Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1082–1099) Measures & Measurement of Healthcare Quality Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Due in part to immunosuppressant medications, patients with rheumatic diseases not only carry a higher risk of herpes zoster reactivation but also worse outcomes. In July 2021 the FDA extended the indication for the recombinant zoster vaccine (Shingrix) to include immunosuppressed adults aged 18 years or older. Shingrix vaccination rates among eligible patients in our rheumatology clinic at the Veterans Affairs (VA) Medical Center remained low. The goal of this quality improvement project is to increase vaccination rates to at least 30% fully vaccinated over a period of 12 months in immunosuppressed patients seen in our rheumatology clinic.
Methods: Patients above the age of 18 seen in the VA Dallas rheumatology clinic and on disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), excluding hydroxychloroquine, were eligible for inclusion. Patients were considered due for vaccination if they were unvaccinated or partially vaccinated (one vaccine dose received at least two months prior to clinic visit). Shingrix vaccination rate was defined as the percentage of patients due for vaccination at time of clinic visit who received a Shingrix vaccine within one week after clinic visit. Baseline data were obtained via chart review of patients seen in our rheumatology clinic during the month of October 2021. We implemented three interventions: a) educating rheumatology fellows and attendings regarding the project and the expanded FDA indication in April 2022, b) attaching a Shingrix vaccination patient information sheet to intake forms from May 2022 to October 2022 and c) providing patients with a detailed map with directions to the separate vaccine clinic. Post-intervention data were collected during the months of June, September, October, and November 2022.
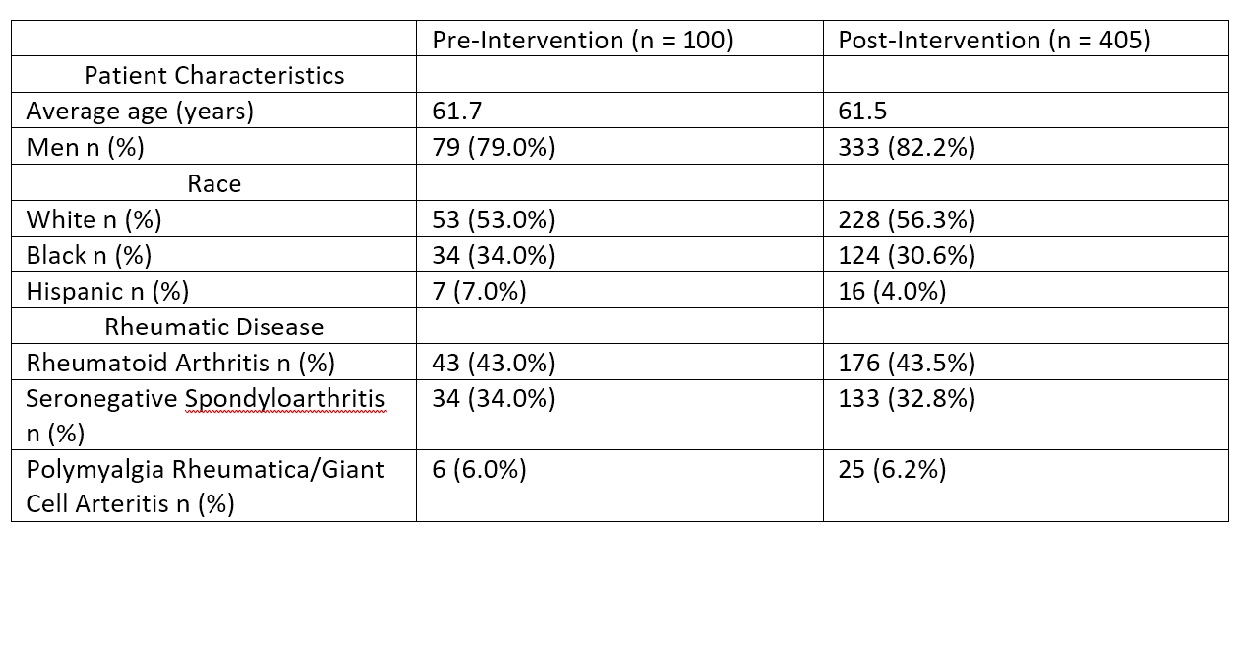
