Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: SLE – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: ABBV-599 is a novel combination of elsubrutinib (ELS; a selective Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor) and upadacitinib (UPA; a selective Janus kinase inhibitor), which targets separate signaling pathways associated with SLE. After 48 weeks of treatment with ABBV-599 high dose (HD; ELS 60 mg + UPA 30 mg) or UPA 30 mg monotherapy in the phase 2 SLEek study, patients with SLE demonstrated improvements in composite disease activity measures (BILAG–based Composite Lupus Assessment [BICLA] and SLE Responder Index-4 [SRI-4]) and flares compared with placebo. Understanding responses in individual organs is important to clinicians and patients. The BILAG index measures disease activity in 9 systems: constitutional, mucocutaneous, neuropsychiatric, musculoskeletal, cardiorespiratory, gastrointestinal, ophthalmic, renal, and hematological. The objective of this post hoc analysis of the SLEek trial was to evaluate changes from baseline at week 48 in BILAG domains in patients with SLE receiving ABBV-599 HD, UPA 30 mg, or placebo.
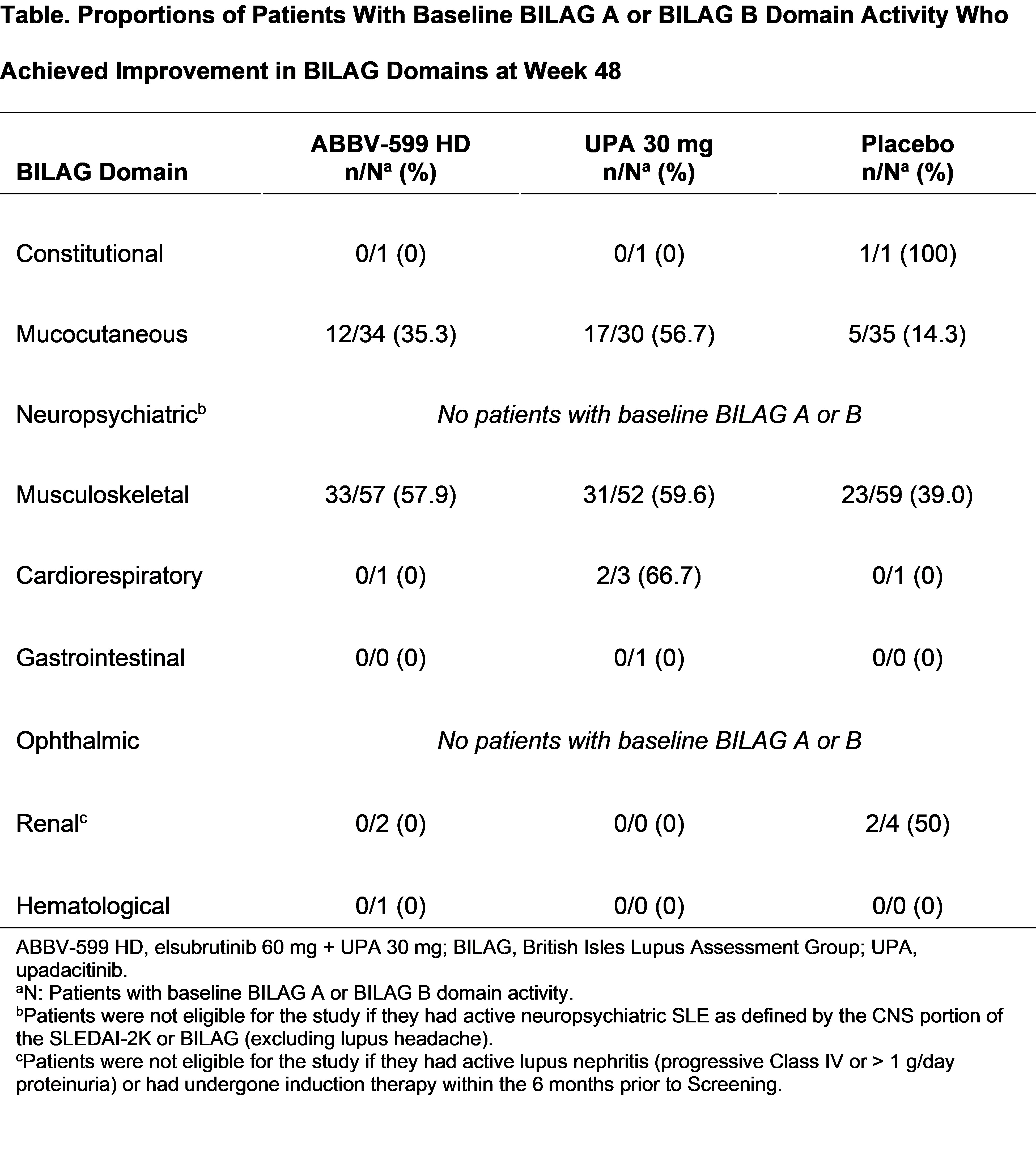
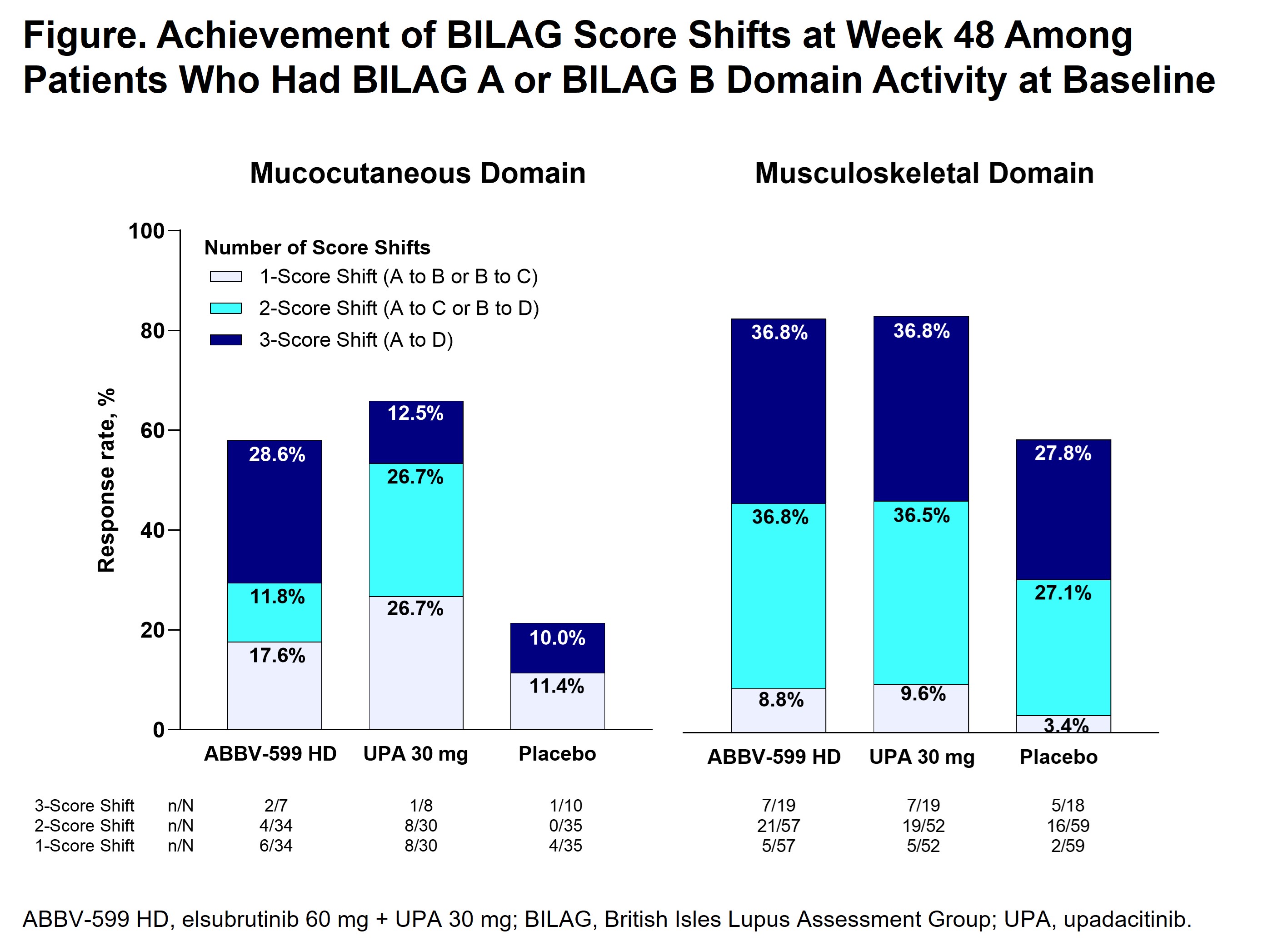
