Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster II: Psoriatic Arthritis I (1329–1363)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Minimal disease activity (MDA) is a common goal for disease control when managing PsA. The aim of this study was to assess the association between MDA achievement and disease activity/patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) after 6 months of biologic DMARD (bDMARD) or targeted synthetic DMARD (tsDMARD) therapy among PsA patients.
Methods: This study included patients with PsA enrolled in CorEvitas’ prospective, multicenter, observational PsA/SpA Registry, who had not attained MDA, were initiating bDMARD or tsDMARD therapy at baseline, and had a 6-month follow-up visit (3/2013-3/2021). MDA was achieved at follow up if ≥5 of the following was met: tender joint count 68 ≤1, swollen joint count 66 ≤1, body surface area ≤3%, patient’s assessment of pain ≤15 (0-100 VAS), patient’s global assessment of disease activity ≤20 (0-100 VAS), HAQ-Disability Index ≤0.5, or Leeds Enthesitis Index ≤1. Baseline patient characteristics of MDA achievers and non-achievers were compared with t-tests and chi-square tests. Relative risk (RR) of achieving minimal clinically important difference (MCID) for PROMs and clinically meaningful improvements in disease activity components was estimated by Poisson generalized linear models adjusted for the baseline PROM or baseline disease activity component. RRs of maintaining or switching the initiated therapy by 6 months were calculated to determine the association with MDA achievement.
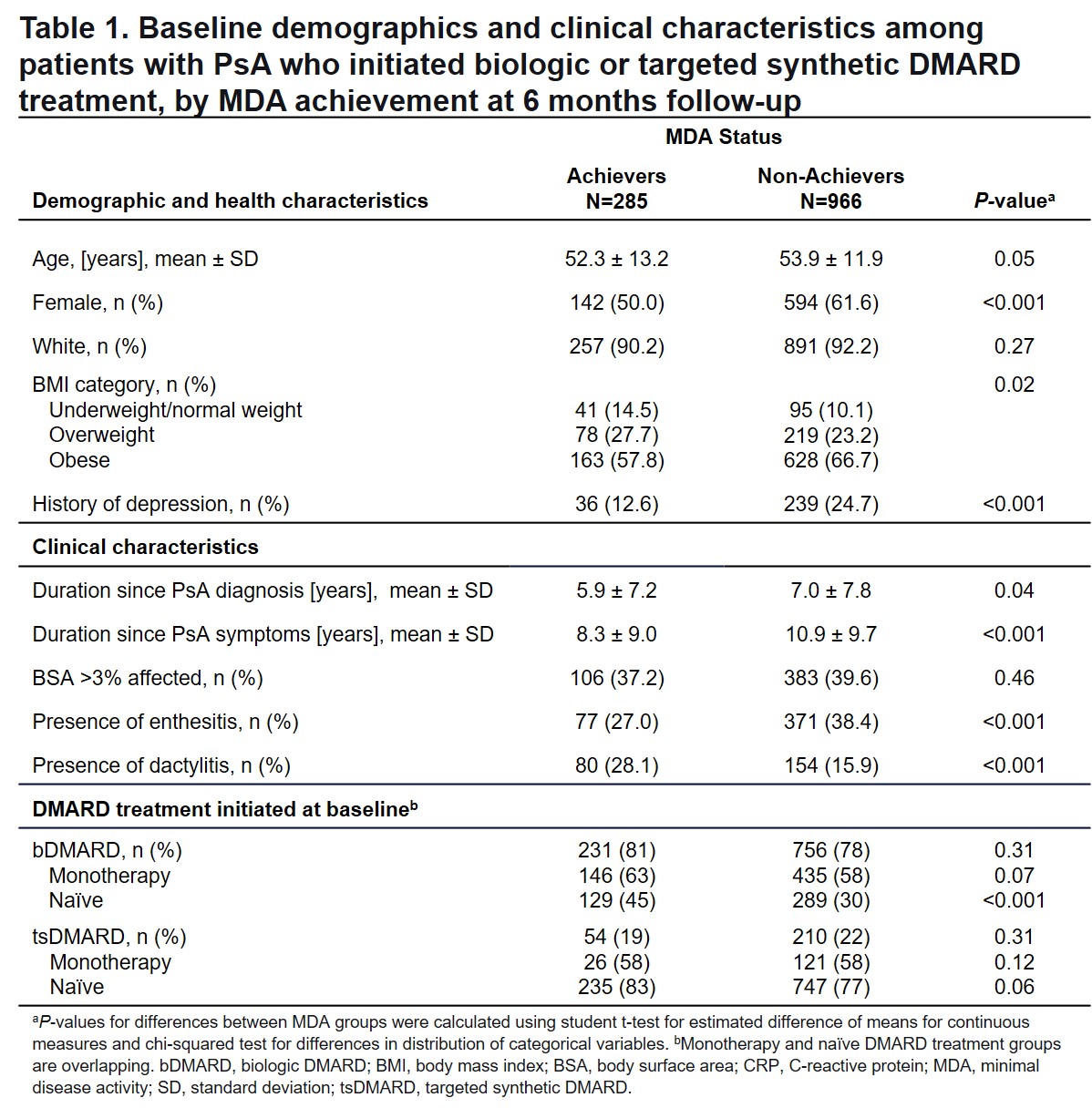
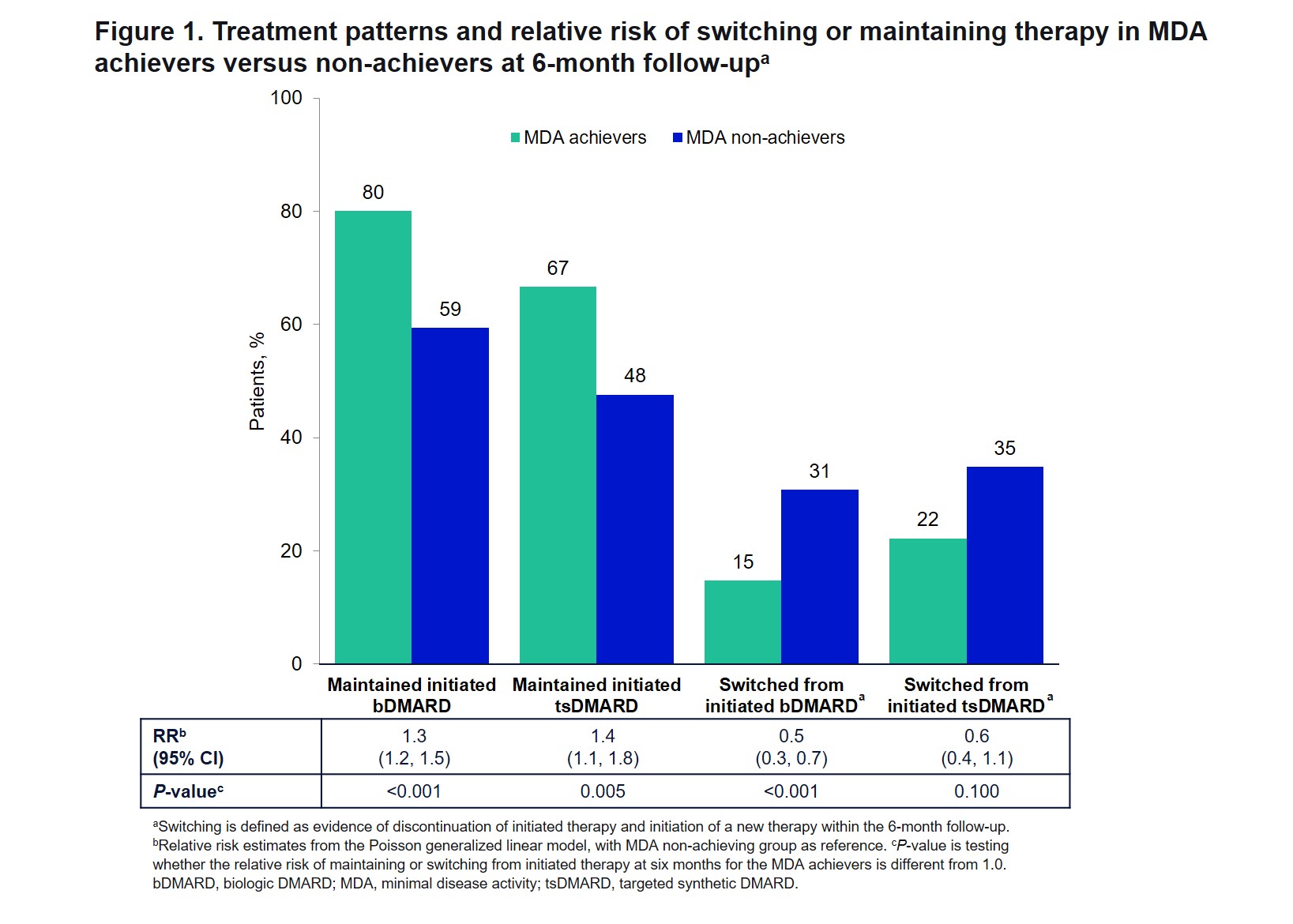
Results: MDA was achieved by 22.8% (285/1251) of patients 6 months after initiating bDMARD (n=987) or tsDMARD (n=264) therapy for PsA. Most baseline characteristics were similar between MDA achievers and non-achievers; however, those who achieved MDA tended to be younger with shorter duration of