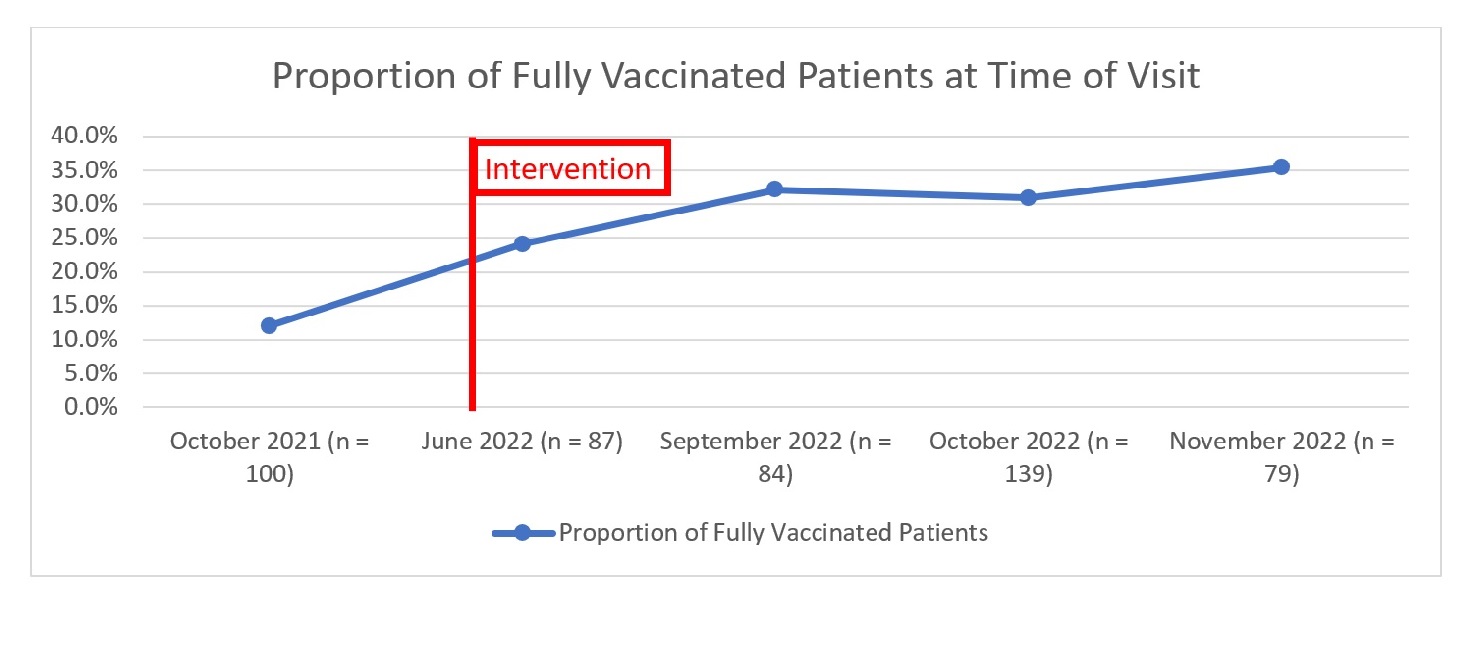
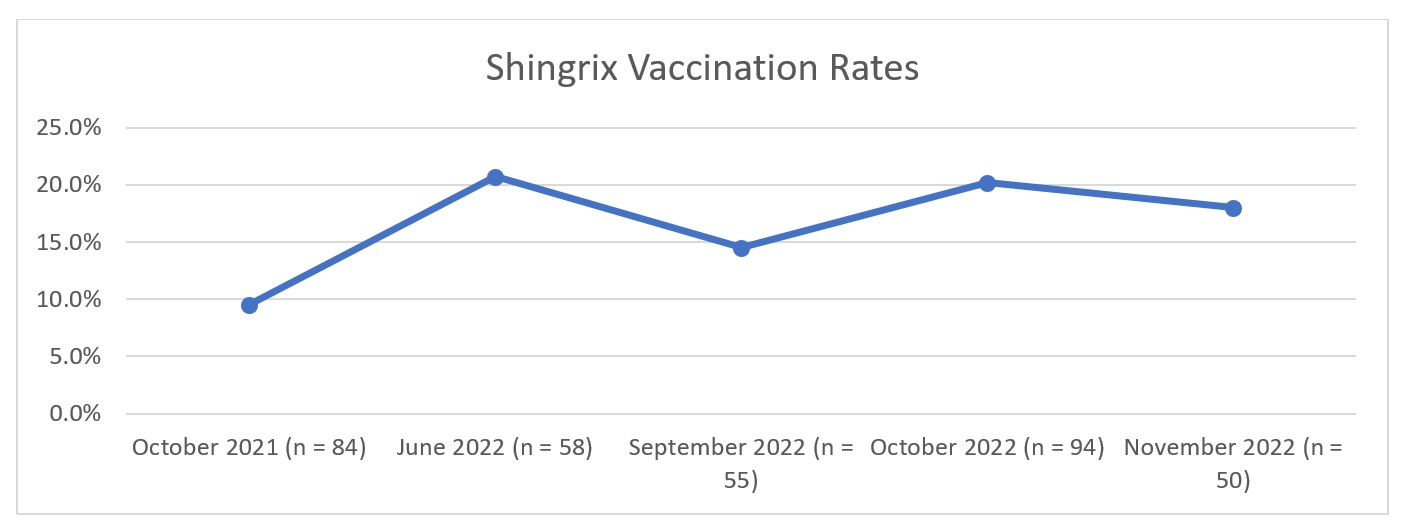
Results: For the baseline month of October 2021, our population sampled (n = 100) was on average 61.7 years old (median 64), 79% were men, 53% white, and 43% had rheumatoid arthritis. At baseline, 12% of eligible patients were fully vaccinated and 77% were unvaccinated at time of clinic visit. The Shingrix vaccination rate of due patients within one week after clinic visit was 9.5% (n = 84). During post-intervention, our population sampled (n = 405) had similar demographics to the baseline (Table 1). For the post-intervention months of June, September, October, and November 2022, the proportion of fully vaccinated patients at time of clinic visit increased from baseline (Figure 1). Vaccination rates also increased during the post-intervention months (Figure 2).
Conclusion: The baseline proportion of fully vaccinated patients and vaccination rates were low among immunosuppressed patients seen in our rheumatology clinic. While our post-intervention evaluation showed an increase in the proportion of fully vaccinated patients as well as vaccination rates, overall post-intervention vaccination rates remained low at < 50%, leaving room for improvement. Our next steps will include streamlining our vaccination processes, and considering alternative communication approaches to educate our patients, especially those with vaccine hesitancy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pokala N, Gardner B, Amratia A, Emesiani D, Mathew J, Arora R, Makris U, Reddy S. Improving Recombinant Zoster Vaccination Rates Among Immunosuppressed Veterans in an Academic Rheumatology Clinic [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improving-recombinant-zoster-vaccination-rates-among-immunosuppressed-veterans-in-an-academic-rheumatology-clinic/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improving-recombinant-zoster-vaccination-rates-among-immunosuppressed-veterans-in-an-academic-rheumatology-clinic/