Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
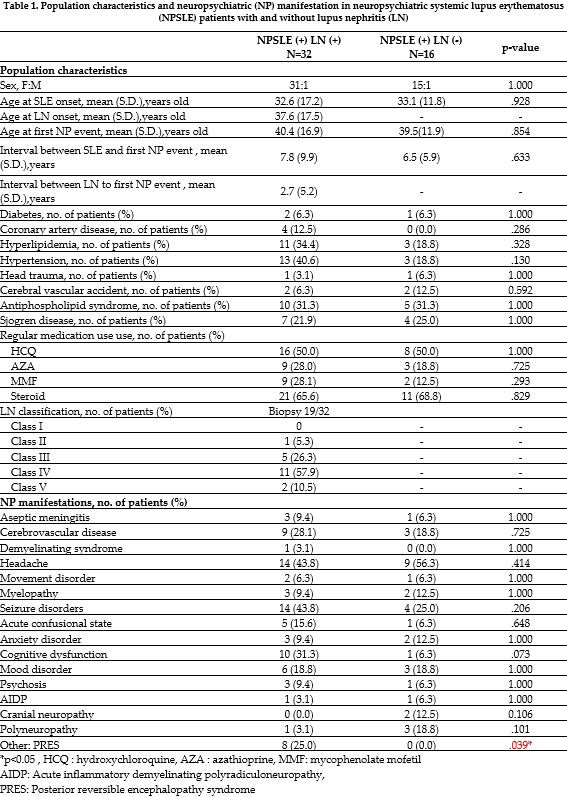
Background/Purpose: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disorder with diverse organ involvement, notably affecting the kidneys and nervous system. Lupus nephritis (LN) and neuropsychiatric SLE (NPSLE) are severe complications associated with increased morbidity and mortality. This retrospective study analyzes data from SLE patients with newly diagnosed NPSLE to explore the correlation between LN and NPSLE, focusing on clinical outcomes and potential predictive factors.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed medical records from SLE patients with NPSLE at Tri-Service Hospital from November 2005 to December 2023. Data on demographic information, clinical manifestations, laboratory tests, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (SELENA-SLEDAI), complications, treatment, and mortality were collected.
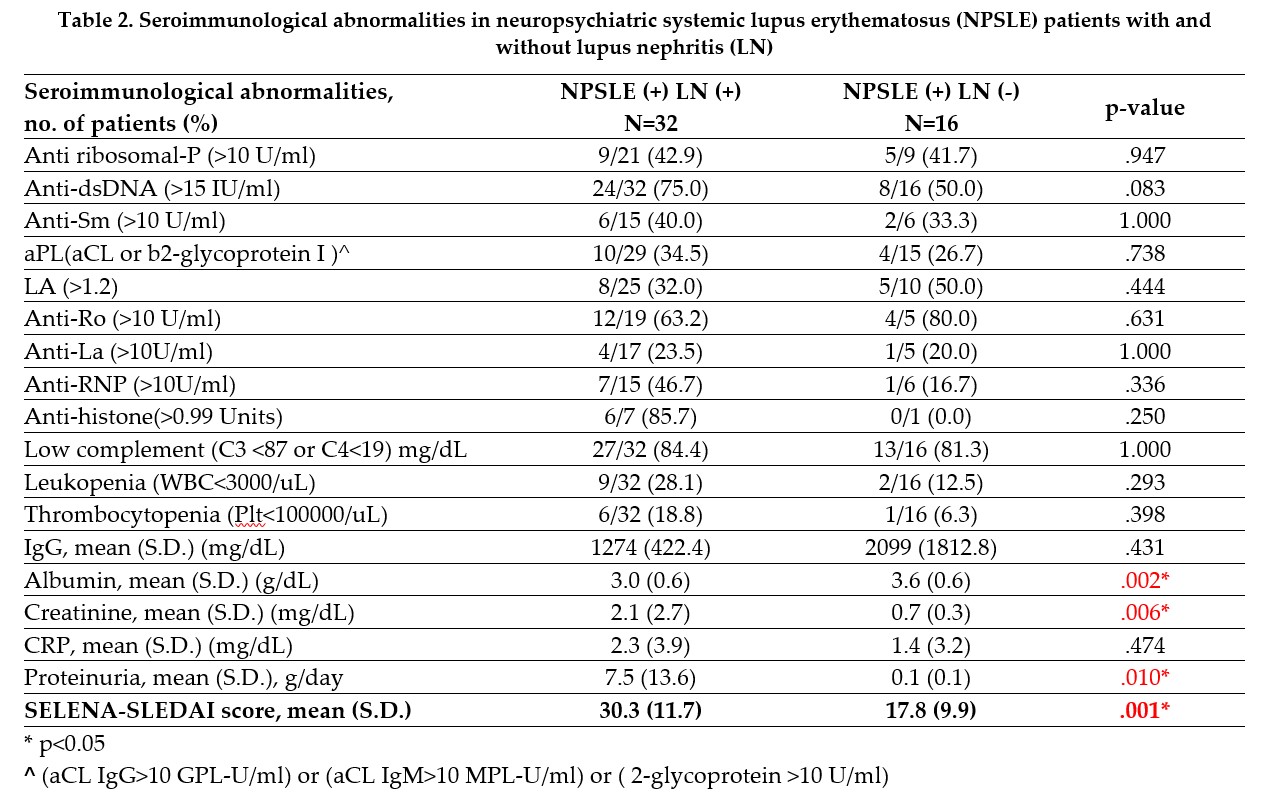
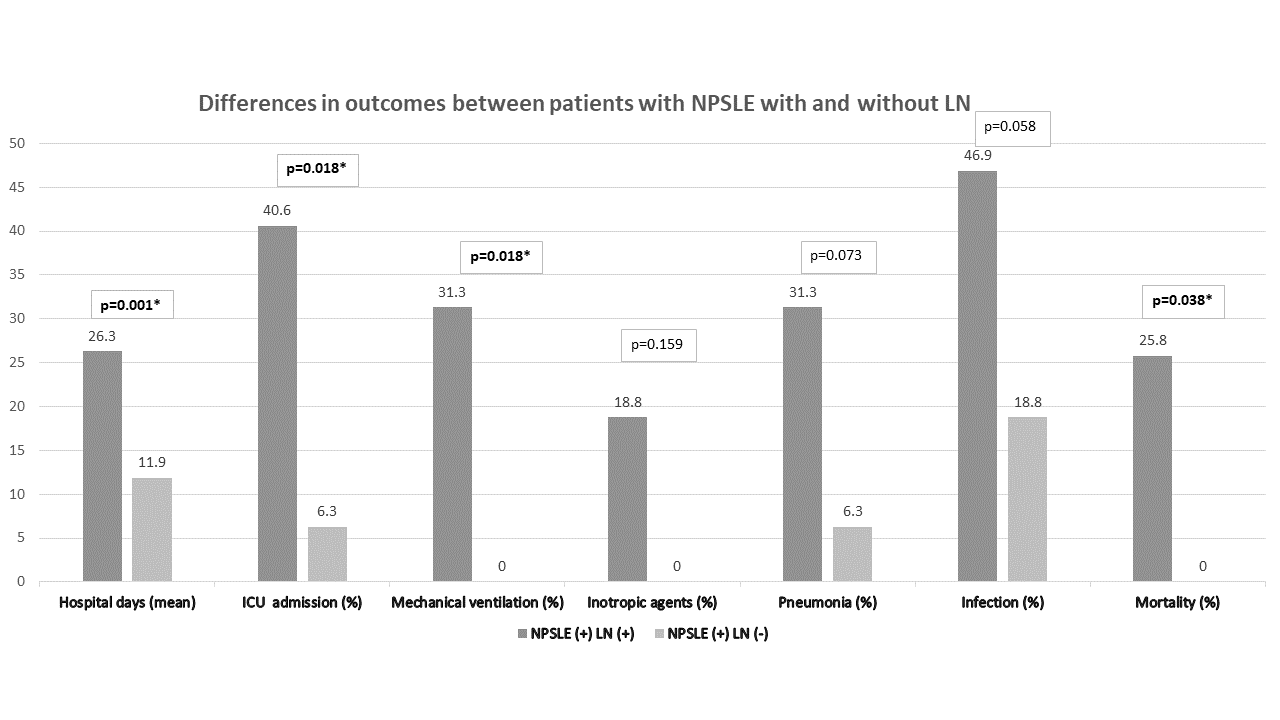
Results: Our study included 48 NPSLE patients, with 32 meeting the criteria for LN diagnosis. NPSLE patients were categorized into LN+ (with lupus nephritis) and LN− (without lupus nephritis) groups. The LN+ group had a higher SELENA-SLEDAI score (p=0.001). Regarding hospitalization, the LN+ group (mean: 26.3 days) exceeded the LN− group (mean: 11.9 days) (p=0.001). The LN+ group also had a higher percentage of intensive care unit (ICU) admission (40.6% vs. 6.3%, p=0.018) and mechanical ventilation use (31.3% vs. 0.0%, p=0.020). Although the LN+ group showed higher infectious complications (46.9%) compared to the LN− group (18.8%), it did not reach statistical significance (p = 0.058). However, the LN+ group’s elevated mortality rate (25.8%) achieved statistical significance compared to the LN− group (0.0%) (p = 0.038).
Conclusion: This study underscores the substantial impact of LN on the clinical outcomes of NPSLE, revealing increased lupus activity, prolonged hospitalization, higher ICU admissions, greater use of mechanical ventilation, and a higher mortality rate in the LN+ group compared to the LN− group.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fang P, Kuo P, Lu C. Impact of Lupus Nephritis on Neuropsychiatric SLE Outcomes [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-lupus-nephritis-on-neuropsychiatric-sle-outcomes/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-lupus-nephritis-on-neuropsychiatric-sle-outcomes/