Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0510–0542) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment: AxSpA Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Axial SpA (axSpA) and FM manifest with overlapping clinical features such as pain, fatigue, and stiffness, yet their treatment is distinctly different. FM is a comorbidity with axSpA in 4–21% of patients (pts), and extreme BASDAI pain and fatigue scores have been suggested as surrogate markers for FM1. The Janus kinase inhibitor upadacitinib (UPA) is approved for the treatment of AS and non-radiographic axSpA (nr-axSpA), and has demonstrated efficacy in pts with axSpA in the Phase 3 SELECT-AXIS 2 study through 14 weeks (wks) of treatment2,3. The objective of this post hoc analysis was to compare the baseline (BL) characteristics of pts with extreme or non-extreme BL BASDAI and/or Maastricht AS Enthesitis Score (MASES) and to assess the efficacy of UPA vs placebo (PBO) in these subgroups.
Methods: The SELECT-AXIS 2 program was comprised of 1 study of pts with active nr-axSpA (PBO-controlled for 52 wks) and 1 study of pts with active AS and inadequate response to biologic DMARDs (PBO-controlled for 14 wks). Pts with a concomitant diagnosis of active FM according to the treating physician were excluded. The primary endpoint in both studies was ≥40% improvement in Assessment of SpA international Society score (ASAS40) at wk 14. Subgroup analysis was performed on pooled data: ‘extreme BASDAI’ was defined as a score of ≥8 for ≥3/5 BASDAI components, and ‘extreme MASES’ was defined as a score of ≥10; cutoffs reflected the top quartile range of each measure. Demographics and disease characteristics were summarized descriptively. Efficacy measures were evaluated at wk 14 and reported using non-responder imputation incorporating multiple imputation to handle missing data due to COVID-19; statistical comparisons were adjusted for screening high-sensitivity CRP level and study.
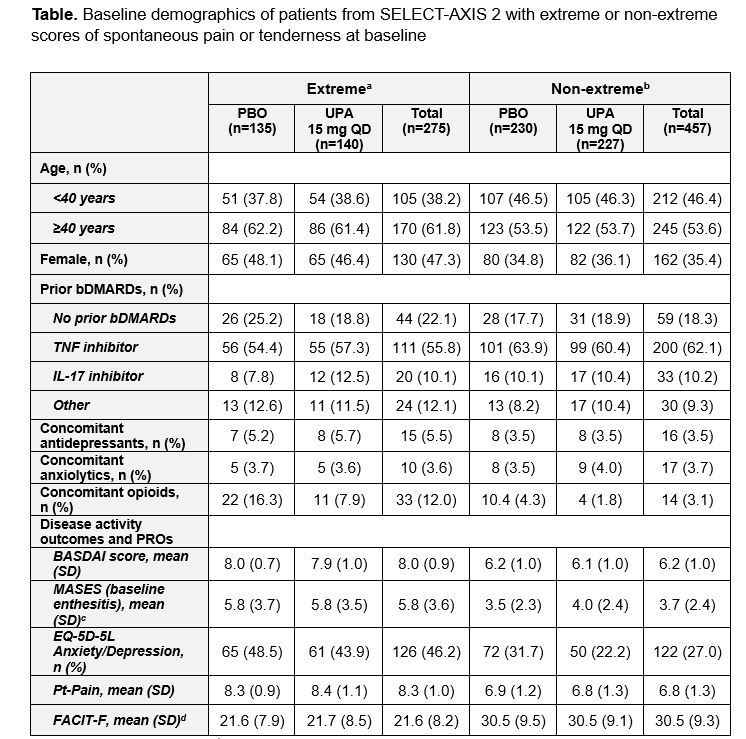
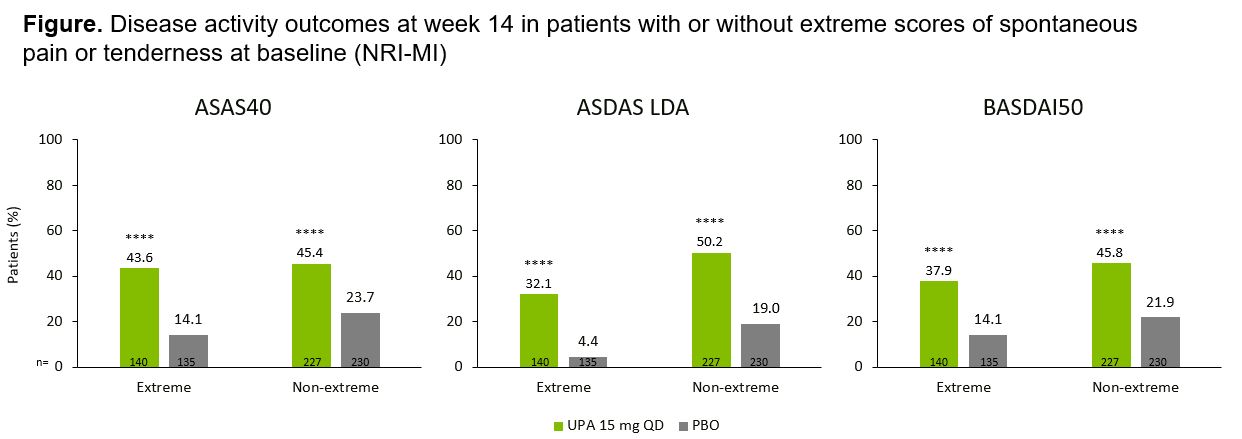
Results: Overall, 732 pts were evaluated, including 275 with extreme scores (PBO, n=135; UPA, n=140) and 457 with non-extreme scores (PBO, n=230; UPA, n=227). At BL, of the 275 extreme pts, 232 (84.4%) met BASDAI criteria only, 19 (6.9%) met MASES criteria only, and 24 (8.7%) met both criteria. Compared with non-extreme pts, more extreme pts were female, ≥40 years old, and had higher BL rates of anxiety/depression (validated cutoff scores from EuroQol-5D-5L, 43.9% vs 22.2% for extreme vs non-extreme pts with UPA), pain (Pt’s Assessment of Pain, 8.4 and 6.8, respectively), and