitinib 10 mg BID, 0.10; TNFi, 0.10.
Conclusion: In pts aged ≥ 50 yrs with RA and ≥ 1 additional CV risk factor, overall incidence of infections was higher for tofacitinib vs TNFi, with notably higher HZ IRs. Incidence of SIEs was numerically higher for both tofacitinib doses vs TNFi and for tofacitinib 10 vs 5 mg BID; for tofacitinib 10 mg BID vs TNFi, 95% CIs for SIE HRs were > 1.
- Fleischmann R et al. Lancet 2017; 390: 457-68.
- Kremer JM et al. ACR Open Rheumatol 2021; 3: 173-84.
Acknowledgments: Study sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Medical writing support was provided by S Piggott, CMC Connect, funded by Pfizer Inc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bălănescu A, Citera G, Pascual-Ramos V, Connell C, Gold D, Chen A, Shi H, Shapiro A, Pope J, Schulze-Koops H. Incidence of Infections in Patients Aged ≥ 50 Years with RA and ≥ 1 Additional Cardiovascular Risk Factor: Results from a Phase 3b/4 Randomized Safety Study of Tofacitinib vs TNF Inhibitors [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/incidence-of-infections-in-patients-aged-%e2%89%a5-50-years-with-ra-and-%e2%89%a5-1-additional-cardiovascular-risk-factor-results-from-a-phase-3b-4-randomized-safety-study-of-tofacitinib-vs-tnf-inhib/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/incidence-of-infections-in-patients-aged-%e2%89%a5-50-years-with-ra-and-%e2%89%a5-1-additional-cardiovascular-risk-factor-results-from-a-phase-3b-4-randomized-safety-study-of-tofacitinib-vs-tnf-inhib/