Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Brazil is among the countries with the highest numbers of confirmed cases and deaths by COVID-19. CoronaVac (SARS-CoV-2 inactivated vaccine) has been largely used as the main available immunogen for COVID-19 in several countries and it is reported to have 50.7% efficacy. However, its immunogenicity in immunocompromised individuals has not been established. The objective is to evaluate the immunogenicity and safety of the inactivated virus vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 (CoronaVac) in autoimmune rheumatic diseases (ARD) patients.
Methods: This was a prospective controlled study of 910 adult ARD patients and 182 age- and sex-matched control group (CG) who received two doses of CoronaVac. Both groups had negative serology and neutralizing antibodies for COVID-19 at baseline. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG and neutralizing antibodies (NAb) were assessed prior to each vaccine shot (D0 and D28) and 6 weeks after the 2nd dose (D69). Blood samples were collected from all participants for quantitative serological testing for IgG antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 S1/S2 proteins (DiaSorin) and NAb (GenScript). The primary outcome was immunogenicity (seroconversion rate of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG, and frequency of patients with NAb) at D69. Geometric mean titers (GMT) and factor increase in GMT (FI-GMT) of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG, and median (interquartile) percentage of neutralizing activity of NAb were also calculated. ARD patients and CG were vaccinated with standardized schedule (28-days interval) and evaluated using COVID-19 symptoms and adverse events (AE) diaries, three face-to-face visits, and 24-hs available phone, Whatsapp and e-mail contact. Symptomatic cases were tested by RT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2 and a subgroup of positive samples were evaluated for the presence of variants of concern (P.1, B.1.1.7, and B.1.351 lineages).
Results: We observed significant lower anti-SARS-Cov-2 IgG seroconversion (70.4% vs. 95.5%,p< 0.001) and GMT [12.1(95%CI 11.0-13.2) vs. 29.7(95%CI 26.3-33.5),p< 0.001], frequency of NAb (56.3% vs. 79.3%),p< 0.001) and median (interquartile range) neutralization activity [58.7(43.1-77.2)% vs. 64.5(48.4-81.4)%,p=0.013] in ARD patients compared to CG. Vaccine safety analysis revealed similar AE between the groups, with no moderate/severe event. Thirty-nine incident symptomatic cases of COVID-19 confirmed by RT-PCR were observed among ARD patients and CG [36/910 (4%) vs. 3/182 (1.6%), p=0.186] throughout the study. Frequency of cases occurring from D0-D39 (up to 10 days after the second dose) was higher compared to D40-D79 [33/1092 (3.0%) vs. 6/1057 (0.6%), p< 0.0001]. Four ARD patients were hospitalized (up to 10 days after second dose) and none deceased due to COVID-19.
Conclusion: CoronaVac has an excellent safety profile and reasonable rates of seroconversion (70.4%) and adequate neutralization activity (56.3%) in ARD patients. The impact of this reduced immunogenicity in vaccine effectiveness warrants further evaluation.
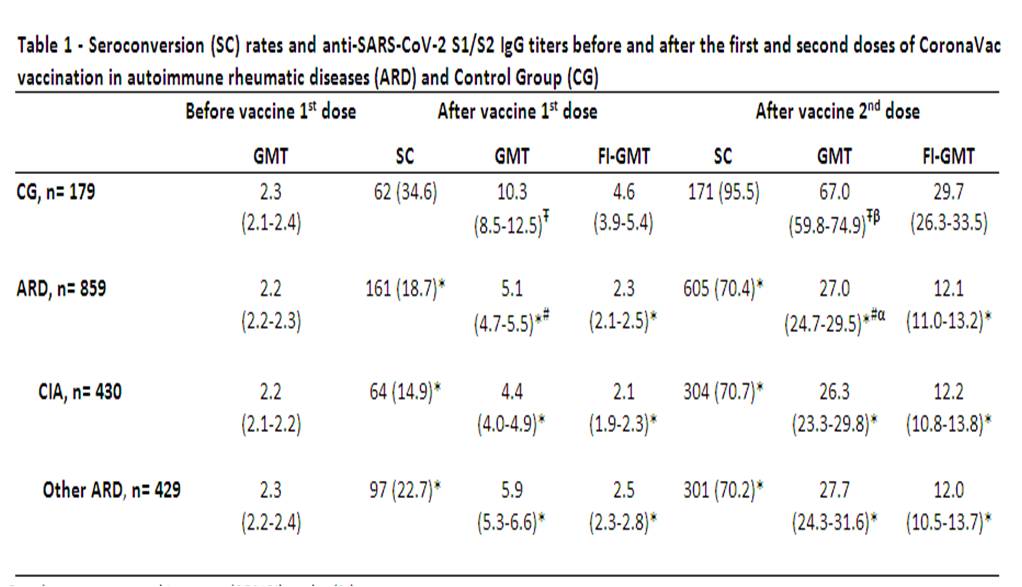 Results are expressed in geometric mean (95%CI) and n (%). GMT – Geometric mean titers (AU/mL); SC – seroconversion (defined as post vaccination titer > 15 AU/mL – Indirect ELISA, LIAISON® SARS-CoV_2 S1/S2 IgG, DiaSorin, Italy); FI-GMT – factor increase of Geometric mean titers; ARD – autoimmune rheumatic diseases; CG – control group; CIA – chronic inflammatory arthritis (rheumatoid arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis and psoriatic arthritis); Other ARD– systemic lupus erythematosus, primary vasculitis, systemic sclerosis, primary Sjögren syndrome, idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and primary antiphospholipid syndrome; * – p < 0.001 in comparison among ARD and CG at the same time points; # - p < 0.001 for longitudinal comparisons of GMT in ARD at D28 and D69 vs. baseline; α - p < 0.001 for longitudinal comparison of GMT in ARD at D69 vs. D28; Ŧ - p < 0.001 for longitudinal comparison of GMT in CG at D28 and D69 vs. baseline; β - p < 0.001 for longitudinal comparison of GMT in CG at D69 vs. D28.
