Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: 3S112: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders I: Miscellaneous Disorders (945–950)
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Behçet’s syndrome is a chronic, multi-system inflammatory disorder characterized by painful, recurrent oral ulcers (OU) that can impair quality of life (QoL). Apremilast (APR), an oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, demonstrated efficacy in the treatment of OU of Behçet’s syndrome in a phase III, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo (PBO)-controlled study (RELIEF). We report short- and long-term results from RELIEF for the efficacy of APR treatment on QoL and physical function for up to 64 weeks.
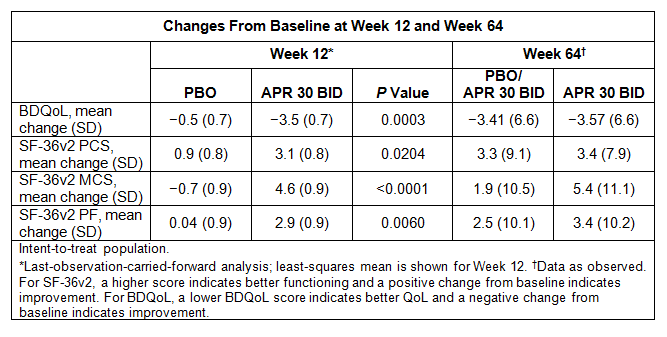
Methods: A total of 207 patients were randomized (1:1) to APR 30 mg twice daily (APR 30 BID) or PBO twice daily for a 12-week PBO-controlled phase, followed by a 52-week active treatment extension. Eligible patients were ≥18 years old, had active Behçet’s syndrome, with ≥3 OU at randomization or ≥2 OU at screening and randomization and without active major organ involvement. The primary efficacy endpoint was area under the curve for the number of OU over 12 weeks (AUCWk0-12). Clinical improvement of OU was evaluated by assessments of OU pain (100 mm visual analogue scale) and measures of disease activity and QoL. Disease activity measures included the Behçet’s Syndrome Activity Score (BSAS) and Behçet’s Disease Current Activity Index Form (BDCAF; including 3 components: Behçet’s Disease Current Activity Index, Patient’s Perception of Disease Activity, Clinician’s Overall Perception of Disease Activity). QoL assessments included the Behçet’s Disease QoL (BDQoL) score and the 36-item Short-Form Health Survey version 2 (SF-36v2), consisting of the Physical and Mental Component Summary (PCS and MCS) scores and Physical Functioning domain (PF) score. An analysis of covariance model was used to analyze the primary endpoint and change from baseline in BDQoL score and SF-36v2 PCS, MCS and PF scores at Week 12. Data at Week 64 are as observed.
Results: The primary efficacy endpoint of AUCWk0-12 for the number of OU was significantly lower in APR 30 BID vs PBO patients (P< 0.0001); improvement in the number of OU and OU pain was sustained in patients continuing APR 30 BID treatment for up to 64 weeks and emerged in patients switched from PBO to APR 30 BID for Weeks 12 to 64. Significant improvements were observed with APR 30 BID vs PBO in mean change from baseline at Week 12 in BSAS (P< 0.0001), BDCAF components (P≤0.0335), and BDQoL score (P=0.0003). The improvements in BSAS, BDCAF, and BDQoL outcomes were maintained in patients continuing APR 30 BID treatment for up to 64 weeks, and comparable effects were observed at Week 64 among patients who switched from PBO to APR 30 BID. Significant improvements were also observed in mean change from baseline at Week 12 in SF-36v2 PCS (P=0.0204), MCS (P< 0.0001), and PF (P=0.0060) scores in APR 30 BID vs PBO patients. These effects in SF-36v2 scores were also maintained at Week 64 among patients initially randomized to APR 30 BID, and the improvements were generally similar among patients who switched from PBO to APR 30 BID (Table).
Conclusion: Patients with active Behçet’s syndrome treated with APR 30 BID vs PBO experienced significant reductions in OU and clinically meaningful improvements at Week 12 in disease activity and QoL. Improvements were sustained at Week 64 in patients continuing APR treatment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hatemi G, Mahr A, Takeno M, Kim D, Melikoglu M, Cheng S, McCue S, Paris M, Chen M, Yazici Y. Improvements in Disease Activity and Quality of Life for up to 64 Weeks in Patients with Behçet’s Syndrome: Results from a Phase III Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improvements-in-disease-activity-and-quality-of-life-for-up-to-64-weeks-in-patients-with-behcets-syndrome-results-from-a-phase-iii-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improvements-in-disease-activity-and-quality-of-life-for-up-to-64-weeks-in-patients-with-behcets-syndrome-results-from-a-phase-iii-study/