Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Current knowledge on the health status of patients (pts.) with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) mainly focusses on physical function and disease activity. Using a generic measure for physical- or mental health (SF36), a hierarchical relationship between disease activity, spinal damage, spinal mobility, physical function and overall health has been demonstrated in pts. with radiographic axSpA (r-axSpA) 1. Disease-specific global functioning and health can be assessed in pts. with axSpA using the ASAS Health Index (ASAS HI), which encompasses physical function, as well as aspects of emotional and social functioning and aspects of activity and participation. To build a structural model that visualizes interrelationships of different patient- and disease characteristics with global functioning and health in pts. with early axSpA.
Methods: Data of pts. with axSpA from the DESIR cohort was analyzed, which included information on socio-demographics (age, BMI), disease activity (ASDAS), physical function (BASFI), spinal mobility (BASMI), structural damage (mSASSS), disease-specific global functioning (ASAS HI), and comorbidity count. Information on patient- and disease characteristics was retrieved from the visit performed 72 months after inclusion, which was the first time point of ASAS HI collection. A Bayesian network (BN) was used to obtain insight of the underlying structural model. BNs are probabilistic graphical models consisting of “nodes” (representing specific variables) joined by “edges” (lines representing directions of effects). They are capable of capturing complex relationships between variables and allow the incorporation of existing (prior) knowledge from previous studies.
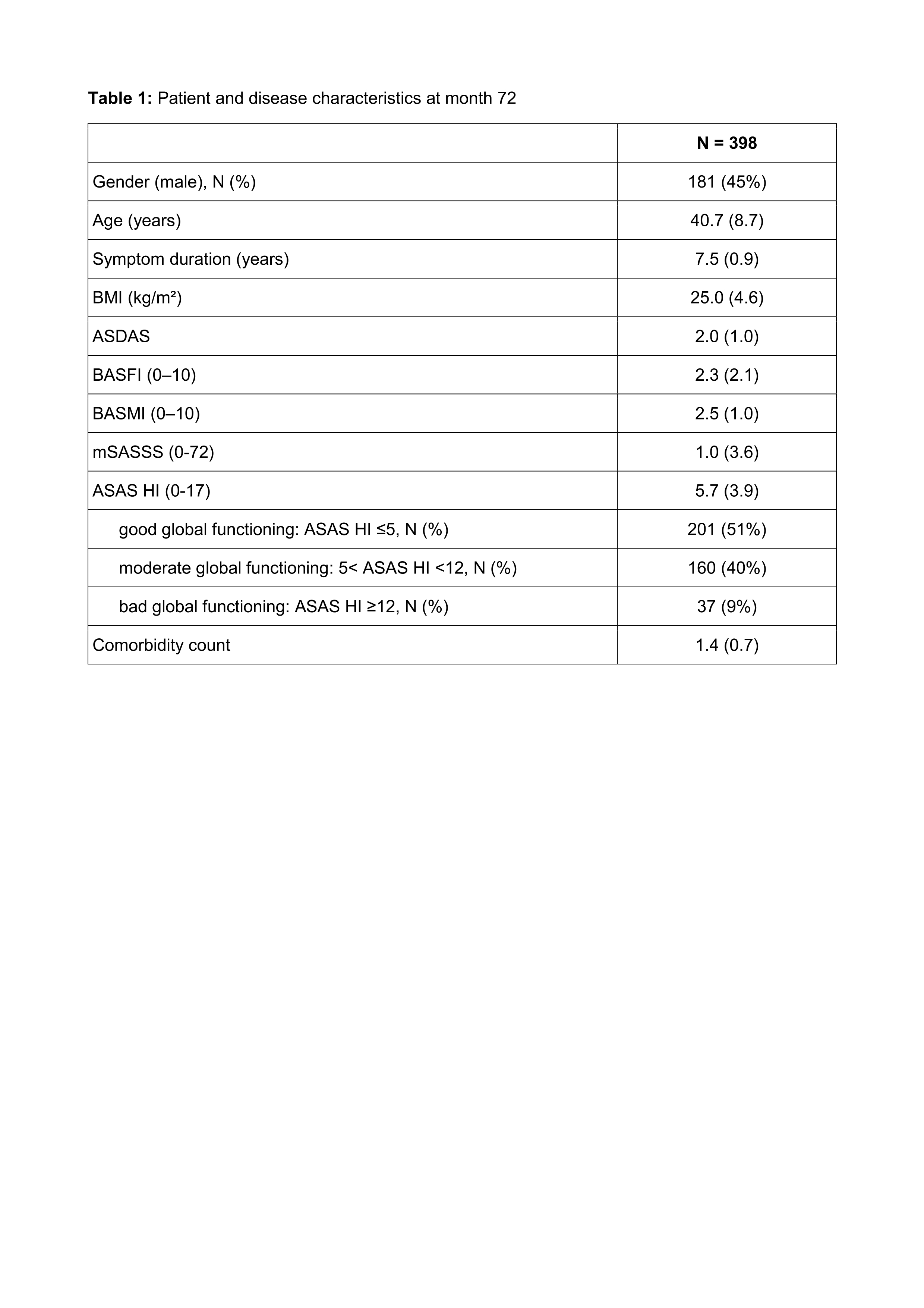
Results: The DESIR cohort contained data from 582 pts. at month 72, of whom 398 had data for ASAS HI. Descriptive information of these pts. is shown in Table 1. The mean ASAS HI was 5.7 (range: 0 – 16). Applying existing cut-offs for ASAS HI, 51% had ‘good’ global functioning (ASAS HI ≥5), 40% had ‘moderate’ global functioning (5< ASAS HI < 12) and 9% had ‘bad’ global functioning (ASAS HI ≥12). The structural model that was constructed from combining data and prior expert knowledge is visualized in Figure 1. It suggests that ASDAS and BASFI have a direct effect on ASAS HI as well that ASDAS has an indirect effect via BASFI. Moreover, the model suggests that BMI is also determined by ASDAS, and that BASFI determines BASMI, which is in turn also influenced by age and mSASSS. In addition, it suggests a direct effect of age, BMI and ASAS HI on the comorbidity count. The model denies a relationship between BASMI or mSASSS and ASAS HI.
Conclusion: The BN-analysis approach, that combines prior knowledge and measured data, serves to better understand the construct of global functioning and health in pts. with early axSpA. Our model shows that global functioning (ASAS-HI) is determined both by patient reported physical function (BASFI) and by disease activity (ASDAS), which confirms the hierarchical model once proposed by Machado et al. The observed directional relationship between ASAS HI and comorbidity count is counterintuitive and requires further investigation.
Reference: Machado P, ARD 2011.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Redeker I, Landewé R, van der Heijde D, Ramiro S, Boonen A, Dougados M, Braun J, Kiltz U. Impact of Patient and Disease Characteristics on Global Functioning and Health in Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis: A Bayesian Network Analysis of Data from an Early axSpA Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-patient-and-disease-characteristics-on-global-functioning-and-health-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-bayesian-network-analysis-of-data-from-an-early-axspa-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-patient-and-disease-characteristics-on-global-functioning-and-health-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-bayesian-network-analysis-of-data-from-an-early-axspa-cohort/