Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is becoming a public health concern because of increasing disease and economic burdens. Epidemiological information on SLE, especially its incidence rate, was limited in developing countries. We aimed to investigate the incidence, prevalence, and cost burdens of SLE in urban China.
Methods: We conducted a nationwide population-based cohort study using the databases of Urban Employee Basic Medical Insurance and Urban Resident Basic Medical Insurance between 2013 and 2017, covering 23 provinces in China. Incidence and prevalence rates were age- and gender-standardized to China 2010 national census data. Average annual costs and hospital visit times were also calculated.
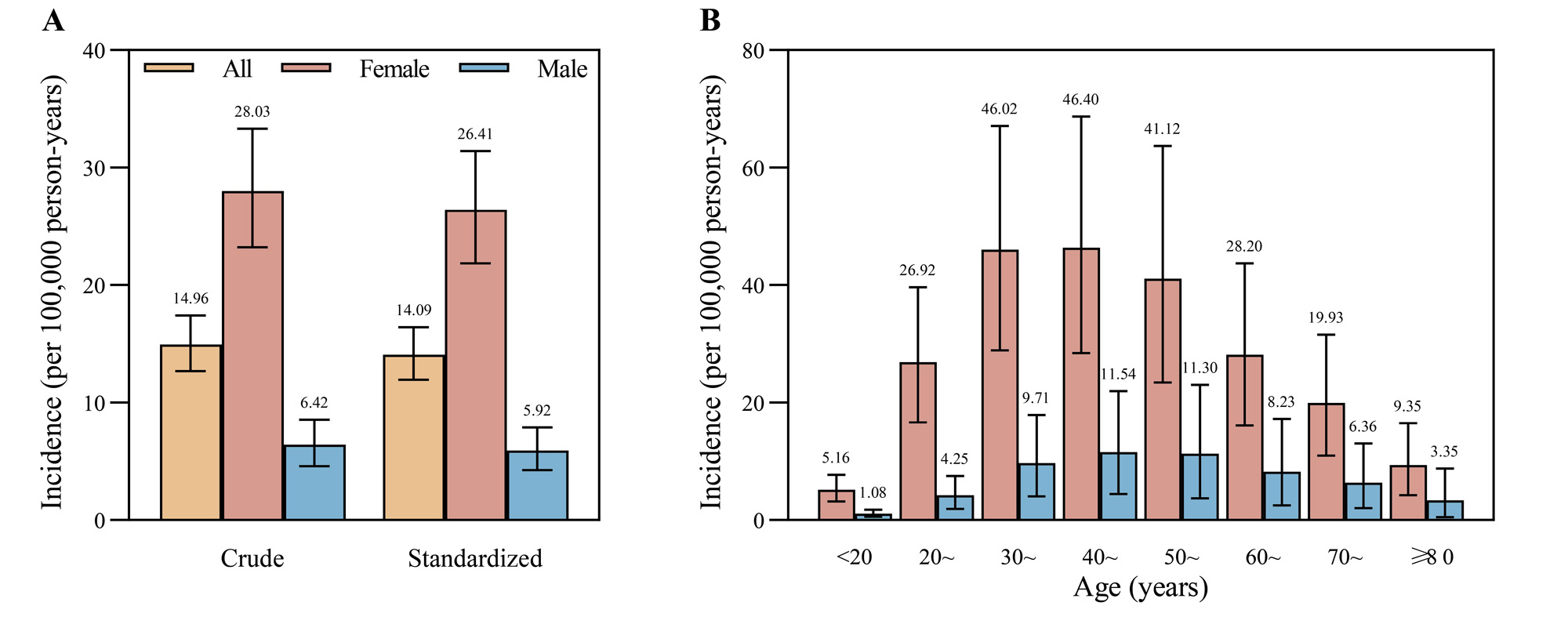
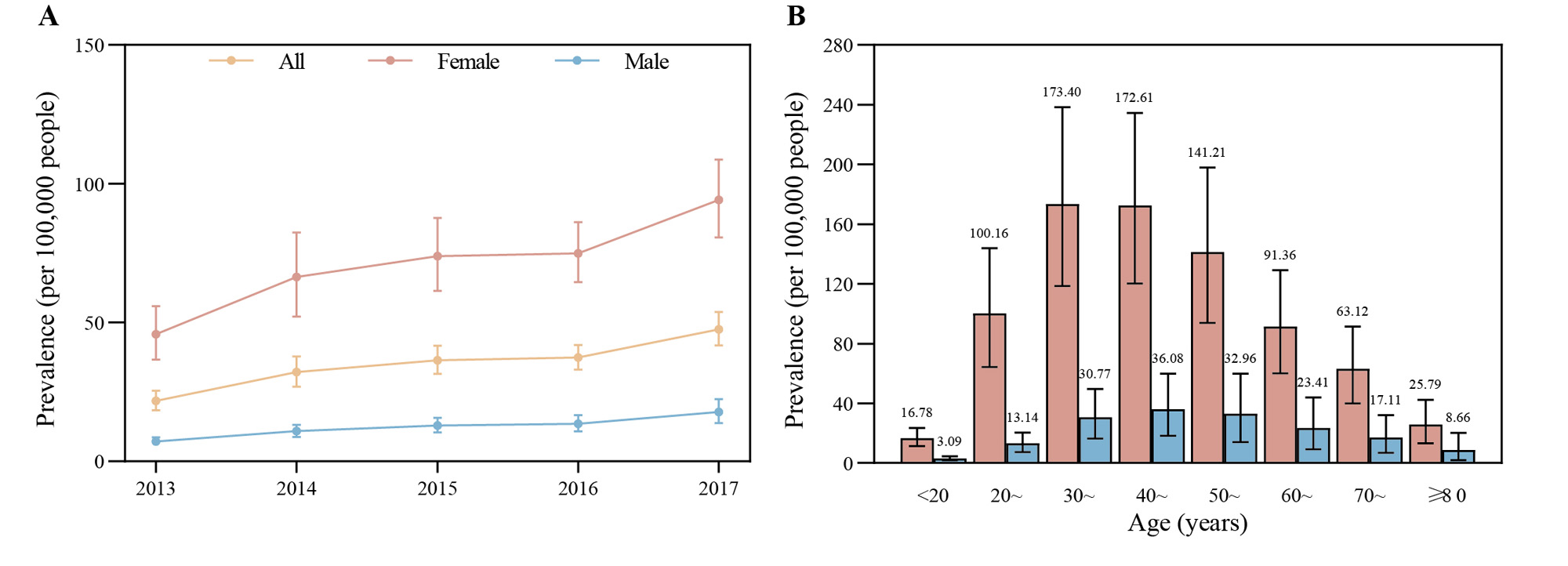
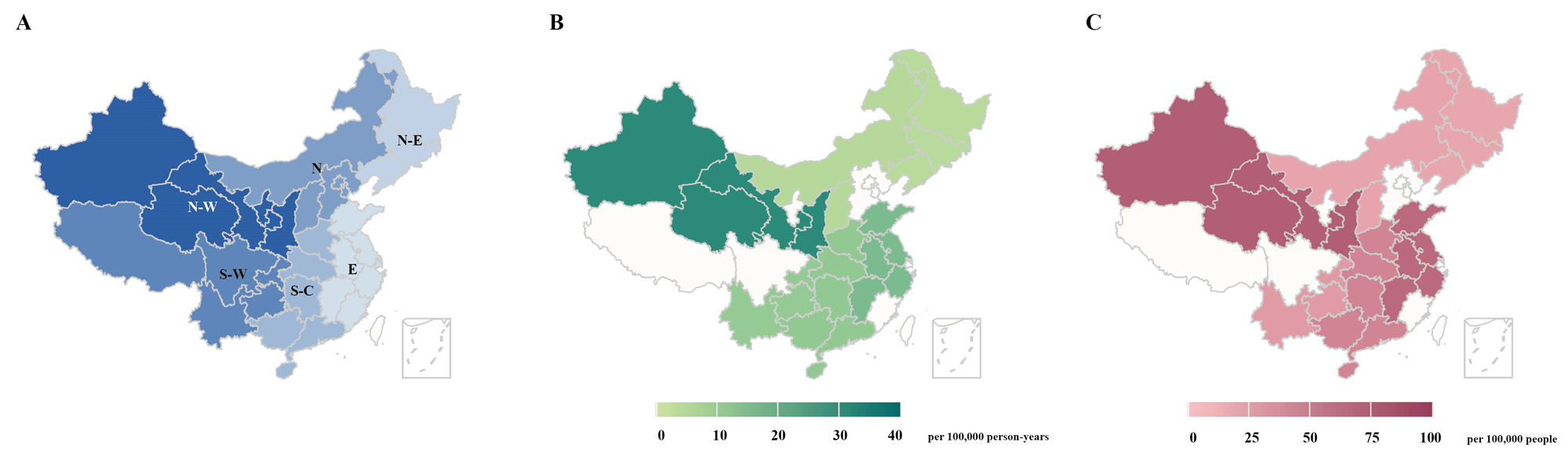
Results: Total 132,258 patients with SLE were identified during the study period. The mean age was 43.03 (SD, 15.29) years. Overall 81.33% of patients were women. The standardized incidence of SLE in China in 2017 was 14.09 (95%CI, 11.95-16.41) per 100,000 person-years (Figure 1). Women had higher incidence than men (26.41 vs 5.92 per 100,000 person-years). The standardized prevalence in 2017 were 47.61 (95%CI, 41.77-53.83), 94.16 (80.67-108.69), and 17.86 (13.84-22.38) per 100,000 people in overall, female, and male patients (Figure 2). The average annual rates of increase in prevalence were 21.50%, 19.72%, and 25.67% from 2013 to 2017 in overall, female, and male patients. The age-specific incidence peaked at 30-49 years old in women and at 40-59 years old in men. SLE incident and prevalent cases were most common in north-western and less in south and east China (Figure 3). Additionally, the average estimated annual cost per-capita was US$1,599.34 in SLE patients. Costs of adolescent and young adult patients were the highest among age groups.
Conclusion: SLE population in China is rapidly expanding. Younger age at onset, especially in women, has placed considerable burdens in China. The distinct signatures of different incidence rates with respect to geographic variations were consistent with regions’ exposure to ultraviolet radiation in China.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Li M, Li C, Cao M, Lu K, Wu C, zhao J, Wang Q, Tian X, Tang X, Li M, Zeng x, Gao P. Incidence and Prevalence of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Urban China, 2013-2017: A Nationwide Population-based Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/incidence-and-prevalence-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-in-urban-china-2013-2017-a-nationwide-population-based-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/incidence-and-prevalence-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-in-urban-china-2013-2017-a-nationwide-population-based-study/