Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2015
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus - Clinical Aspects and Treatment Poster Session II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The
10 mg dose of PF-04236921 showed evidence of efficacy in
a phase 2 randomized controlled trial (RCT) in SLE.1,2 Here patient-reported
outcomes (PROs) from this trial are presented.
Methods: Subjects
with active SLE (SLEDAI-2K ≥6; BILAG A in ≥1 organ system or B in
≥2 organ systems) received PF-04236921 10, 50, or
200 mg, or placebo, SC every 8 weeks; the 200 mg dose was prematurely
discontinued due to safety findings. The primary endpoint was the SLE Responder
Index-4 (SRI-4) at Week 24. Secondary endpoints included Short Form-36
(SF-36), Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy (FACIT)-Fatigue, and
European Quality of Life (EQ-5D) visual analog scale (VAS). These PROs were
analyzed by least squares (LS) mean changes from baseline at Week 24, without
imputation. An enriched population of subjects with one or more indicators of
high baseline disease activity (SLEDAI-2K ≥10, detectable anti-dsDNA
levels, prednisone >7.5 mg/day, and/or low complement) was defined for a
post-hoc analysis.
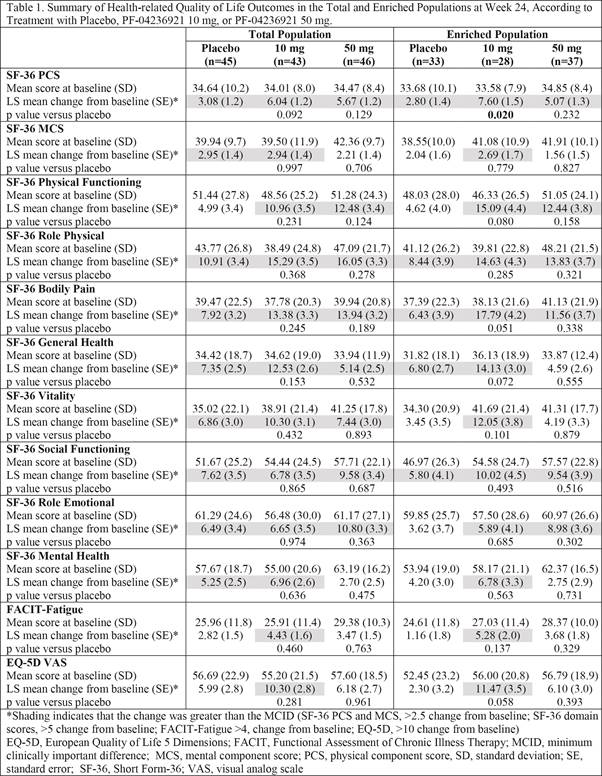
Results:
Baseline
SF-36 physical (PCS) and mental component summary (MCS), and domain scores were
lower than age- and gender-matched US norms and other RCTs in SLE,3
indicating that subjects enrolled in this trial were more impacted by their
disease. In the enriched population, statistically significant improvements in
SF-36 PCS scores were reported with 10 mg versus placebo, and physical
functioning, bodily pain, general health and vitality domain scores approached statistical
significance; all of which exceeded minimum clinically important differences
(MCID; Table 1). Numerical improvements in FACIT-Fatigue and EQ-5D VAS with 10
mg exceeded MCID in both total and enriched populations. Improvements reported
with 50 mg differed from placebo, but statistical significance was not achieved
in either population (Table 1).
Conclusion:
These results demonstrate statistically significant and clinically important improvements
in SF-36 PCS scores for the 10 mg dose in the enriched population, supported by
changes >MCID in 4 of 8 SF-36 domains, FACIT-Fatigue, and EQ-5D VAS. These
results are consistent with the primary efficacy data and indicate greater
benefit following treatment with PF-04236921 10 mg in the enriched population.
ClinicalTrials.gov identifier, NCT01405196
1. Wallace D et al. ACR Annual Meeting 2014
2. Smolen J et al. EULAR Annual Meeting 2015
3. Strand V et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73:838-844
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Strand V, Diehl A, Christensen J, Wajdula J, Sridharan S, Healey PJ. Improvements in Health-Related Quality of Life and Fatigue Following Administration of an IL-6 Monoclonal Antibody (PF-04236921) in an Enriched Population of Subjects with Active SLE [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improvements-in-health-related-quality-of-life-and-fatigue-following-administration-of-an-il-6-monoclonal-antibody-pf-04236921-in-an-enriched-population-of-subjects-with-active-sle/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improvements-in-health-related-quality-of-life-and-fatigue-following-administration-of-an-il-6-monoclonal-antibody-pf-04236921-in-an-enriched-population-of-subjects-with-active-sle/