disease and were less likely to be female, obese, or have a history of depression (Table 1). DMARD therapy at initiation was similar between MDA achievers and non-achievers, except that more achievers were bDMARD-naïve at baseline (Table 1). Patients who achieved MDA were more likely to maintain the initiated bDMARD (RR =1.3, 95% CI 1.2-1.5) or tsDMARD (RR =1.4, 95% CI 1.1-1.8) therapy and less likely to switch from the initiated bDMARD (RR=0.5, 95% CI 0.3-0.7) and tsDMARD (RR=0.6, 95% CI 0.4-1.1) therapy (Figure 1). MDA achievement was associated with higher probability of achieving MDA components and MCID in PROMs at 6 months (Figure 2).
Conclusion: In this real-world study, MDA achievement was associated with a higher probability of achieving clinically meaningful improvements in disease activity and PROMs, suggesting MDA as a viable target endpoint for disease control. Patients who achieved MDA were also more likely to be persistent on b/tsDMARD therapy. This data underscores the importance of utilizing MDA in clinical practice in order to achieve optimal outcomes for patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ogdie A, McLean R, Marchese M, Blachley T, Anatale-Tardiff L, Saffore C, Douglas K, Quach D, Mease P. Impact of Achieving Minimal Disease Activity on Patient-Reported Outcome Measures and Disease Activity Among Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis Treated with Biologic and Targeted Synthetic DMARDs [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-achieving-minimal-disease-activity-on-patient-reported-outcome-measures-and-disease-activity-among-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-treated-with-biologic-and-targeted-synthetic-dmards/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-achieving-minimal-disease-activity-on-patient-reported-outcome-measures-and-disease-activity-among-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-treated-with-biologic-and-targeted-synthetic-dmards/