Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0176–0195) Healthcare Disparities in Rheumatology Poster I: Lupus
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Social determinants of health (SDOH) have a significant impact on the health outcomes of many chronic conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The purpose of this study is to assess the impact of SDOH on adherence in RA, PsA and SLE patients.
Methods: In this cohort study of fully insured commercial and Medicare members of a large national health plan between 1/1/2018 and 1/1/2023, members ≥ 18 years old were included if they had at least 2 visits for RA (ICD-10 code: M05 or M06), PsA (L40.5), or SLE (M32) during the study period and received medication therapy for their disease. Members were excluded if they did not maintain continuous eligibility 6 months before or after entrance into the study, had multiple conditions of interest, or had missing socioeconomic status (SES) data. Medication adherence was measured using proportion of days covered (PDC), defined as the number of days with medication coverage divided by the number of days between index date into the study and the exhaust date of the last prescription. Adherence was defined as PDC ≥ 0.8. Continuous variables were assessed with analysis of variance or Kruskal-Wallis tests; categorical variables were assessed with the Chi2 test. Logistic regression was used to examine the impact of SDOH factors on medication adherence; p-values < 0.05 are significant.
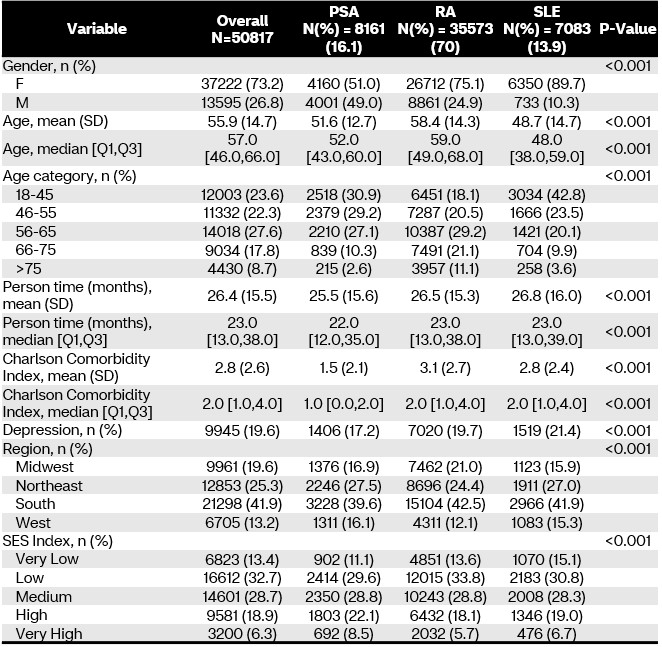
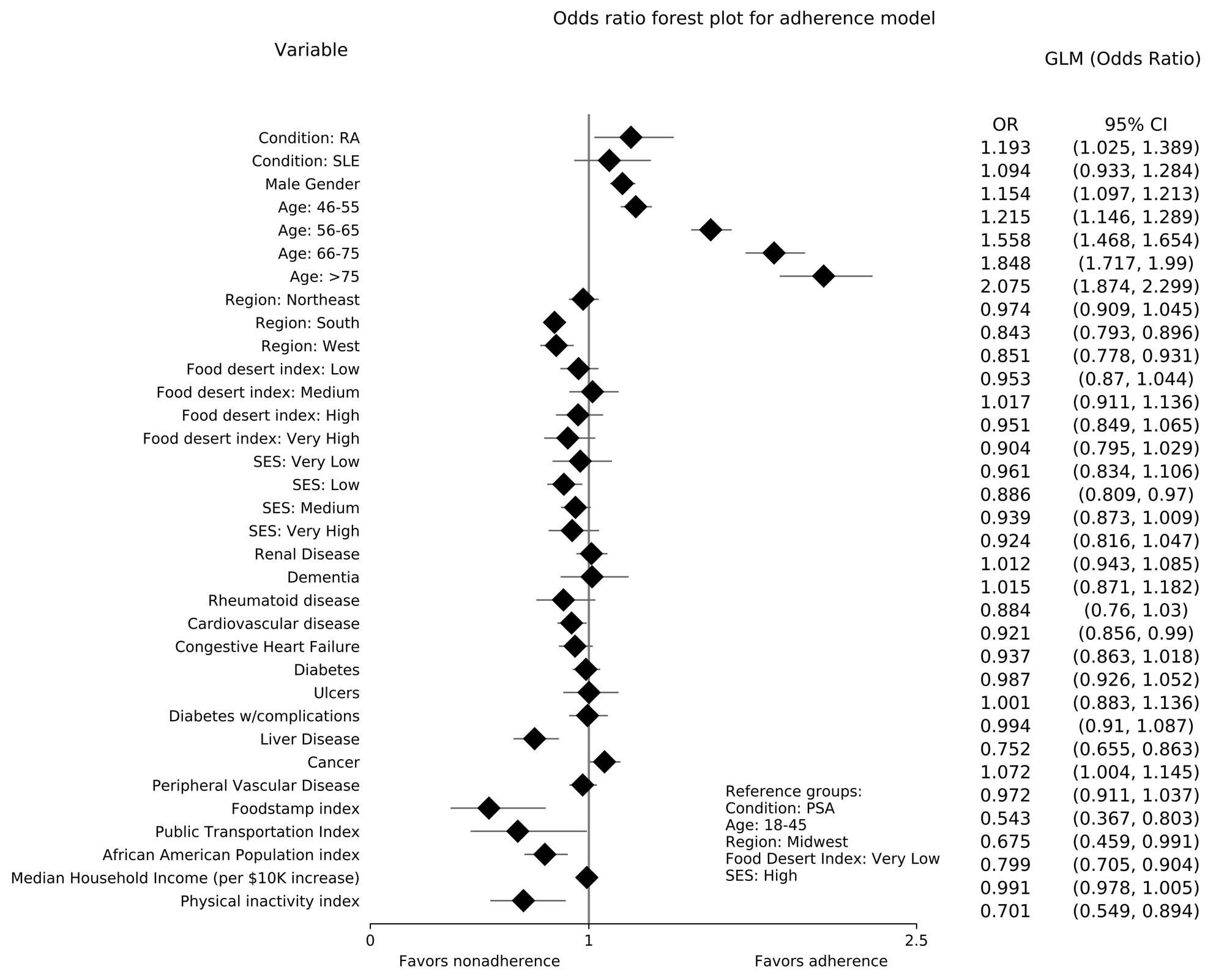
Results: Of the 50,817 members included in this study, 35,573 (70%) had RA, 7,083 (13.9%) had SLE, and 8,161 (16.1%) had PsA. There were significant differences (Table 1) in baseline demographics between disease states, with RA members being older (mean age [standard deviation (SD)]: 58.4 [14.3] vs. 51.6 [12.7] and 48.7 [14.7] years in PsA and SLE, respectively; p< 0.001) and more ill at baseline (mean Charlson Comorbidity Index [SD]: 3.1 [2.7] vs. 1.5 [2.1] and 2.8 [2.4] in PsA and