Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Upadacitinib (UPA), an oral selective JAK1 inhibitor, has demonstrated favorable efficacy and acceptable safety in five Phase 3 global studies in patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis (RA).1–5 This analysis reports the efficacy and safety of UPA in predefined RA patient subgroups based on differences in baseline demographics and disease activity.
Methods: Data were pooled from three pivotal, double-blind, PBO-controlled, multicenter, Phase 3 studies in patients with RA who had an inadequate response (IR) to conventional synthetic DMARDs (csDMARD-IR: SELECT-NEXT [N=661]), MTX (MTX-IR; SELECT-COMPARE [N=1629]), or biologic DMARDs (bDMARD-IR: SELECT-BEYOND [N=498]). Two integrated analysis sets were evaluated: one comparing UPA 15 mg QD vs PBO (SELECT-NEXT, SELECT-COMPARE, SELECT-BEYOND) and the other comparing UPA 15 mg QD and UPA 30 mg QD vs PBO (SELECT-NEXT, SELECT-BEYOND). All patients received background treatment with csDMARDs. The proportion of patients achieving ACR20 and DAS28(CRP) ≤3.2 at Week 12 was evaluated by predefined baseline demographics and disease activity measure groups, including age, sex, weight, BMI, race, geographic region, duration of RA, RF, and ACPA status, and level of high sensitivity CRP. Non-responder imputation was used for missing data. Subgroup analyses for safety were performed for age, race, sex, weight, BMI, and Asian region.
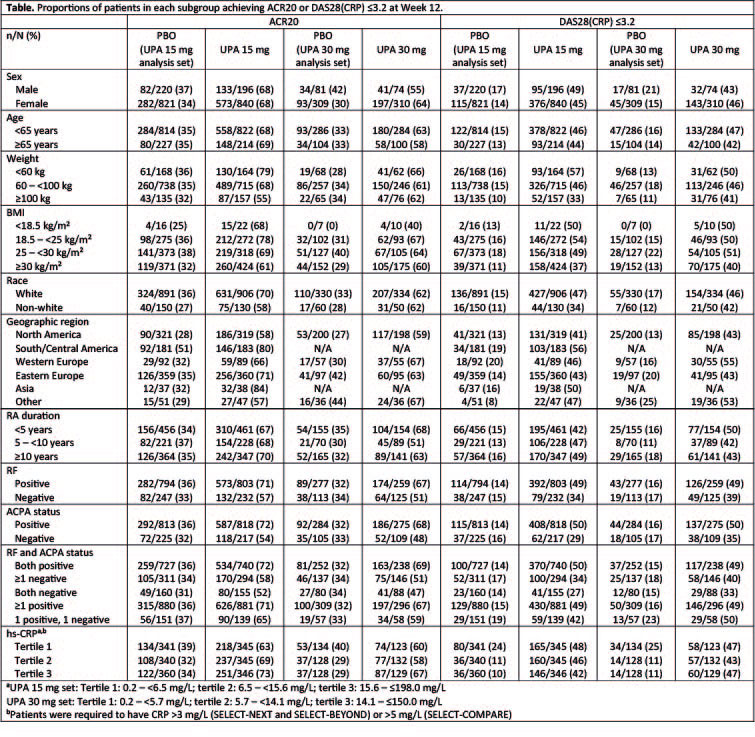
Results: Across the three Phase 3 studies, 1036, 384, and 1041 patients received UPA 15 mg QD, UPA 30 mg QD or PBO, respectively. The demographic and baseline disease characteristics in the two integrated analysis sets were balanced across treatment groups. ACR20 and DAS28 ≤3.2 response rates at Week 12 were consistently higher with UPA 15 mg and UPA 30 mg vs PBO across the evaluated demographic and baseline disease characteristics (Table). The efficacy of UPA 15 mg QD was generally similar to that observed with UPA 30 mg QD. At 12 weeks, the proportion of patients with treatment-emergent AEs, serious AEs, severe AEs, and AEs leading to discontinuation were generally comparable across different age, sex, race, weight, and BMI groups. Compared with the global population, patients receiving UPA in the Asian region had a higher rate of CPK elevations (UPA 30 mg only) and herpes zoster; herpes zoster also has been observed to be higher in the Asian region with other JAK inhibitors.6,7
Conclusion: In this analysis of pooled integrated efficacy data in csDMARD-IR or bDMARD-IR patients with RA, UPA 15 mg or 30 mg QD in combination with csDMARDs improved efficacy outcomes at Week 12 when compared with PBO across all predefined subgroups evaluated.
References
- Burmester GR, et al. Lancet 2018 23;391:2503–2512;
2. Genovese MC, et al. Lancet 2018; 391:2513–24;
3. Smolen JS, et al. Lancet 2019 May 23 [Epub ahead of print];
4. van Vollenhoven R, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2018;70(Suppl. 10): Abstract 891;
5. Fleischmann R, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2018;70(Suppl. 10): Abstract 890;
6. Winthrop KL, et al. Arthritis Rheum 2014;66:2675-84;
7. Winthrop KL, et al. ACR 2016 [Abstract 3027]
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Weinblatt M, Mysler E, Östör A, Broadwell A, Jeka S, Dunlap K, Suboticki J, Enejosa J, Hendrickson B, Zhong S, Cherny K, Wright G. Impact of Baseline Demographics and Disease Activity on Outcomes in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Receiving Upadacitinib [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-baseline-demographics-and-disease-activity-on-outcomes-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-receiving-upadacitinib/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-baseline-demographics-and-disease-activity-on-outcomes-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-receiving-upadacitinib/