Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Patient-reported outcomes (PROs) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are critical in evaluating RA treatment effects on function and health-related quality of life (HR-QoL). Significant improvement in PROs has been reported in RA studies of biologic agents, including etanercept (ETN), but most studies have been conducted in patients with established disease. In addition to assessing treatment effects in early RA, there is interest in therapeutic strategies that allow dose reduction or withdrawal of biologic therapy (biologic-free) after induction of response. The PRIZE trial is an ongoing, 3-period study to evaluate the efficacy of combined ETN and methotrexate (MTX) therapy in patients with early, moderate-to-severe RA and to assess whether efficacy (remission) can be maintained with ETN dose reduction or biologic-free (Period 2) or drug-free (Period 3). Herein we report PROs associated with ETN 50 mg QW plus MTX (ETN50/MTX) therapy administered for 52 wks in Period 1 (induction) of the PRIZE trial.
Methods: In Period 1, MTX- and biologic-naïve patients with early, active RA (symptom onset ≤12 mo from enrollment; DAS28 >3.2) received open-label ETN50/MTX for 52 wks. The starting dose of MTX was 10 mg QW; at the discretion of the investigator, titration was permitted up to a maximum of 25 mg QW to achieve remission. Corticosteroid boosts were administered to patients not achieving low disease state at wks 13 and 26, unless contraindicated or not tolerated. PROs were assessed using the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) total score; Patient Acceptable Symptom State (PASS); EuroQol-5 Dimensions (EQ-5D) total index; Short Form Health Survey (SF-36); Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy (FACIT)-Fatigue; Work Instability Scale for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA-WIS); and Work Productivity and Activity Impairment Questionnaire: Rheumatoid Arthritis (WPAI:RA).
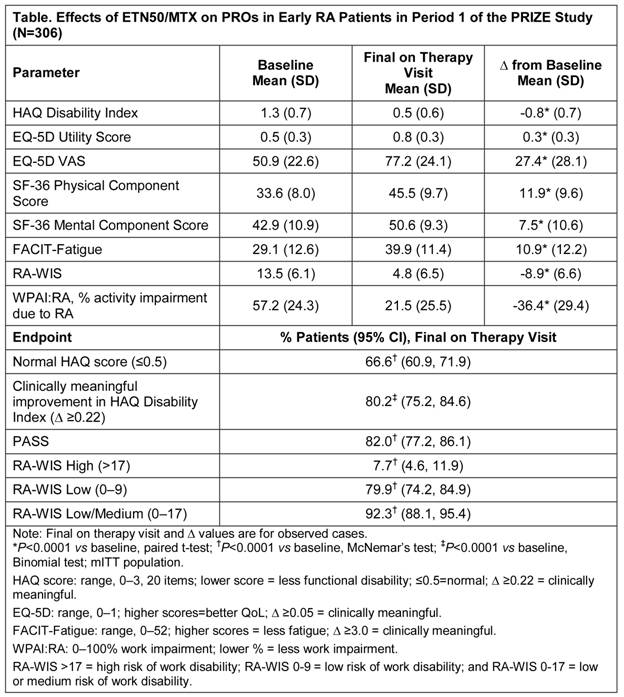
Results: A total of 306 patients received treatment in Period 1 (mITT population); 222 (73%) patients completed the period. The majority of patients were female (70%), with a mean age of 50 y, mean DAS28 of 6.0 (median, 6.0), and duration of disease symptoms from onset of 6.5 months (median, 6.3 mo). Significant and clinically meaningful improvements in PROs, including in HAQ, EQ-5D, SF-36, and FACIT-Fatigue, were demonstrated with ETN50/MTX therapy from baseline to the final on therapy visit (Table; P<0.0001). Similar improvements were observed in all dimensions of RA-WIS and WPAI:RA (Table; P<0.0001).
Conclusion: Combination therapy with ETN50/MTX for 52 wks in patients with <12 mo of symptomatic, active RA resulted in significant, clinically important improvements in measures of physical function, including normal HAQ (66.6% of patients), HR-QoL, fatigue, and work productivity. These outcomes are consistent with those reported in prior studies in patients with more established disease.
Disclosure:
P. Emery,
Pfizer Inc,
2,
Pfizer Inc,
5;
P. Wiland,
None;
W. Spieler,
None;
J. Dudler,
Pfizer Inc,
5;
S. Gaylord,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
T. Williams,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
R. Pedersen,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
A. S. Koenig,
Pfizer Inc,
3,
Pfizer Inc,
1;
B. Vlahos,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
S. Kotak,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-etanercept-methotrexate-therapy-on-patient-reported-outcomes-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-with-up-to-12-months-of-symptoms/