SLE, respectively; p< 0.001). Adherence was high during this study (mean PDC [SD]: 0.88 [0.19]). RA members had the highest PDC (mean [SD]: 0.88 [0.19] vs. 0.87 [0.18] and 0.85 [0.21] compared to PsA and SLE members, respectively; p< 0.001). In regression analysis, RA members were more likely to be adherent compared to PsA members (odds ratio [OR, 95% confidence interval (CI)]: 1.19 [1.02-1.39]); SLE was not associated with changes in adherence (Figure 1). Other factors associated with increased adherence include male gender (OR [95%CI]: 1.15 [1.10-1.21]); cancer diagnoses (OR [95%CI]: 1.07 [1.00-1.15]); and increasing age. Factors associated with decreased adherence were: low SES compared to high SES (OR [95%CI]: 0.89 [0.81-0.97]); liver disease (OR [95%CI]: 0.75 [0.66-0.86]); cardiovascular disease (OR [95%CI]: 0.92 [0.86-0.99]); increases in food stamps (OR [95%CI]: 0.54 [0.37-0.80]), public transportation (OR [95%CI]: 0.68 [0.46-0.99]), African American population (OR [95%CI]: 0.80 [0.71-0.90]), and physical inactivity (OR [95%CI]: 0.70 [0.55-0.89]) indices.
Conclusion: Members with RA had significantly higher rates of adherence compared to members with PsA and SLE. SDOH factors associated with decreased adherence included SES, increases in food stamps, public transportation, African American population, and physical inactivity indices.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Park J, Rutter W, Avalos-Reyes E, Liu C, Cavers W, Verbrugge D, Johnson K. Impact of Social Determinants of Health Factors on Medication Adherence in Members with Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis, and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-social-determinants-of-health-factors-on-medication-adherence-in-members-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-psoriatic-arthritis-and-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-social-determinants-of-health-factors-on-medication-adherence-in-members-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-psoriatic-arthritis-and-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/