Methods: In this multicenter, double-blind trial (NCT03978520), patients with moderately to severely active SLE were randomized 1:1:1:1:1 to receive once daily ABBV-599 HD, ABBV-599 low dose (LD; ELS 60 mg + UPA 15 mg), ELS 60 mg, UPA 30 mg, or placebo. After a planned interim analysis, the ABBV-599 LD and ELS 60 mg groups were discontinued for lack of efficacy. This post hoc analysis evaluated BILAG domains and improving score shifts from baseline to week 48 in the continued treatment groups. For this analysis, definitions of 1-score shifts were BILAG A to B or B to C, 2-score shifts were BILAG A to C or B to D, and 3-score shifts were BILAG A to D.
Results: Among patients with BILAG A or B domain activity at baseline, a higher proportion of the ABBV-599 HD or UPA 30 mg groups than placebo achieved improvements in the BILAG musculoskeletal (57.9%, 59.6%, and 39.0%, respectively) and mucocutaneous (35.3%, 56.7%, and 14.3%, respectively) domains at week 48 (Table). Among patients in the UPA 30 mg and ABBV-599 HD groups who achieved an improvement, 2- or 3-score shifts from baseline to week 48 were achieved by > 80% and > 50% of patients in the musculoskeletal and mucocutaneous domains, respectively (Figure). Conclusions could not be drawn regarding the remaining BILAG domains due to small sample sizes and exclusion of patients with active neuropsychiatric SLE or severely active lupus nephritis.