fatigue (Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue, 21.7 and 30.5, respectively; Table). Regardless of extreme or non-extreme scores at BL, UPA demonstrated improvement across multiple disease activity outcomes vs PBO at wk 14 including ASAS40 (p< 0.0001; Figure). Extreme pts reported a numerically lower efficacy response within both UPA and PBO treatment groups at wk 14 vs non-extreme pts.
Conclusion: Pts with axSpA and extreme BL BASDAI/MASES reported higher BL rates of anxiety/depression, pain, and fatigue than those with non-extreme scores. UPA demonstrated greater efficacy than PBO among pts with both extreme and non-extreme BL BASDAI/MASES scores.
References:
- Santos-Faria D, et al. Rheumatol Int 2019;39:141–6
- Deodhar A, et al. Lancet 2022:400;369–79
- Van der Heijde D, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2022;81:1515–23
AS, ankylosing spondylitis; BASDI, Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index; bDMARD, biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug; EQ-5D-5L, EuroQoL-5D-5L; FACIT-F, Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue; IL, interleukin; MASES, Maastricht AS Enthesitis Score; nr-axSpA, non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis; PBO, placebo; PRO, patient-reported outcome; Pt-Pain, Patient’s Assessment of Pain; QD, once daily; SD, standard deviation; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; UPA, upadacitinib.
ASDAS(CRP) LDA defined as <2.1. Data are based on NRI-MI, adjusted for screening hsCRP level and study.
ASAS40, ≥40% improvement in Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society score; ASDAS, Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score; ASDAS-CRP, ASDAS with CRP; BASDAI50, ≥50% improvement in Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index; hsCRP, high-sensitivity CRP; LDA, low disease activity; NRI-MI, non-responder imputation incorporating multiple imputation to handle missing data due to COVID_19; PBO, placebo; QD, once daily; UPA, upadacitinib.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dougados M, Bulbin D, Jones H, Gao T, Shmagel A, Poznanski T, Danve A, Gaffney K. Impact of Extreme Baseline BASDAI and/or Maastricht AS Enthesitis Score on Treatment Response to Upadacitinib in Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-extreme-baseline-basdai-and-or-maastricht-as-enthesitis-score-on-treatment-response-to-upadacitinib-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-extreme-baseline-basdai-and-or-maastricht-as-enthesitis-score-on-treatment-response-to-upadacitinib-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis/