Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Upadacitinib (UPA) has been shown to be effective and well tolerated in patients with active ankylosing spondylitis (AS) [1]. However, improvements in global functioning and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in patients treated with UPA, and their relationship with established clinical response measures have not been fully characterized. We evaluate the effect of UPA on the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society Health Index (ASAS HI) and Ankylosing Spondylitis Quality of Life (ASQoL) questionnaire and to quantify incremental improvements in ASAS HI and ASQoL response in patients achieving established AS disease activity and physical function improvements at week 14.
Methods: This was a post-hoc analysis of the SELECT-AXIS 1 trial [1]. Patients were randomized to either UPA 15 mg once daily or placebo (PBO) for 14 weeks. Mean change in ASAS HI and ASQoL from baseline (BL) to weeks 4, 8 and 14 for UPA and PBO were calculated and UPA vs PBO responses were compared. Achievement of changes in ASAS HI and ASQoL above the minimum clinically important difference (MCID ≥3-point improvement for both measures) and ASAS HI ‘good health state’ (ASAS HI score ≤5) at week 14 were determined. Changes from BL in ASAS HI and ASQoL were assessed within the combined UPA and PBO group reaching established improvement thresholds across AS clinical response measures at week 14, including ASAS response criteria, ASDAS improvement criteria, and BASFI MCID. Mean ASAS HI and ASQoL changes across groups within each clinical measure and magnitude of ASAS HI and ASQoL change between responders and non-responders were compared.
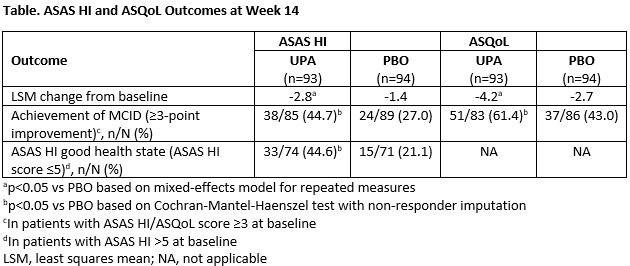
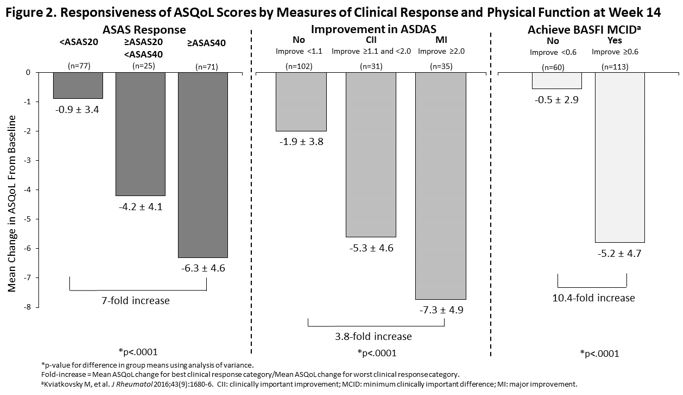
Results: UPA treatment resulted in significant improvement from BL in ASAS HI and ASQoL at week 14 with more patients achieving a MCID and ASAS HI good health state vs PBO (Table). Significant improvements were observed earlier for ASAS HI than for ASQoL, starting at Week 4. At week 14, achievement of clinical improvement thresholds was associated with increasing improvements in both ASAS HI and ASQoL scores (Figures 1 and 2). The magnitude of improvement between the best and worst clinical response categories was greater for ASAS HI than ASQoL: 43-fold vs 7-fold for ASAS response, 5-fold vs 3.8-fold for ASDAS improvement, and 34-fold vs 10.4-fold for BASFI MCID achievement.
Conclusion: UPA treatment in patients with active AS resulted in significant and clinically meaningful improvements compared with PBO in global functioning and HRQoL as measured by ASAS HI and ASQoL, with both measures showing discriminatory ability. Earlier UPA vs PBO response and greater magnitude of change across known clinical response groups suggests that ASAS HI may demonstrate greater responsiveness and ability to capture improvements in AS disease activity and physical function achieved with treatment and translate them to a patient-centric measure.
References: [1] van der Heijde D, et al. Lancet 2019;394:2108–17.
Original abs: Ann Rheum Dis. 2020; 79(S1):416.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kiltz U, Sieper J, Deodhar A, Zueger P, Song I, Chen N, van der Heijde D. Improvements in Global Functioning and Health-related Quality of Life and Their Association with Disease Activity and Functional Improvement in Patients with Active Ankylosing Spondylitis Treated with Upadacitinib [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improvements-in-global-functioning-and-health-related-quality-of-life-and-their-association-with-disease-activity-and-functional-improvement-in-patients-with-active-ankylosing-spondylitis-treated-with/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improvements-in-global-functioning-and-health-related-quality-of-life-and-their-association-with-disease-activity-and-functional-improvement-in-patients-with-active-ankylosing-spondylitis-treated-with/