Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: DISCOVER 1 & 2 are phase-3 trials of guselkumab (GUS, an IL-23 inhibitor) in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA). In both trials, treatment with GUS led to significantly more improvement than placebo (PBO) in the primary endpoint (ACR20) and in other measures of arthritis and psoriasis at week (w) 24,1,2 and these improvements were maintained through 1 year of active treatment.3,4 Here we evaluate the effect of GUS on fatigue in DISCOVER 1 & 2 using the patient reported outcome (PRO) FACIT-Fatigue, which has demonstrated content validity and strong psychometric properties in clinical trials.5
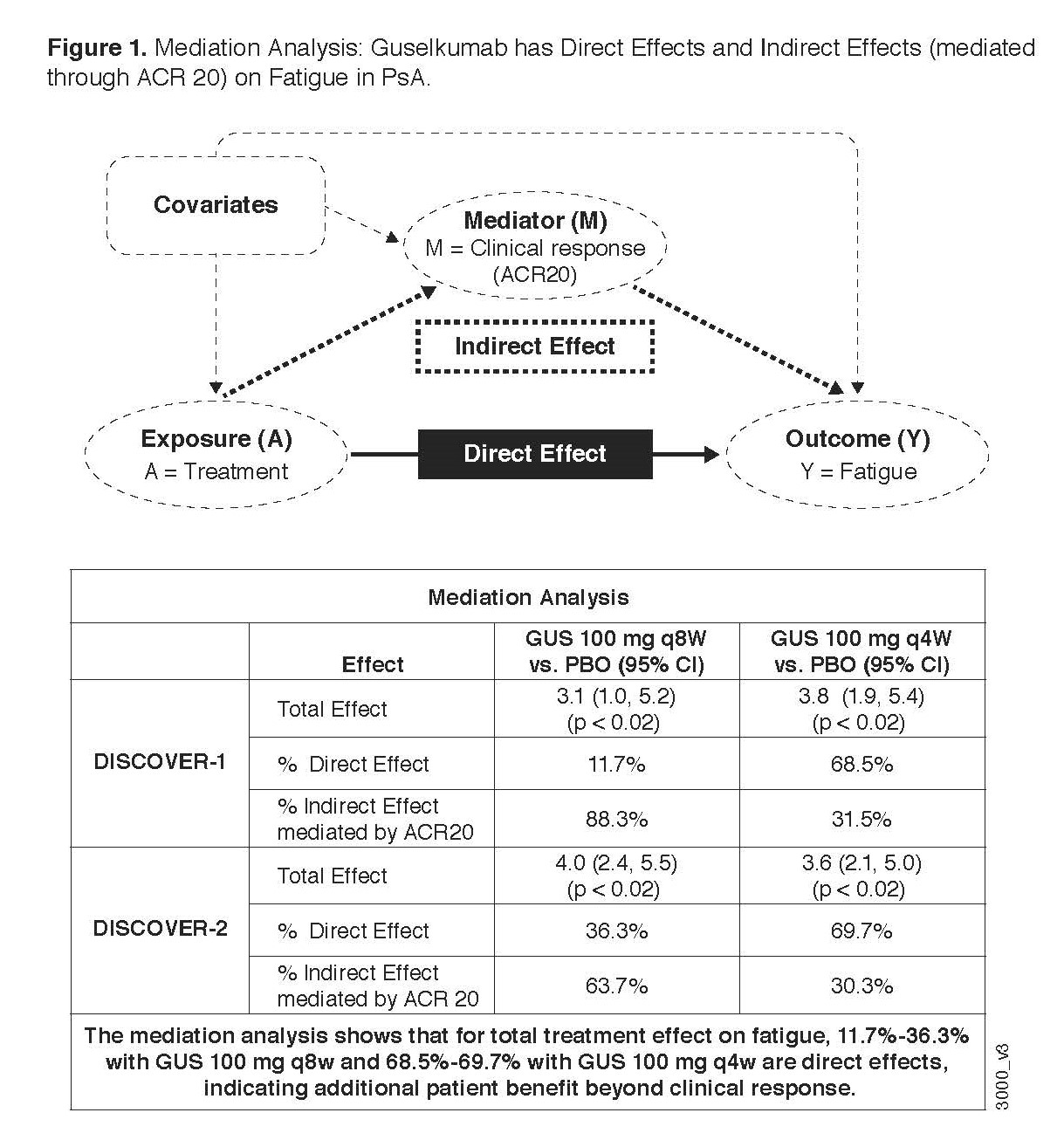
Methods: DISCOVER 1 & 2 enrolled patients with active PsA, despite non-biologic DMARDS or NSAIDS, who were biologic naïve except ~30% of patients in DISCOVER 1 who had received 1-2 TNFi. Patients were randomized (1:1:1) in a blinded fashion to subcutaneous GUS 100 mg at w0, w4, then every (q) 8w; GUS 100 mg q4w; or matching PBO. At w24, PBO patients were switched to GUS q4w. Concomitant treatment with select non-biologic DMARDS, oral corticosteroids, and NSAIDs was allowed. The FACIT-Fatigue is a 13-item PRO assessing fatigue and its impact on daily activities and function over the past 7 days, total score ranging from 0 to 52, higher score denoting less fatigue. A change of ≥4 points is considered clinically meaningful.5 The change from baseline in FACIT-Fatigue presented below is based on observed data. Mediation analysis6 was applied to the treatment effect of GUS on FACIT-Fatigue to estimate the natural direct and indirect effects, after adjusting for ACR20 response (Figure 1).
Results: At baseline in DISCOVER 1 & 2, the mean FACIT-fatigue scores (SD) were 30.4 (10.4) and 29.7 (9.7), respectively, indicating that patients with PsA experienced fatigue worse than the general population. At w24 in the DISCOVER trials, treatment with GUS led to significant improvements in FACIT-Fatigue scores compared with PBO, as early as w16 in DISCOVER 1 and w8 in DISCOVER 2. Improvements in fatigue were similar between GUS q4w and q8w doses, and the improvements at w24 were maintained through w52 (Figure 2). After a switch to GUS q4w at w24, PBO patients achieved FACIT-Fatigue scores that were comparable to those of GUS patients (Figure 2). 54%-63% of GUS patients compared with 35%-46% of PBO patients achieved clinically meaningful improvement (≥4 points) in FACIT-Fatigue at w24 (P≤0.003). At w52, 61%-70% of both GUS and PBO-to-GUS groups reached this improvement. As evaluated by mediation analysis at w24, GUS had independent positive treatment effects on fatigue (12%-36% in the q8w GUS dosing group and 69%-70% in the q4w GUS group) after adjustment for ACR20 response (Figure 1).
Conclusion: In 2 phase-3 trials, GUS treatment improved fatigue when compared to PBO during PBO-controlled periods and maintained improvements through 1 year of active treatment. Substantial proportions of those effects were independent of the effects on ACR 20, especially for the q4W dosing group.
References:
- Deodhar. Lancet. 2020;395:1115
- Mease. Lancet. 2020;395:1126
- Ritchlin. EULAR20. SAT0397
- McInnes. EULAR20. SAT0402
- Cella. J Patient-Reported Outcomes. 2019;3:30
- Valeri. Psychologic Meth. 2013;18:137
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rahman P, Helliwell P, Deodhar A, Kollmeier A, Hsia E, Zhou B, Lin X, Han C, Mease P. In Two Phase-3 Trials, Guselkumab Reduced Fatigue over 52 Weeks in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis and Demonstrated Independent Treatment Effects on Fatigue After Adjustment for Clinical Response (ACR20) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/in-two-phase-3-trials-guselkumab-reduced-fatigue-over-52-weeks-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-and-demonstrated-independent-treatment-effects-on-fatigue-after-adjustment-for-clinical-response-a/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/in-two-phase-3-trials-guselkumab-reduced-fatigue-over-52-weeks-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-and-demonstrated-independent-treatment-effects-on-fatigue-after-adjustment-for-clinical-response-a/