Results are expressed in geometric mean (95%CI) and n (%). GMT – Geometric mean titers (AU/mL); SC – seroconversion (defined as post vaccination titer > 15 AU/mL – Indirect ELISA, LIAISON® SARS-CoV_2 S1/S2 IgG, DiaSorin, Italy); FI-GMT – factor increase of Geometric mean titers; ARD – autoimmune rheumatic diseases; CG – control group; CIA – chronic inflammatory arthritis (rheumatoid arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis and psoriatic arthritis); Other ARD– systemic lupus erythematosus, primary vasculitis, systemic sclerosis, primary Sjögren syndrome, idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and primary antiphospholipid syndrome; * – p < 0.001 in comparison among ARD and CG at the same time points; # - p < 0.001 for longitudinal comparisons of GMT in ARD at D28 and D69 vs. baseline; α - p < 0.001 for longitudinal comparison of GMT in ARD at D69 vs. D28; Ŧ - p < 0.001 for longitudinal comparison of GMT in CG at D28 and D69 vs. baseline; β - p < 0.001 for longitudinal comparison of GMT in CG at D69 vs. D28.
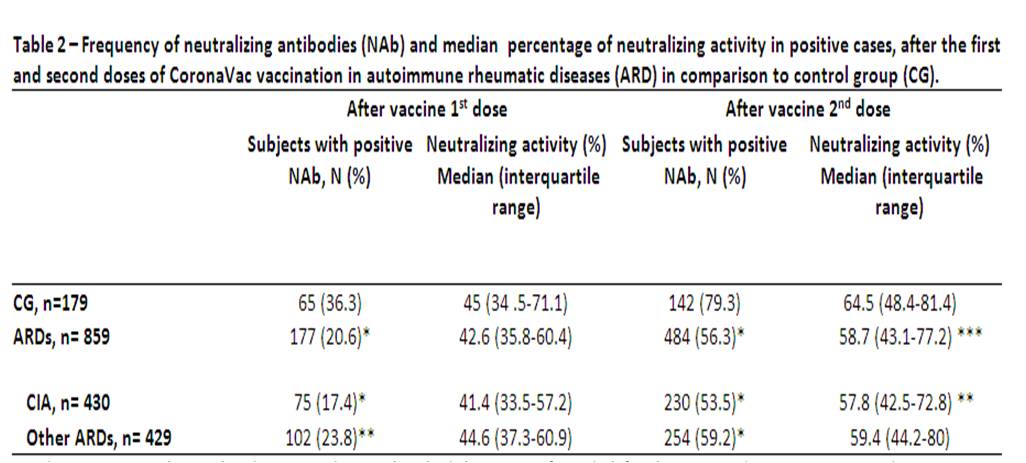 Results are expressed in median (interquartile range) and n (%). Positivity for Nab defined as a neutralizing activity ≥30 % (cPass sVNT Kit, GenScript, Piscataway, USA) ***p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and *p < 0.001 in comparison to CG ARD – autoimmune rheumatic diseases; CG – control group; CIA – chronic inflammatory arthritis (rheumatoid arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis and psoriatic arthritis); Other ARD – systemic lupus erythematosus, primary vasculitis, systemic sclerosis, primary Sjögren syndrome, idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and primary antiphospholipid syndrome.
Results are expressed in median (interquartile range) and n (%). Positivity for Nab defined as a neutralizing activity ≥30 % (cPass sVNT Kit, GenScript, Piscataway, USA) ***p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and *p < 0.001 in comparison to CG ARD – autoimmune rheumatic diseases; CG – control group; CIA – chronic inflammatory arthritis (rheumatoid arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis and psoriatic arthritis); Other ARD – systemic lupus erythematosus, primary vasculitis, systemic sclerosis, primary Sjögren syndrome, idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and primary antiphospholipid syndrome.
