Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster I: Axial Spondyloarthritis (0908–0939)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Although Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) low disease activity (LDA) is a common treatment target for disease control when managing AS, real-world research describing ASDAS LDA achievement among patients treated with biologic DMARDs (bDMARD) is limited. The aim of this study was to describe disease activity and patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) among patients with AS who achieved and did not achieve ASDAS LDA after 6 months of bDMARD treatment.
Methods: This analysis included patients diagnosed with AS in CorEvitas’ PsA/SpA Registry, a prospective, observational, disease-based registry. Eligible patients initiated bDMARD treatment (baseline) between March 2013 and March 2021, were not in ASDAS LDA at initiation, and had a 6-month follow-up visit. Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics were compared between patients who did and did not achieve ASDAS LDA (ASDAS < 2.1) at follow-up using t-tests, Wilcoxon ranked-sum tests, chi-square tests, or Fisher exact tests. Clinical outcomes at 6 months (assessment in AS [ASAS] 20, 40, and partial remission [PR]) were described for both groups.
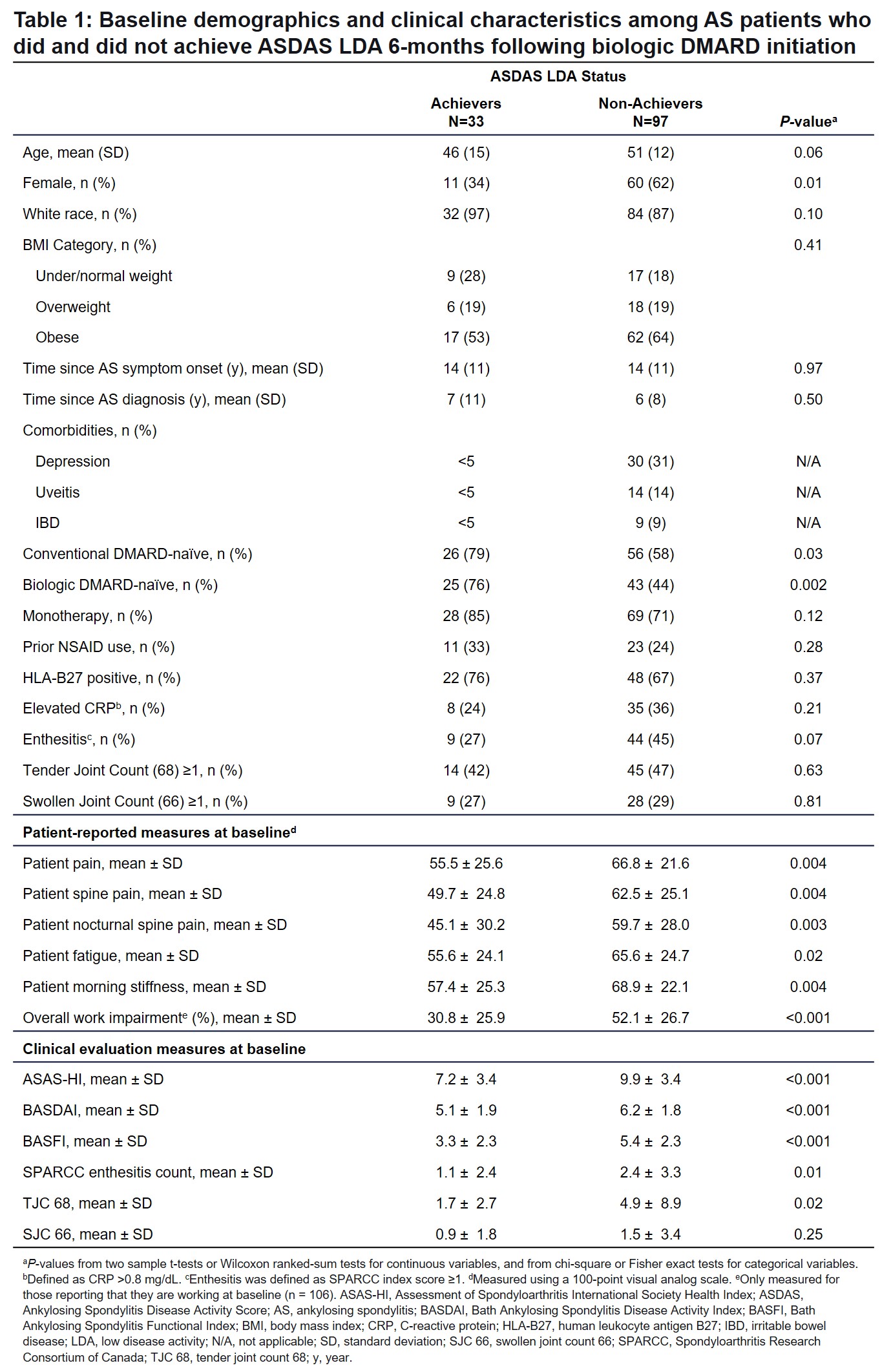
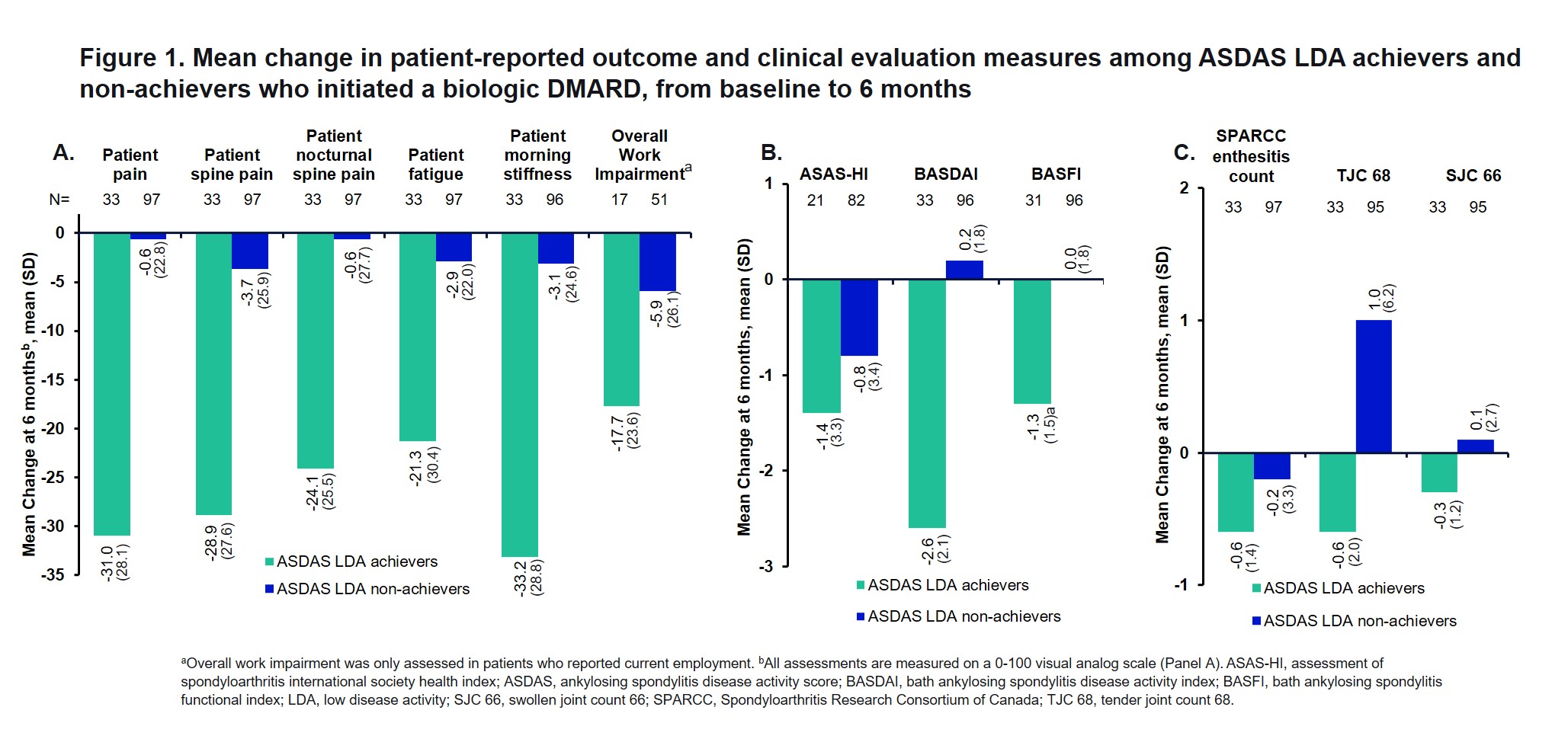
