Session Information
Date: Wednesday, November 15, 2023
Title: Abstracts: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders III: Innovation
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is a large vessel vasculitis in adults that commonly involves the aorta and branching arteries, resulting in multiple symptoms including vision loss. IL-6 has been identified as key to GCA pathogenesis, and treatment with IL6 receptor (IL-6R) antibody, tocilizumab, induces steroid-free disease remission in many patients with GCA. Not all patients with GCA have favorable clinical response to tocilizumab. A relatively common SNP in IL-6R, Asp358Ala, results in increased solubilization of the IL-6R that then binds the ubiquitous IL-6 co-receptor, gp130, leading to more pro-inflammatory soluble IL-6 signaling, known as trans signaling. This contrasts with classical membrane bound IL-6R signaling, found on hepatocytes and lymphocytes, that results in anti-inflammatory effects and release of C-reactive protein. We hypothesized that the Asp358Ala IL-6R variant in patients with GCA impact IL-6 mediated T cell activity and response to tocilizumab.
Methods: Samples and clinical data were obtained from patients who met the 2022 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria for GCA. Genetic sequencing was completed to identify GCA patients with the Asp358Ala variant. Serum from patients was used to quantitate serum soluble IL-6R levels by ELISA. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) evaluated for expression of IL-6R and its co-receptor, gp130, using flow cytometry. The same PBMCs were stimulated ex vivo with IL-6 and evaluated for downstream targets of IL-6, STAT3 phosphorylation and IL-17A expression, also using flow cytometry. Clinical symptoms, laboratory values, and response to tocilizumab was identified by chart review. Active disease was defined by clinical signs and symptoms.
