Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2338–2376) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) are at increased risk for major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) and venous thromboembolism (VTE), yet the comparative safety of biologic therapies remains poorly defined. This study aimed to compare the risk of MACE and VTE among users of IL-17, IL-12/23, and IL-23 inhibitors, with anti-TNF agents serving as the reference group.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX Research Network, a de-identified, federated electronic health record database (accessed May 28, 2024). Adults (≥18 years) diagnosed with PsA (ICD-10: L40.5) between 2004 and 2024 on at least one biologic agent including anti-TNF, anti-IL-17, IL-23 or IL-12/23 were included. Eligible patients had at least one year of follow-up. Exclusion criteria included: use of multiple biologic agents from different drug classes, known hypercoagulable state, pregnancy and malignancy (prostate, lung, colon, bladder, kidney, lymphoma, leukemia, endometrial, ovarian, stomach, and pancreatic). Primary outcomes were new onset myocardial infarction (MI), stroke (ischemic and hemorrhagic), deep vein thrombosis (DVT), and pulmonary embolism (PE). Patients with prior history of these outcomes were excluded from analyses.To address baseline differences across treatment groups, we conducted weighted logistic regression using inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) based on the average treatment effect (ATE) and a threshold of < 0.1. Propensity scores were estimated using covariates listed in Table 1. These weights were then applied in logistic regression models to assess the association between biologic therapy and the primary outcomes. Results are presented as odds ratios with 95% confidence intervals, and findings from both unweighted and weighted models are reported.
Results: A total of 28,973 patients with PsA treated with biologic agents were included in the study. The majority received anti-TNF therapy, followed by IL-17 inhibitors, IL-12/23 inhibitors, and IL-23 inhibitors (Table 1). Prior to weighting, comorbid conditions varied across groups; however, after IPTW baseline characteristics were well balanced. The mean age was 52.2 years, 56% were female, and common comorbidities included hypertension (31.1%), hyperlipidemia (28.4%), obesity (19.8%), and diabetes (12.2%) (Table 1). In PsA cohort, IL-17 inhibitor use was associated with significantly reduced odds of DVT (OR 0.58, p < 0.001), PE (OR 0.45, p < 0.001), MI (OR 0.50, p < 0.001), and stroke (OR 0.56, p < 0.001). Similarly, IL-23 inhibitor use was associated with lower odds of DVT (OR 0.49, p = 0.02), PE (OR 0.12, p = 0.005), MI (OR 0.29, p < 0.001), and stroke (OR 0.35, p = 0.002) compared to anti-TNF agents. In contrast, IL-12/23 inhibitor use was associated with increased odds of stroke (OR 1.41, p = 0.04), with no significant differences observed for DVT, PE, or MI (Table 2).
Conclusion: In PsA, IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitors were consistently associated with significantly lower odds of stroke, MI, DVT, and PE compared to anti-TNF agents. In contrast, IL-12/23 inhibitor use was linked to increased odds of stroke and showed no significant protective effect across other outcomes.