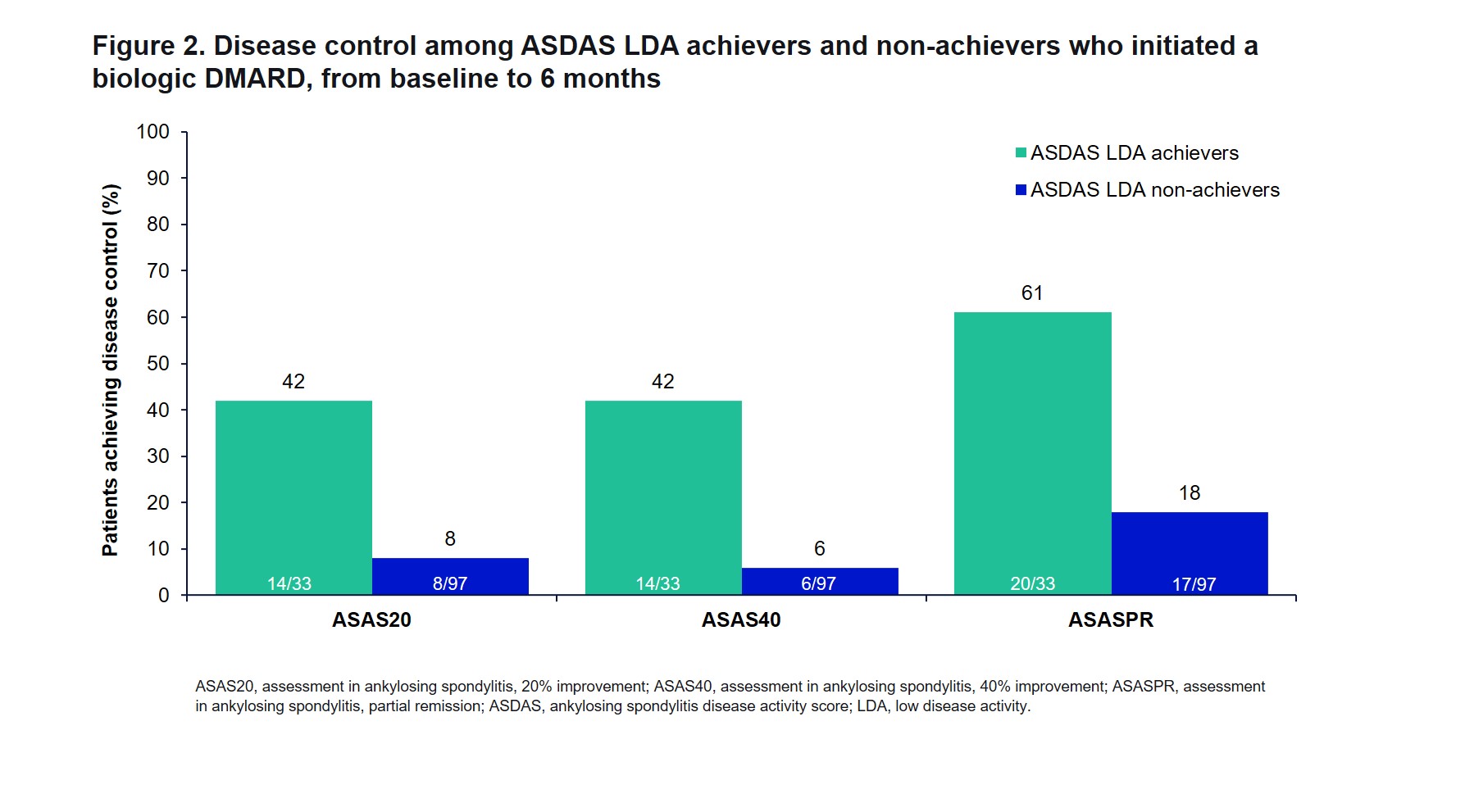
Results: Of 130 patients, 25% (n=33) achieved ASDAS LDA 6 months after bDMARD initiation and 75% (n=97) did not. At baseline, a greater percentage of ASDAS LDA achievers were naïve to conventional DMARDs (79% vs 58%; P=0.03), and ASDAS LDA achievers were more likely to be naïve to bDMARDs (76% vs 44%; P=0.002; Table 1). ASDAS LDA achievers were less likely to be women compared with the non-achiever group (34% vs 62%; P=0.01). A higher number of ASDAS LDA non-achievers had comorbidities such as depression, uveitis, and inflammatory bowel disease. After 6 months of bDMARD therapy, those who achieved ASDAS LDA reported substantial improvements (mean change [standard deviation]) in PROMs (measured on a 0-100-point visual analog scale), including patient-reported pain (-31.0 [28.1]), spine pain (-28.9 [27.6]), nocturnal spine pain (-24.1 [25.5]), fatigue (-21.3 [30.4]), morning stiffness (-33.2 [28.8]), and overall work impairment (-17.7 [23.6]) (Figure 1A). ASDAS LDA achievers had improved clinical characteristics of peripheral arthritis, including Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada enthesitis count (mean change [standard deviation]; -0.6 [1.4]), tender joint count (-0.6 [2.0]), and swollen joint count (-0.3 [1.2]) (Figure 1B-C). Patients with ASDAS LDA achievement had numerically higher rates of ASAS20, ASAS40, and ASASPR attainment than non-achievers (42% vs 8%, 42% vs 6%, 61% vs 18%, respectively) (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Among our real-world patients with AS, those who achieved ASDAS LDA demonstrated substantial improvements in PROMs and achievement of key clinical milestones of ASAS20, ASAS40, and ASASPR, suggesting ASDAS LDA as an important target for disease control when managing patients with AS. Key patient characteristics such as sex and comorbidities were different between patients who did and did not achieve ASDAS LDA and may need to be considered when managing patients with AS.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease P, McLean R, Blachley T, Marchese M, Anatale-Tardiff L, Saffore C, Quach D, Biljan A, Ogdie A. Impact of Achieving ASDAS LDA on Disease Activity and Patient-Reported Outcome Measures Among Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis Treated with Biologic DMARDs [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-achieving-asdas-lda-on-disease-activity-and-patient-reported-outcome-measures-among-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-treated-with-biologic-dmards/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-achieving-asdas-lda-on-disease-activity-and-patient-reported-outcome-measures-among-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-treated-with-biologic-dmards/