Conclusion: Both the ABBV-599 HD and UPA 30 mg treatment groups showed improvements in the musculoskeletal and mucocutaneous BILAG domains at week 48 compared with placebo. Although this phase 2 study was not designed or powered to assess efficacy in individual organs, musculoskeletal and mucocutaneous activity has been observed in up to 80% of patients in SLE trials [1]. This analysis allows an early comparison of these frequent individual manifestations in a smaller trial and highlights the importance of examining improvement in each. A large global phase 3 program to expand the evaluation of UPA in SLE is ongoing (NCT05843643).
1. Connelly K, et al. Rheumatology 2022;61:1341–53.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Saxena A, Touma Z, Vital E, Morand E, Mosca M, D'Silva K, Wung P, Cheng L, Iglesias-Rodriguez M, Kafka S, Merrill J. Improvements in BILAG Musculoskeletal and Mucocutaneous Domains at Week 48 in a Phase 2 Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial of ABBV-599 (Elsubrutinib + Upadacitinib Combination) and Upadacitinib Monotherapy for Treatment of Moderately to Severely Active Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improvements-in-bilag-musculoskeletal-and-mucocutaneous-domains-at-week-48-in-a-phase-2-double-blind-placebo-controlled-trial-of-abbv-599-elsubrutinib-upadacitinib-combination-and-upadacitinib-mon/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improvements-in-bilag-musculoskeletal-and-mucocutaneous-domains-at-week-48-in-a-phase-2-double-blind-placebo-controlled-trial-of-abbv-599-elsubrutinib-upadacitinib-combination-and-upadacitinib-mon/