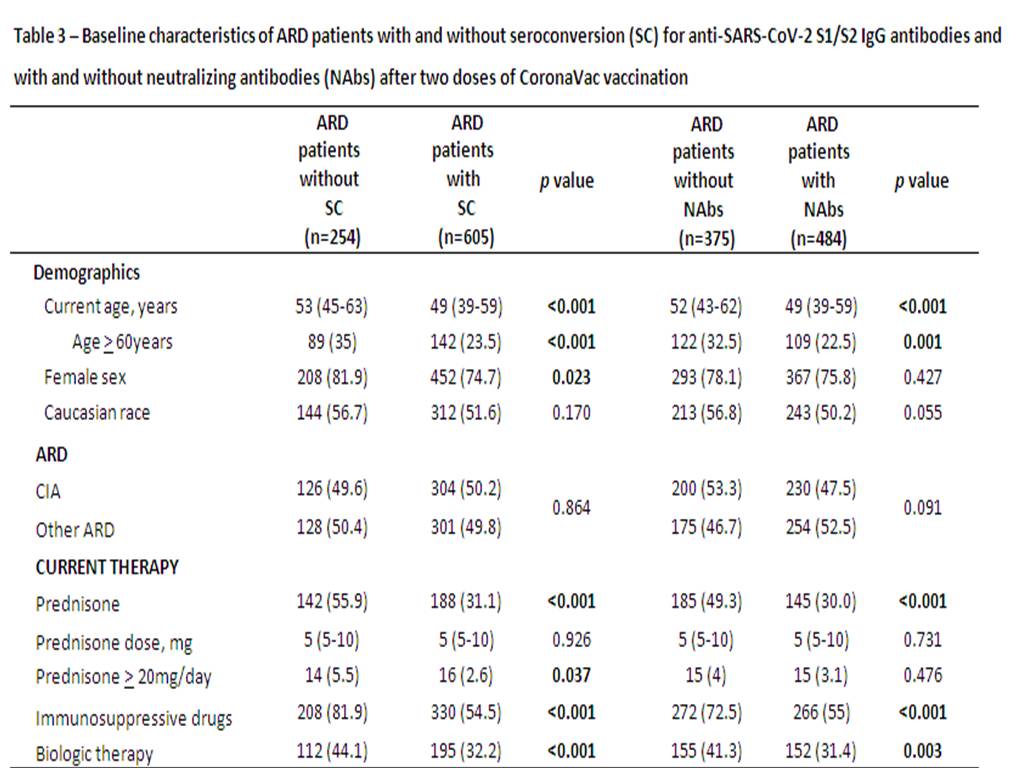 Results are expressed in median (interquartile range) and n (%). ARD – autoimmune rheumatic disease; CIA – chronic inflammatory arthritis (rheumatoid arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis and psoriatic arthritis); Other ARD – systemic lupus erythematosus, primary vasculitis, systemic sclerosis, primary Sjögren syndrome, idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and primary antiphospholipid syndrome. SC – seroconversion defined as a positive serology (IgG titer > 15 AU/ml) for anti-SARS-CoV_2 S1/S2 IgG antibodies after vaccination (Indirect ELISA, LIAISON® SARS-CoV_2 S1/S2 IgG, DiaSorin, Italy). Positivity for Nabs defined as a neutralizing activity ≥ 30 % (cPass sVNT Kit, GenScript, Piscataway, USA).
Results are expressed in median (interquartile range) and n (%). ARD – autoimmune rheumatic disease; CIA – chronic inflammatory arthritis (rheumatoid arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis and psoriatic arthritis); Other ARD – systemic lupus erythematosus, primary vasculitis, systemic sclerosis, primary Sjögren syndrome, idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and primary antiphospholipid syndrome. SC – seroconversion defined as a positive serology (IgG titer > 15 AU/ml) for anti-SARS-CoV_2 S1/S2 IgG antibodies after vaccination (Indirect ELISA, LIAISON® SARS-CoV_2 S1/S2 IgG, DiaSorin, Italy). Positivity for Nabs defined as a neutralizing activity ≥ 30 % (cPass sVNT Kit, GenScript, Piscataway, USA).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Medeiros-Ribeiro A, Aikawa N, Saad C, Figueiredo Vieira Neves Yuki E, do Nascimento Pedrosa T, Fusco S, Rojo P, Pereira R, Shinjo S, Andrade D, Sampaio-Barros P, Ribeiro C, Deveza G, Oliveira Martins V, Silva C, Lopes M, Duarte A, Antonangelo L, Sabino E, Kallas E, Gofinet Pasoto S, Bonfá E. Immunogenicity and Safety of an Inactivated Virus Vaccine Against SARS-CoV-2 in Patients with Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immunogenicity-and-safety-of-an-inactivated-virus-vaccine-against-sars-cov-2-in-patients-with-autoimmune-rheumatic-diseases/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immunogenicity-and-safety-of-an-inactivated-virus-vaccine-against-sars-cov-2-in-patients-with-autoimmune-rheumatic-diseases/