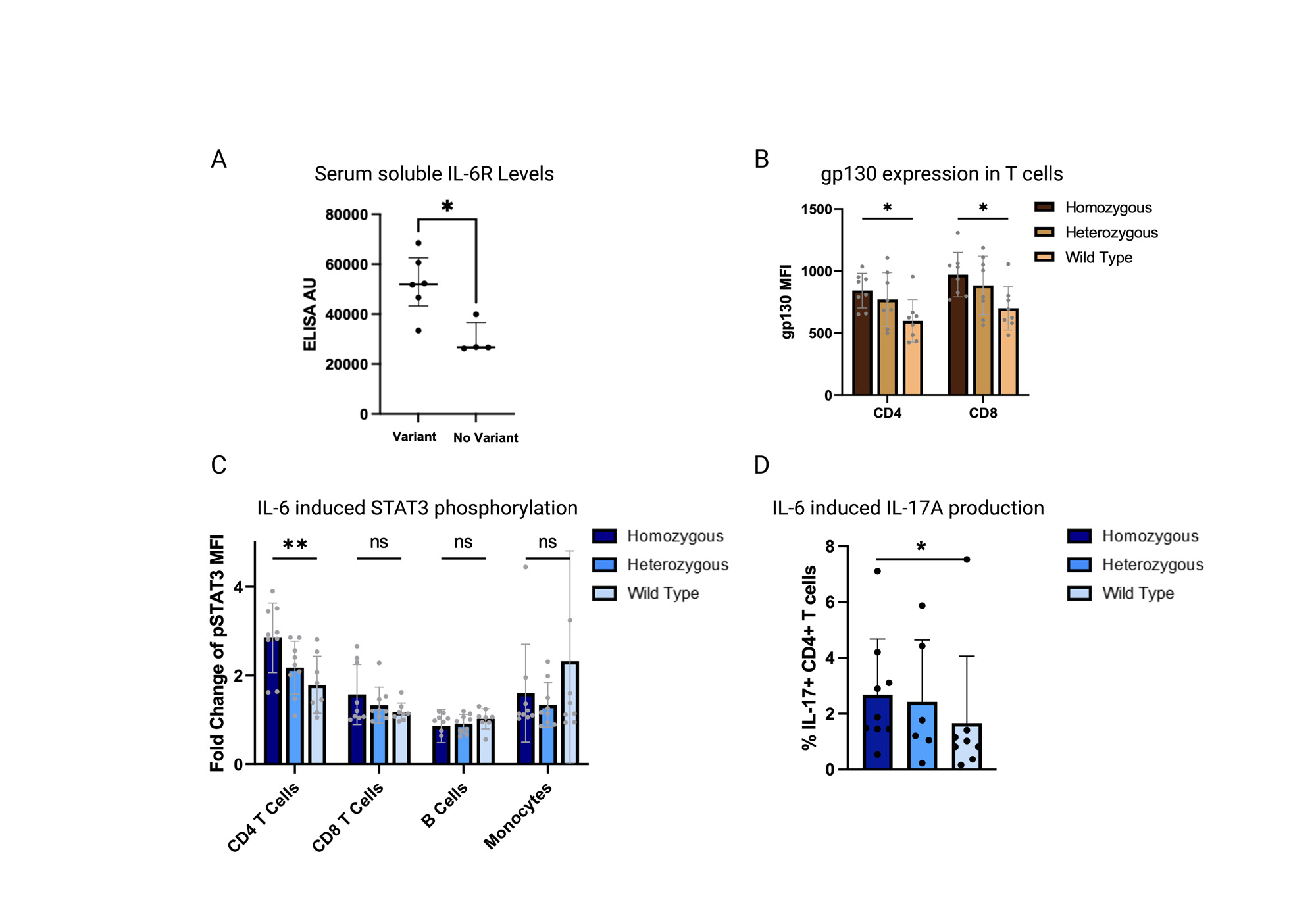
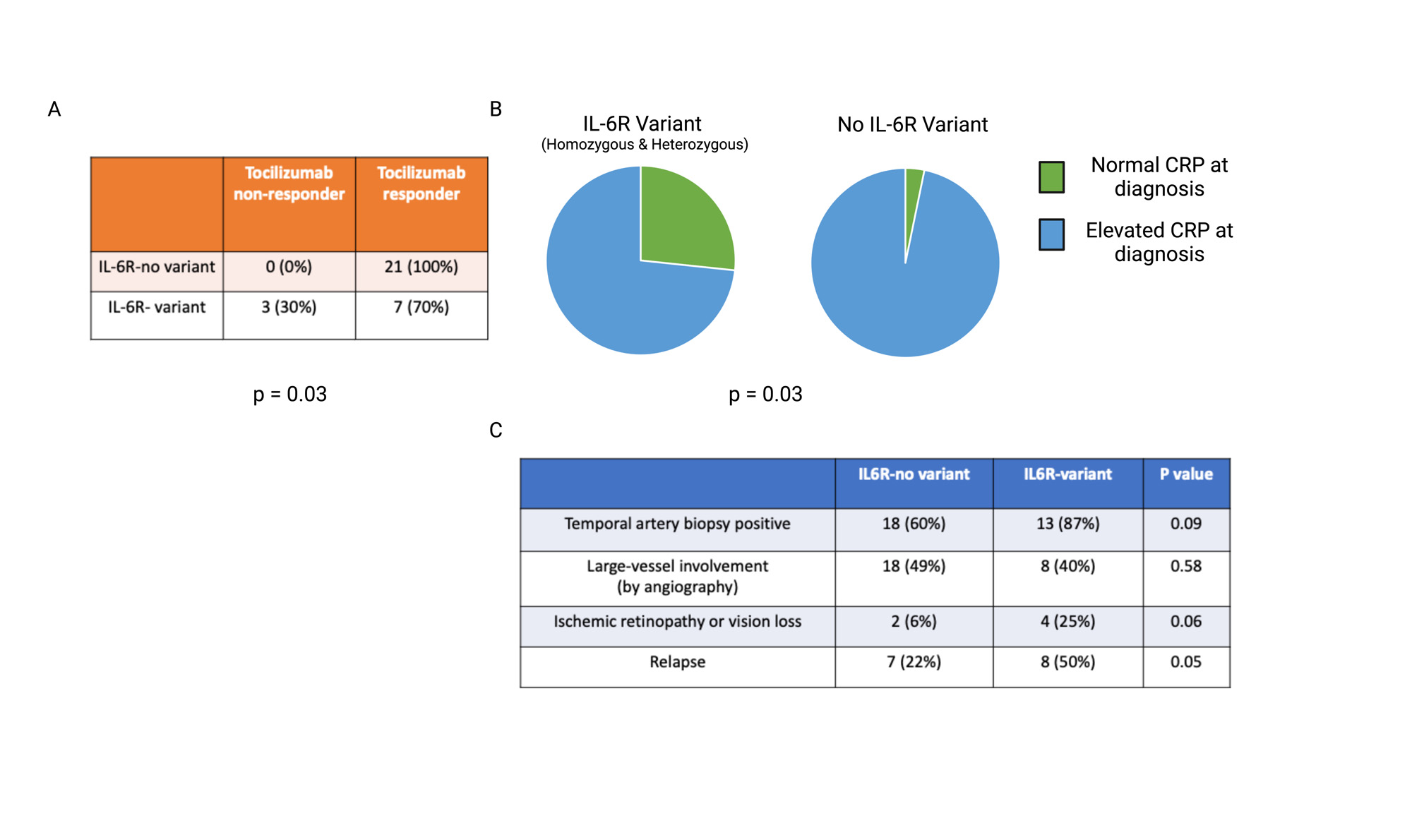
Results: Patients with GCA and the Asp358Ala IL-6R variant had increased serum soluble IL-6 receptor levels (Fig 1A) as well as higher lymphocyte expression of surface gp130 (Fig 1B). When stimulated ex vivo with IL-6, CD4+ T cells in patients with Asp358Ala had increased STAT3 phosphorylation and IL17A expression (Fig 1C and 1D). Similar associations were not seen in other leukocyte subsets or in CD4+ T cells from healthy controls by variant status. Clinically, patients with the Asp358Ala SNP had a higher likelihood of treatment failure to tocilizumab (Fig 2A), lower CRP values at diagnosis (Fig 2B), and a higher rate of relapse (Fig 2C).
Conclusion: The Asp358Ala IL6R variant may result in increased pro-inflammatory trans IL-6 signaling via increased soluble IL-6R and surface gp130 expression, leading to more robust STAT3 phosphorylation and IL-17A production in T cells. IL-6R inhibition via tocilizumab in patients with the Asp358Ala variant may be insufficient to achieve disease control. This variant may be a useful biomarker to predict treatment response to tocilizumab and to identify patients who may respond more favorably to alternative therapeutic approaches.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Redmond C, Zorc R, Sylvester M, Rankin C, Kuan R, Wells K, Dai L, Quinn K, Gadina M, Grayson P. Impact of IL-6 Receptor Small Nucleotide Polymorphism Asp358Ala on T Cell Activity and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Giant Cell Arteritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-il-6-receptor-small-nucleotide-polymorphism-asp358ala-on-t-cell-activity-and-clinical-outcomes-in-patients-with-giant-cell-arteritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-il-6-receptor-small-nucleotide-polymorphism-asp358ala-on-t-cell-activity-and-clinical-outcomes-in-patients-with-giant-cell-arteritis/