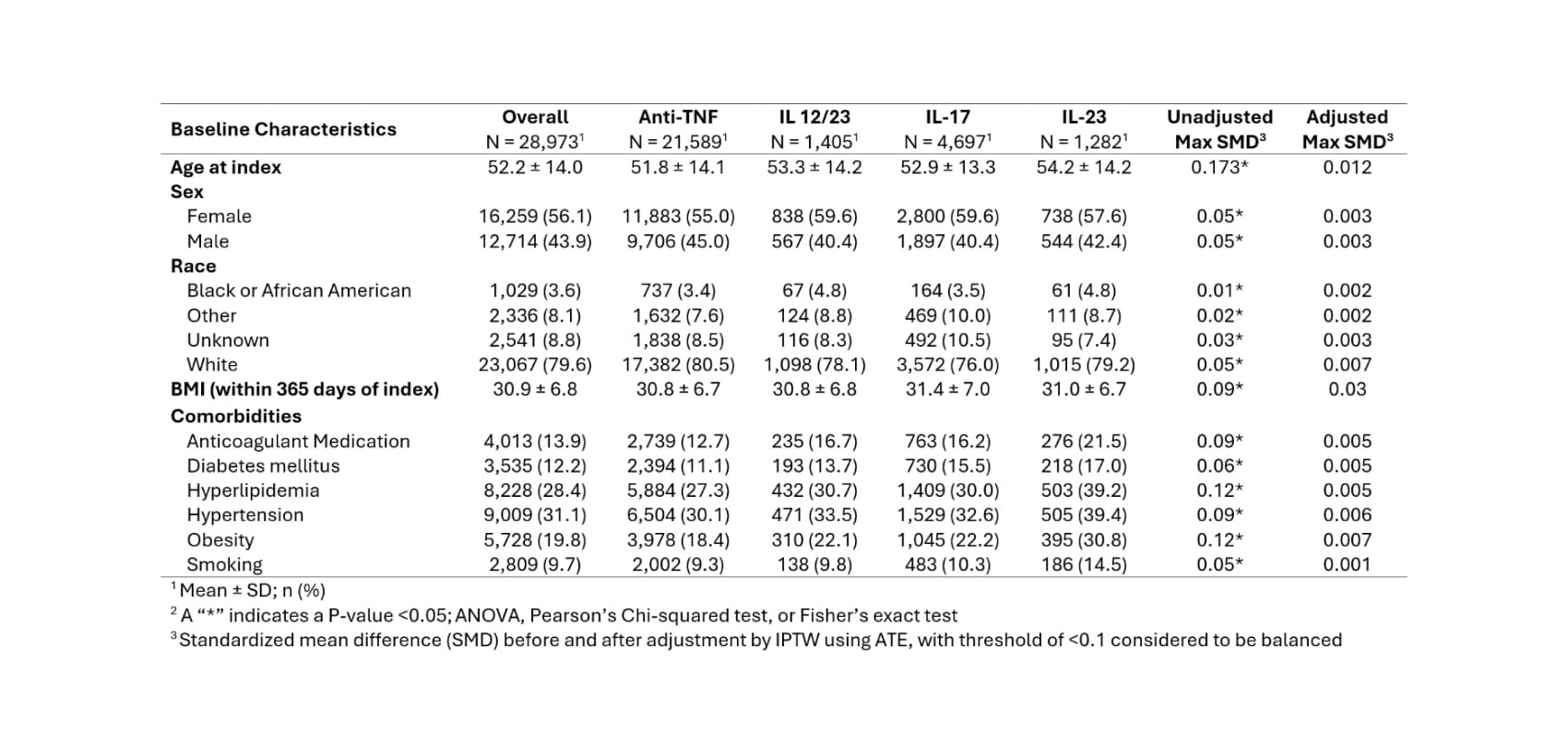 Table 1. Baseline characteristics across biologic therapy classes, with standardized mean differences (SMD) shown before and after inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) adjusted by the average treatment effect (ATE).
Table 1. Baseline characteristics across biologic therapy classes, with standardized mean differences (SMD) shown before and after inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) adjusted by the average treatment effect (ATE).
.jpg) Table 2. Incidence (n (%)) and odds ratios (OR; 95% confidence interval) between biologic classes, before and after adjustment for covariates by IPTW. Reference category is denoted by “—.”
Table 2. Incidence (n (%)) and odds ratios (OR; 95% confidence interval) between biologic classes, before and after adjustment for covariates by IPTW. Reference category is denoted by “—.”
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Heydari-Kamjani M, Murphy J, Magrey M. Impact of Biologic Therapies on Cardiovascular and Venous Thromboembolic Events in Psoriatic Arthritis: Real-World Evidence [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-biologic-therapies-on-cardiovascular-and-venous-thromboembolic-events-in-psoriatic-arthritis-real-world-evidence/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-biologic-therapies-on-cardiovascular-and-venous-thromboembolic-events-in-psoriatic-arthritis-real-world-evidence/
